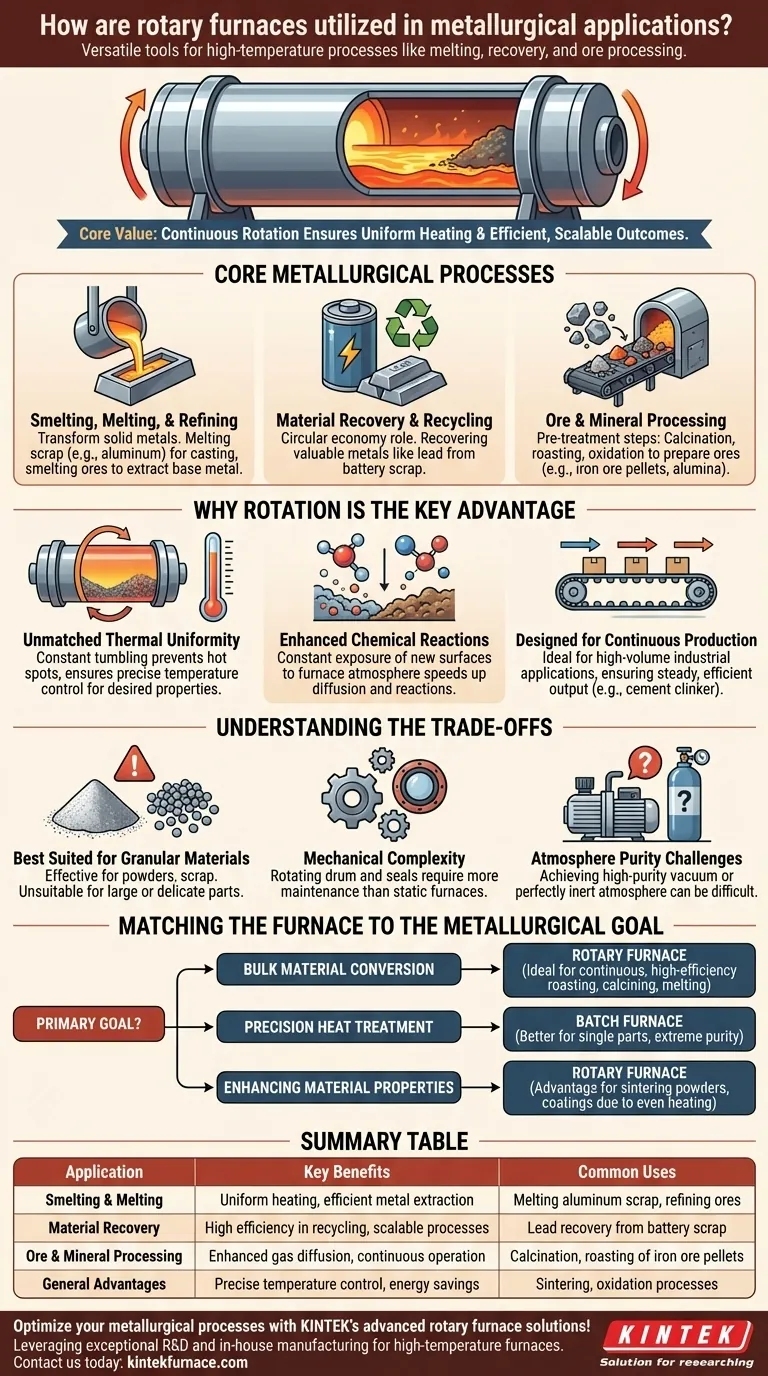
In metallurgy, rotary furnaces are versatile tools used for a wide range of high-temperature processes. Their primary applications include melting and smelting metals like aluminum, recovering valuable materials such as lead from battery scrap, and processing raw ores and minerals through processes like calcination and roasting to prepare them for further refinement.
The core value of a rotary furnace lies in its continuous rotation. This tumbling action ensures every particle of material is uniformly heated and exposed to process gases, leading to highly consistent, efficient, and scalable metallurgical outcomes.
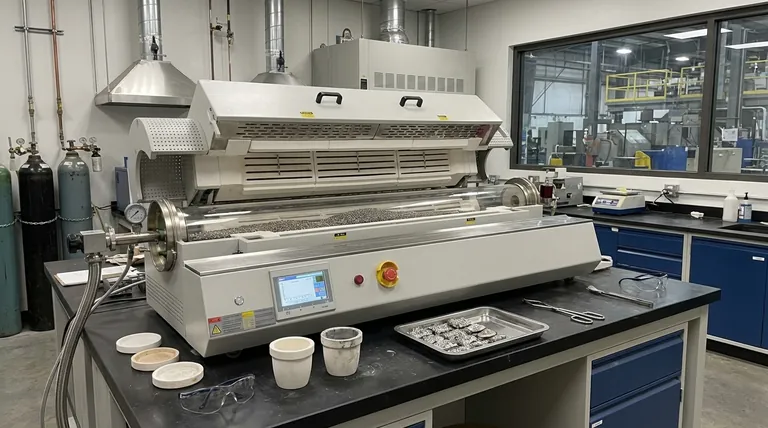

Core Metallurgical Processes in a Rotary Furnace
Rotary furnaces are not a one-size-fits-all solution; they excel at specific, large-scale thermal transformation tasks that are fundamental to metal production and recycling.
Smelting, Melting, and Refining
The most direct application is the transformation of solid metals. Rotary furnaces are commonly used for melting scrap, such as aluminum, to prepare it for casting or alloying.
They are also employed in smelting operations, where heat and chemical reducing agents are used to extract a base metal from its ore.
Material Recovery and Recycling
Rotary furnaces play a critical role in the circular economy, particularly in recovering valuable metals from waste products.
A prominent example is the recovery of lead from battery scrap. The furnace efficiently melts the lead components, separating them from other materials for reuse.
Ore and Mineral Processing
Before metals can be extracted, their ores must often be prepared. Rotary furnaces are essential for these pre-treatment steps.
Processes include calcination (thermal decomposition to remove impurities or water), roasting, and oxidation, which modify the chemical state of materials like iron ore pellets and alumina, making them suitable for smelting.
Why Rotation Is the Key Advantage
The defining feature of the furnace—its rotation—is directly responsible for its effectiveness in the applications listed above. This mechanical principle provides several key benefits over static furnace designs.
Unmatched Thermal Uniformity
The constant tumbling of the material load is the simplest and most effective way to ensure uniform heating. This prevents hot spots and cold zones, ensuring that the entire batch reaches the target temperature.
This precise temperature control is critical for achieving desired material properties, whether sintering powders into a dense solid or inducing a specific phase transition.
Enhanced Chemical Reactions
Many metallurgical processes rely on reactions between a solid material and a gas. The tumbling action constantly exposes new surfaces of the material to the furnace's atmosphere.
This dramatically improves gas diffusion, speeding up chemical reactions like oxidation or reduction and making the entire process faster and more energy-efficient.
Designed for Continuous Production
Unlike batch-based furnaces, many rotary furnaces (often called kilns) can be fed material continuously at one end and discharge the finished product at the other.
This capability is ideal for high-volume industrial applications, such as the production of cement clinker or iron ore pellets, ensuring a steady and efficient output.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary furnace is not the universal solution for all thermal processing. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Best Suited for Granular Materials
The tumbling action is highly effective for powders, granular materials, scrap, and pellets. It is, however, unsuitable for treating large, single components or delicate parts that could be damaged by the mechanical motion.
Mechanical Complexity
A rotating drum, especially one that must be sealed to control its atmosphere, is mechanically more complex than a simple static box furnace. This can lead to higher maintenance requirements, particularly for the seals and rotational drive system.
Atmosphere Purity Challenges
While gas interaction is excellent, achieving and maintaining a very high-purity vacuum or a perfectly inert atmosphere can be more challenging in a large, dynamic system with seals than in a smaller, fully sealed static furnace.
Matching the Furnace to the Metallurgical Goal
To apply this knowledge, consider the primary goal of your process. Your material's form and the scale of your operation will determine if a rotary furnace is the right choice.
- If your primary focus is bulk material conversion: The continuous processing and high efficiency of a rotary furnace make it ideal for tasks like roasting ores, calcining minerals, or melting large volumes of scrap.
- If your primary focus is precision heat treatment: A batch-style box, vacuum, or retort furnace may be a better choice for treating single, large parts or when an extremely pure, static atmosphere is required.
- If your primary focus is enhancing material properties: For sintering powders or applying coatings where thermal uniformity is paramount, the rotary furnace's even heating provides a distinct advantage.
Choosing the right thermal equipment begins with a clear understanding of both your material's form and your process's primary objective.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Smelting & Melting | Uniform heating, efficient metal extraction | Melting aluminum scrap, refining ores |
| Material Recovery | High efficiency in recycling, scalable processes | Lead recovery from battery scrap |
| Ore & Mineral Processing | Enhanced gas diffusion, continuous operation | Calcination, roasting of iron ore pellets |
| General Advantages | Precise temperature control, energy savings | Sintering, oxidation processes |
Optimize your metallurgical processes with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Rotary, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs in metal production and recycling. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and scalability in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















