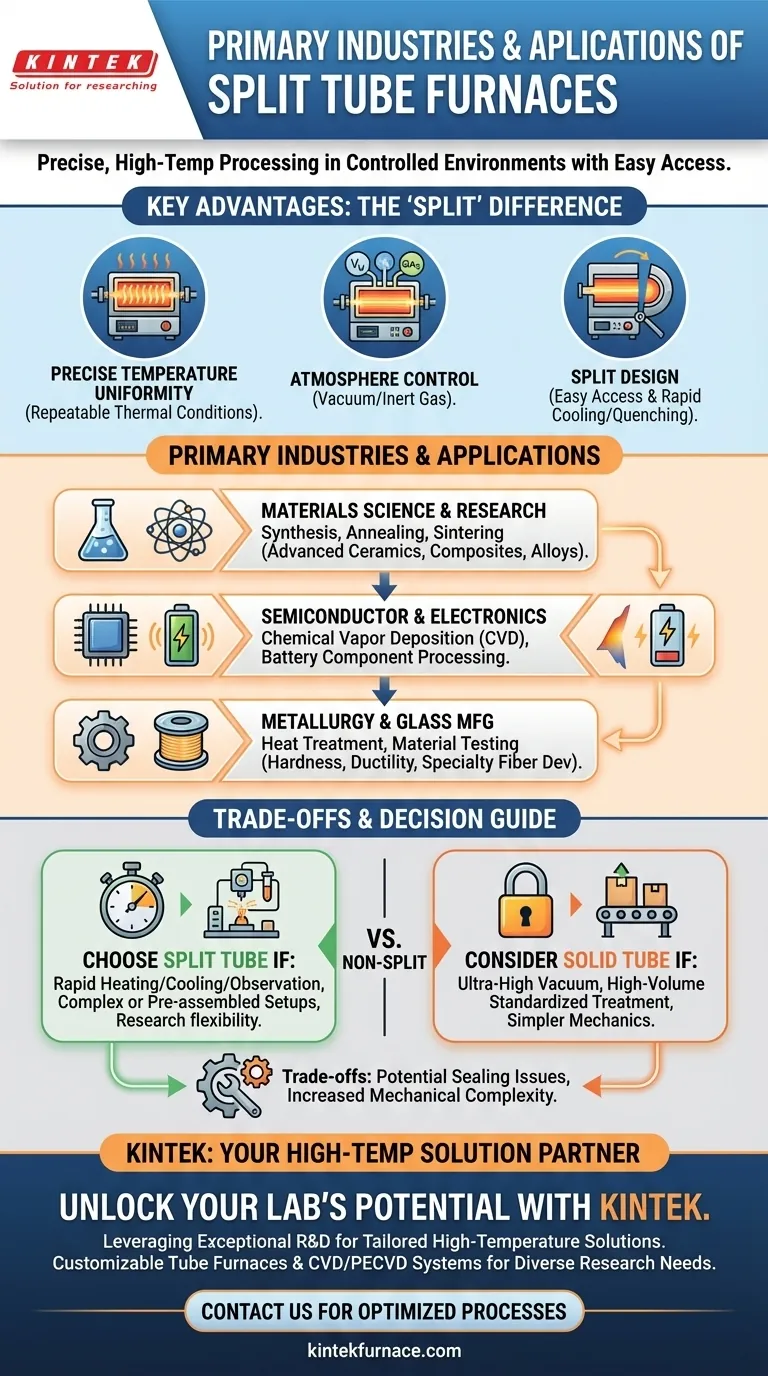
At their core, split tube furnaces are critical tools in any industry that requires precise, high-temperature processing of materials within a controlled environment. While they see use across a wide spectrum, they are most prevalent in materials science, semiconductor manufacturing, metallurgy, and advanced chemical research due to their unique combination of thermal control and physical accessibility.
The defining feature of a split tube furnace isn't just its ability to reach high temperatures uniformly; it's the hinged, split-body design. This provides easy access to the internal sample, making it indispensable for industries that rely on complex setups, rapid sample changes, or in-process observation.

Why Split Tube Furnaces Are Essential
The value of a split tube furnace lies in its ability to solve three fundamental challenges in advanced material processing: temperature control, atmospheric control, and sample accessibility.
Achieving Precise Temperature Uniformity
A key requirement in fields like materials science and metallurgy is repeatability. The cylindrical heating chamber of a tube furnace is engineered to create a highly uniform "hot zone."
This ensures that a material—whether being heat-treated, sintered, or annealed—experiences the exact same thermal conditions every time, leading to consistent material properties and reliable experimental results.
Controlling the Process Atmosphere
Many advanced materials are highly reactive with oxygen at high temperatures. Tube furnaces are designed to be sealed, allowing users to create a vacuum or introduce a specific gas.
This capability is critical for preventing oxidation, enabling processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) for semiconductors, or processing sensitive materials like lithium battery anodes and cathodes in an inert argon or nitrogen atmosphere.
The Critical Advantage of the "Split" Design
The hinged, split-body design is the furnace's main differentiator. It allows the heating chamber to be opened and closed around the process tube.
This offers unparalleled access, which is crucial for applications involving delicate or pre-assembled setups that cannot be slid into a standard furnace. It also enables rapid cooling (or quenching) by simply opening the furnace, a key step in controlling a material's final microstructure.
Key Industrial Applications by Sector
Different industries leverage these core capabilities to achieve specific goals, from fundamental research to industrial production.
Materials Science and Research
This is the most common sector. Researchers in academia and corporate R&D use split tube furnaces for synthesizing new materials, testing thermal stability, and performing heat treatments like annealing and sintering on advanced ceramics, composites, and alloys.
Semiconductor and Electronics
The electronics industry relies on these furnaces for processes that build devices at the atomic level. This includes chemical vapor deposition (CVD), where gases react on a substrate to form thin films, and the high-temperature processing of components for lithium-ion batteries and other new energy technologies.
Metallurgy and Glass Manufacturing
In metallurgy, split tube furnaces are used for the precise heat treatment of metals to achieve desired properties like hardness or ductility. The glass industry uses them for developing specialty glass fibers and testing material properties at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the split tube design is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Sealing and Atmosphere Integrity
The seam where the two halves of the furnace meet can be a potential point of failure for achieving a perfect hermetic seal. While well-designed furnaces mitigate this, applications requiring ultra-high vacuum may be better served by a solid, non-split tube design.
Increased Mechanical Complexity
The hinge mechanism and closing clamps add mechanical complexity compared to a simple, one-piece furnace. This can translate to a higher initial cost and introduce more potential points for mechanical wear over the furnace's lifetime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a furnace depends entirely on your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating and cooling or process observation: The accessibility of a split tube furnace is purpose-built for your needs and is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials in a research setting: A split tube furnace offers the flexibility to accommodate diverse and complex experimental setups.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized heat treatment: A non-split furnace may offer a simpler, more robust, and cost-effective solution if easy sample access is not a priority.
By understanding the interplay between thermal control and physical access, you can determine if a split tube furnace is the right tool for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Science & Research | Synthesis, annealing, sintering | Uniform heating, easy sample access for complex setups |
| Semiconductor & Electronics | Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), battery processing | Atmosphere control, rapid cooling, high precision |
| Metallurgy & Glass Manufacturing | Heat treatment, material testing | Repeatable results, flexibility in experimental design |
Unlock the full potential of your lab with KINTEK's advanced split tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide tailored high-temperature solutions for materials science, semiconductor, and metallurgy industries. Our diverse product line, including Tube Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, is enhanced by deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment



















