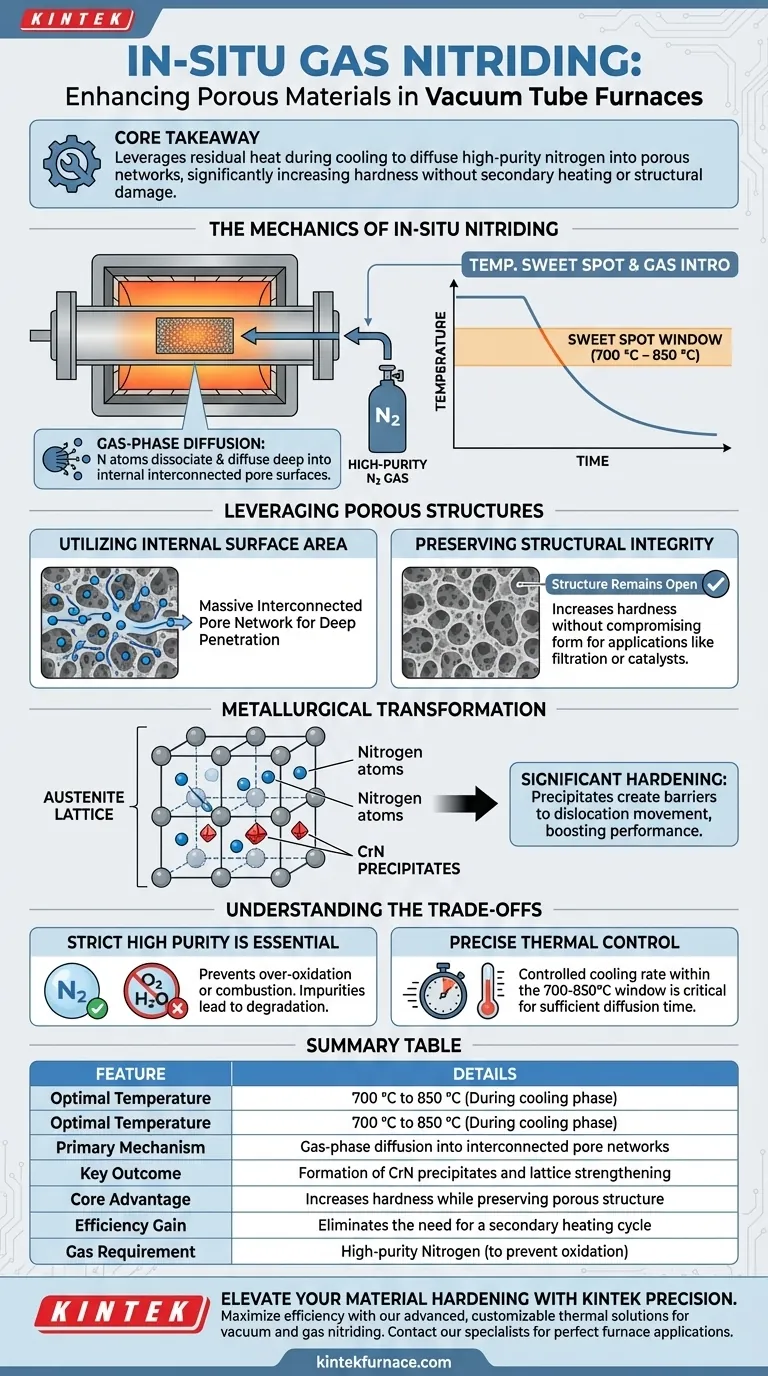
High-purity nitrogen is introduced during the cooling phase (specifically between 700 °C and 850 °C) to initiate an in-situ gas nitriding process. By utilizing the residual thermal energy from the furnace, nitrogen atoms penetrate the material's interconnected pores and diffuse into the lattice structure, significantly increasing hardness without the need for a separate, secondary heating cycle.
Core Takeaway: This technique leverages the material's natural porosity and the furnace's cooling ramp to perform chemical hardening efficiently. It transforms a standard cooling step into a functional diffusion process, creating strengthening precipitates while preserving the complex structure of the porous material.

The Mechanics of In-Situ Nitriding
The Temperature Sweet Spot
The timing of nitrogen introduction is critical. The gas is introduced when the furnace temperature drops to a specific range, typically between 700 °C and 850 °C.
At this thermal window, the material possesses enough energy to facilitate atomic movement, but the temperature is decreasing, which locks in the microstructure as the process completes.
Gas-Phase Diffusion
The process relies on gas-phase diffusion principles.
Nitrogen atoms dissociate from the gas and diffuse into the surface of the material. Because the material is porous, this "surface" extends deep into the internal structure, not just the exterior shell.
Leveraging Porous Structures
Utilizing Internal Surface Area
Porous materials possess a distinct advantage in this process: a massive interconnected pore network.
Unlike dense materials where nitriding is often limited to the outer layer, the high-purity nitrogen gas flows through these internal channels. This allows nitrogen atoms to penetrate deep into the material's volume.
Preserving Structural Integrity
A major benefit of this method is the preservation of the material's physical form.
The process increases hardness without compromising the porous structure. The pores remain open and interconnected, which is often essential for the material's final application (e.g., filtration, catalyst support).
Metallurgical Transformation
Strengthening the Lattice
Once the nitrogen diffuses into the material, it interacts with the metal's crystal structure, specifically the austenite lattice.
The nitrogen atoms form solid solutions or combine with elements like chromium to create chromium nitride (CrN) precipitates.
Significant Hardening
The formation of these precipitates is the primary driver of the material's enhanced performance.
These microscopic changes within the lattice create barriers to dislocation movement, resulting in a significant increase in the material's hardness compared to its untreated state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of High Purity
The "high-purity" aspect of the nitrogen is not optional; it is a strict requirement.
As noted in broader thermal treatment contexts, the presence of oxygen or moisture can lead to over-oxidation or even combustion of the material. If the nitrogen is not pure, the process shifts from hardening (nitriding) to degrading (oxidation), potentially ruining the chemical stability of the support.
Process Control Sensitivity
This method requires precise thermal management.
Because the nitriding occurs during the cooling ramp, the cooling rate must be controlled to allow sufficient time for diffusion within the 700 °C to 850 °C window. Cooling too rapidly through this range would result in insufficient nitriding and lower hardness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the benefits of this process, align your parameters with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Process Efficiency: Utilize this in-situ cooling method to eliminate the time and energy costs associated with a secondary heating cycle.
- If your primary focus is Material Hardness: Ensure the furnace residence time between 700 °C and 850 °C is maximized to allow for saturation of solid solutions and the formation of CrN precipitates.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Verify that the gas flow is sufficient to displace all oxygen, preventing oxidation that could collapse or clog the porous network.
By synchronizing the nitrogen flow with the cooling phase, you turn a passive thermal drop into an active, value-adding manufacturing step.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Optimal Temperature Range | 700 °C to 850 °C (During cooling phase) |
| Primary Mechanism | Gas-phase diffusion into interconnected pore networks |
| Key Outcome | Formation of CrN precipitates and lattice strengthening |
| Core Advantage | Increases hardness while preserving porous structure |
| Efficiency Gain | Eliminates the need for a secondary heating cycle |
| Gas Requirement | High-purity Nitrogen (to prevent oxidation) |
Elevate Your Material Hardening with KINTEK Precision
Maximize your process efficiency and achieve superior material hardness with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique gas nitriding and heat treatment requirements.
Whether you are working with complex porous structures or need precise thermal ramp control, KINTEK delivers the reliability your lab demands.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature workflows? Contact our specialists today to find the perfect furnace for your application.
Visual Guide
References
- Chunheng Liu, Yongbin Wang. Innovative Short Process of Preparation and Nitriding of Porous 316L Stainless Steel. DOI: 10.3390/ma18071564
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a dual-zone tube furnace for APCVD of SnSe2? Master Phase Purity & Stoichiometry
- What are the primary industries that use split tube furnaces? Essential for High-Temp Material Processing
- How does the temperature curve control in a quartz tube sintering furnace affect Ag-P electrode in-situ doping?
- How do you power on and operate a multi zone tube furnace? Master Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- How are horizontal furnaces used in thermal analysis? Precision Heating for Accurate Material Testing
- What are the different heating methods in tube furnaces and their corresponding temperature ranges?
- What are the different types of tube furnaces available? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Lab's Needs
- What role does a Tube Furnace play in HDS catalyst de-oiling? Unlock Efficient Pyrolysis Recovery



















