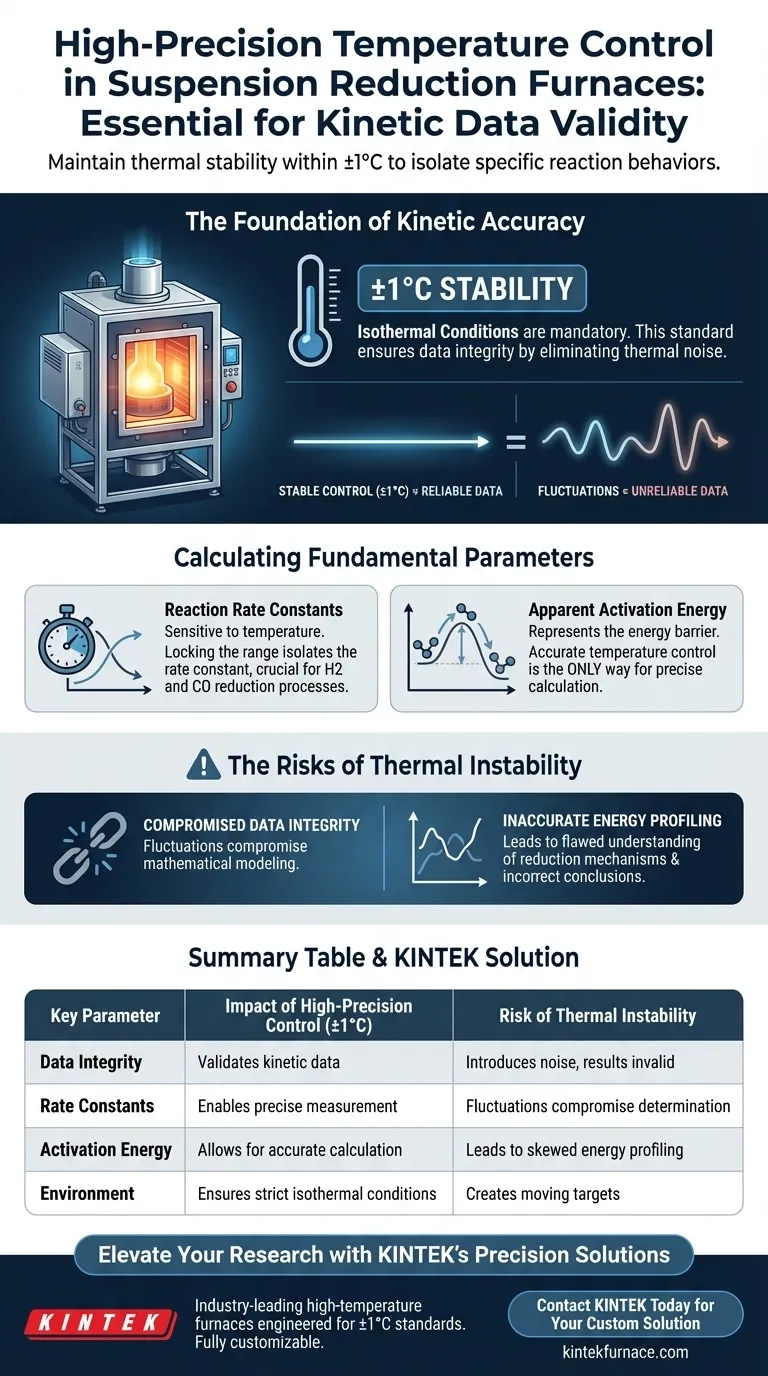
High-precision temperature control is the specific variable that validates kinetic data. In suspension reduction furnaces, maintaining thermal stability within ±1°C is mandatory to isolate specific reaction behaviors. Without this rigorous control, temperature fluctuations introduce noise that renders the determination of reaction rate constants and apparent activation energy scientifically invalid.
Isothermal kinetic experiments require an unwavering thermal environment to ensure data integrity. By eliminating significant temperature variances, researchers can precisely measure reaction rates and derive the true activation energy for reduction processes involving gases like hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
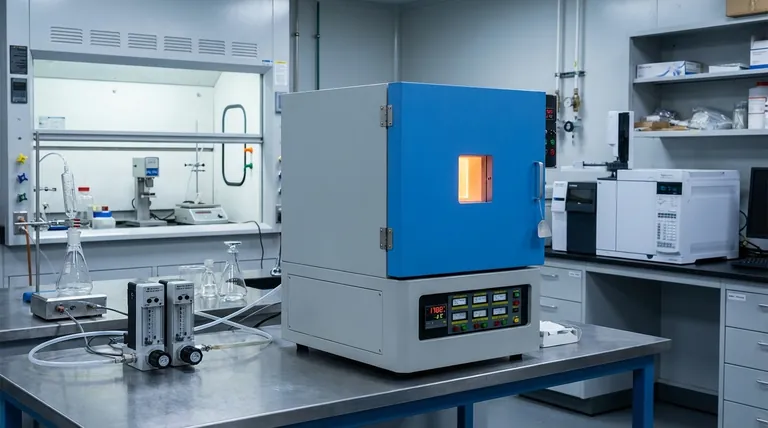

The Foundation of Kinetic Accuracy
To understand the reduction kinetics in suspension reduction furnaces, one must first ensure that the experimental environment is strictly controlled.
The Standard for Isothermal Experiments
The primary requirement for reliable kinetic studies is the maintenance of isothermal conditions.
This means the system must deploy high-precision automatic temperature control systems capable of holding the temperature steady.
The accepted standard for accuracy in these experiments is +/- 1°C.
Eliminating Data Compromise
When temperature varies beyond this narrow window, the data collected becomes unreliable.
Fluctuations create moving targets within the reaction environment, making it impossible to attribute changes in reaction speed solely to chemical kinetics.
Stability ensures that the determination of reaction rate constants remains uncompromised by external thermal noise.
Calculating Fundamental Parameters
The ultimate goal of using high-precision control is to derive accurate fundamental parameters that describe the reduction process.
Determining Reaction Rate Constants
Reaction rate constants are highly sensitive to temperature changes.
By locking the temperature within a tight range, researchers can isolate the rate constant for a specific thermal state.
This isolation is critical when studying complex reduction processes involving gases such as hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
Deriving Apparent Activation Energy
One of the most critical outputs of these experiments is the calculation of apparent activation energy.
This value represents the energy barrier that reacting molecules must overcome.
Accurate maintenance of the temperature is the only way to allow for the precise calculation of this energy value, ensuring the findings accurately reflect the thermodynamics of the system.
The Risks of Thermal Instability
While high-precision control requires sophisticated systems, the alternative—allowing thermal drift—negates the value of the experiment.
Compromised Data Integrity
The primary trade-off in kinetic analysis is between system complexity and data validity.
If the control system cannot maintain the +/- 1°C threshold, the resulting fluctuations directly compromise the mathematical modeling of the reaction.
Inaccurate Energy Profiling
Without stable control, the calculated activation energy will likely be skewed.
This leads to a flawed understanding of the reduction mechanism, potentially resulting in incorrect conclusions about how hydrogen or carbon monoxide interacts with the suspension at high temperatures.
Ensuring Reliable Experimental Outcomes
To successfully study reduction kinetics, you must prioritize thermal stability above other operational variables.
If your primary focus is fundamental research:
- Ensure your control system is calibrated to maintain stability within +/- 1°C to guarantee the validity of your reaction rate constants.
If your primary focus is process modeling:
- Prioritize thermal precision to obtain accurate apparent activation energy values, which are essential for predicting behavior in hydrogen and carbon monoxide reduction atmospheres.
Precise thermal control is not merely an operational detail; it is the prerequisite for calculating the true energy requirements of your chemical process.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | Impact of High-Precision Control (±1°C) | Risk of Thermal Instability |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Validates kinetic data by isolating reaction variables | Introduces noise, rendering results scientifically invalid |
| Rate Constants | Enables precise measurement for H2 and CO reactions | Fluctuations compromise determination of constants |
| Activation Energy | Allows for accurate calculation of energy barriers | Leads to skewed energy profiling and flawed mechanisms |
| Environment | Ensures strict isothermal conditions are met | Creates moving targets that negate experimental value |
Elevate Your Research with KINTEK’s Precision Solutions
Precise thermal stability is the backbone of reliable kinetic data. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature furnaces, including specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all engineered to meet the rigorous ±1°C standards required for fundamental research and process modeling.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to suit your unique reduction kinetics and atmospheric needs. Don't let thermal noise compromise your activation energy calculations—partner with KINTEK for unparalleled accuracy.
Ready to optimize your laboratory's heat treatment?
Contact KINTEK Today to Discuss Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Pengcheng Hou, Yongsheng Sun. Mechanism of effective iron extraction from rare earth-bearing iron ores by low-temperature suspension reduction method. DOI: 10.37190/ppmp/204110
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is the rotary kiln significant in modern industry? Unlock Efficient, Large-Scale Material Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces contribute to material science and chemical engineering? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- How are rotary furnaces utilized in metallurgical applications? Unlock Efficient Metal Processing and Recycling
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What role does the atmosphere control system play in a rotary tube sintering furnace? Enhance Material Quality and Efficiency
- What are the advantages of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniform Heating & Mixing
- What are the challenges associated with direct-fired rotary kilns? Balancing Efficiency vs. Control and Purity
- What types of small parts are commonly processed in rotary retort furnaces? Ideal for Fasteners and Powders



















