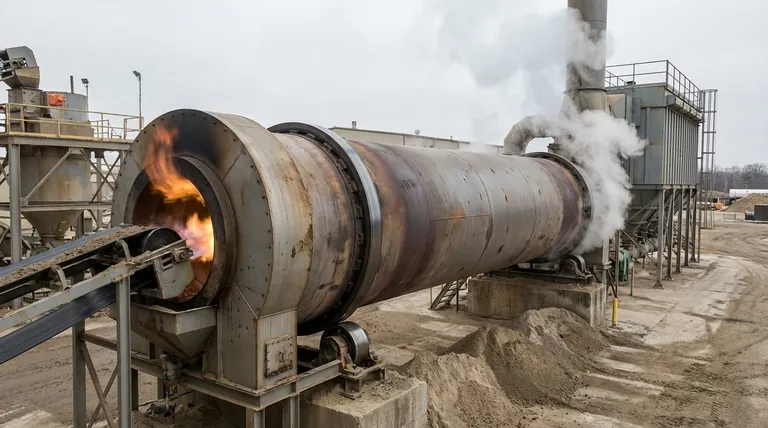
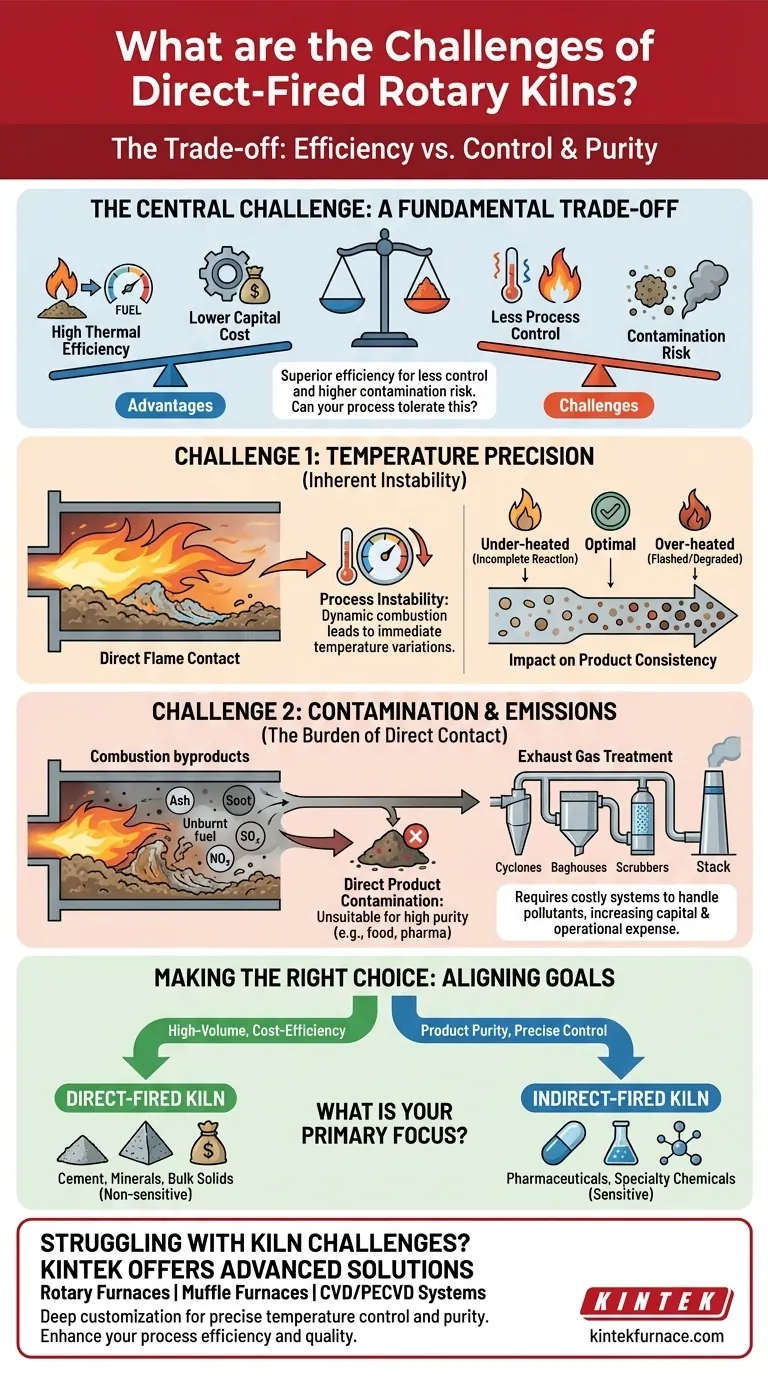
The primary challenges of a direct-fired rotary kiln are its difficulty in maintaining precise temperature control and the inherent risk of contaminating the material being processed with combustion byproducts. These issues stem from the kiln's core design, where the flame and hot gases are in direct contact with the material inside the rotating drum. This requires robust, and often expensive, exhaust gas handling systems to manage pollutants.
A direct-fired kiln forces a fundamental trade-off: it offers superior thermal efficiency and lower initial cost in exchange for less process control and a higher risk of product contamination. The central challenge is not overcoming these issues, but determining if your material and process goals can tolerate them.

The Challenge of Temperature Precision
In a direct-fired system, the burner's flame and combustion gases directly heat the material. While efficient, this creates significant control challenges that can impact the final product quality.
Inherent Process Instability
The combustion process is dynamic. Minor fluctuations in fuel supply, airflow, or fuel quality immediately translate into temperature variations within the kiln. This direct link makes it difficult to hold the material at a precise, stable temperature profile, which is critical for many chemical reactions and phase changes.
Impact on Product Consistency
This lack of precise control can lead to inconsistent product. Some material may be under-heated, resulting in incomplete reactions, while other material may be over-heated or "flashed," leading to degradation, damage, or undesirable properties.
Managing Contamination and Emissions
The direct contact between the combustion gas and the process material is the source of the kiln's greatest operational and environmental challenges.
Direct Product Contamination
Combustion is rarely perfect. Byproducts like ash, soot, and even unburnt fuel can mix with and contaminate the material being processed. This makes direct-fired kilns unsuitable for applications requiring high purity, such as food-grade products, pharmaceuticals, or certain specialty chemicals.
The Burden of Exhaust Gas Treatment
The exhaust stream from a direct-fired kiln contains all the products of combustion, including pollutants like NOx, SOx, and particulates. This gas must be treated before being released, requiring a complex and costly system of cyclones, baghouses, or wet scrubbers to meet environmental regulations. This downstream equipment adds significant capital and operational expense.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The challenges of a direct-fired kiln must be weighed against its significant advantages. Its selection is a strategic decision based on process priorities.
Advantage: High Thermal Efficiency
Because heat is transferred directly from the flame and gases to the material, thermal efficiency is very high. There are minimal heat transfer losses that would occur from heating through a metal shell, as is done in indirect-fired kilns. This translates directly to lower fuel consumption.
Advantage: Lower Capital Cost
The design of a direct-fired kiln is mechanically simpler than an indirect one. It does not require a complex sealed inner tube or an external combustion chamber, which typically results in a lower initial purchase and installation cost.
The Core Limitation: Material Compatibility
The decisive factor is whether your material can withstand direct contact with flue gas. If the material is not sensitive to slight contamination and does not require pinpoint temperature accuracy, the efficiency and cost benefits of a direct-fired kiln are compelling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right kiln technology depends entirely on your process requirements and end-product specifications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume processing where cost-efficiency is paramount: A direct-fired kiln is often the superior choice for materials like cement, minerals, and other bulk solids that are not sensitive to contamination.
- If your primary focus is product purity and precise temperature control: You must use an indirect-fired kiln, as it physically separates the combustion gases from the process material.
Choosing the correct heating technology is about aligning the tool's inherent characteristics with your specific operational objective.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Precision | Difficulty in maintaining stable temperature due to direct flame contact | Inconsistent product quality, incomplete reactions |
| Contamination Risk | Combustion byproducts (e.g., ash, soot) mix with material | Unsuitable for high-purity applications like pharmaceuticals |
| Emissions Management | Requires costly exhaust systems to handle pollutants (e.g., NOx, SOx) | Increased capital and operational expenses |
| Trade-offs | High thermal efficiency and lower initial cost vs. reduced control | Best for non-sensitive materials like cement and minerals |
Struggling with kiln challenges? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with deep customization to ensure precise temperature control and purity for your unique experiments. Enhance your process efficiency and product quality—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource



















