The rotary kiln is a cornerstone of modern heavy industry because of its unique ability to continuously process materials at extreme temperatures with high efficiency and uniformity. This makes it an indispensable tool in sectors ranging from cement manufacturing and metallurgy to chemical processing and waste treatment, where it functions as the "heart of production" for transforming raw inputs into high-value products.
The true significance of the rotary kiln lies not in any single feature, but in the powerful synergy of its design: it combines continuous material flow with uniform heat treatment, enabling the mass production of consistent, high-quality materials on a scale that batch processing cannot match.

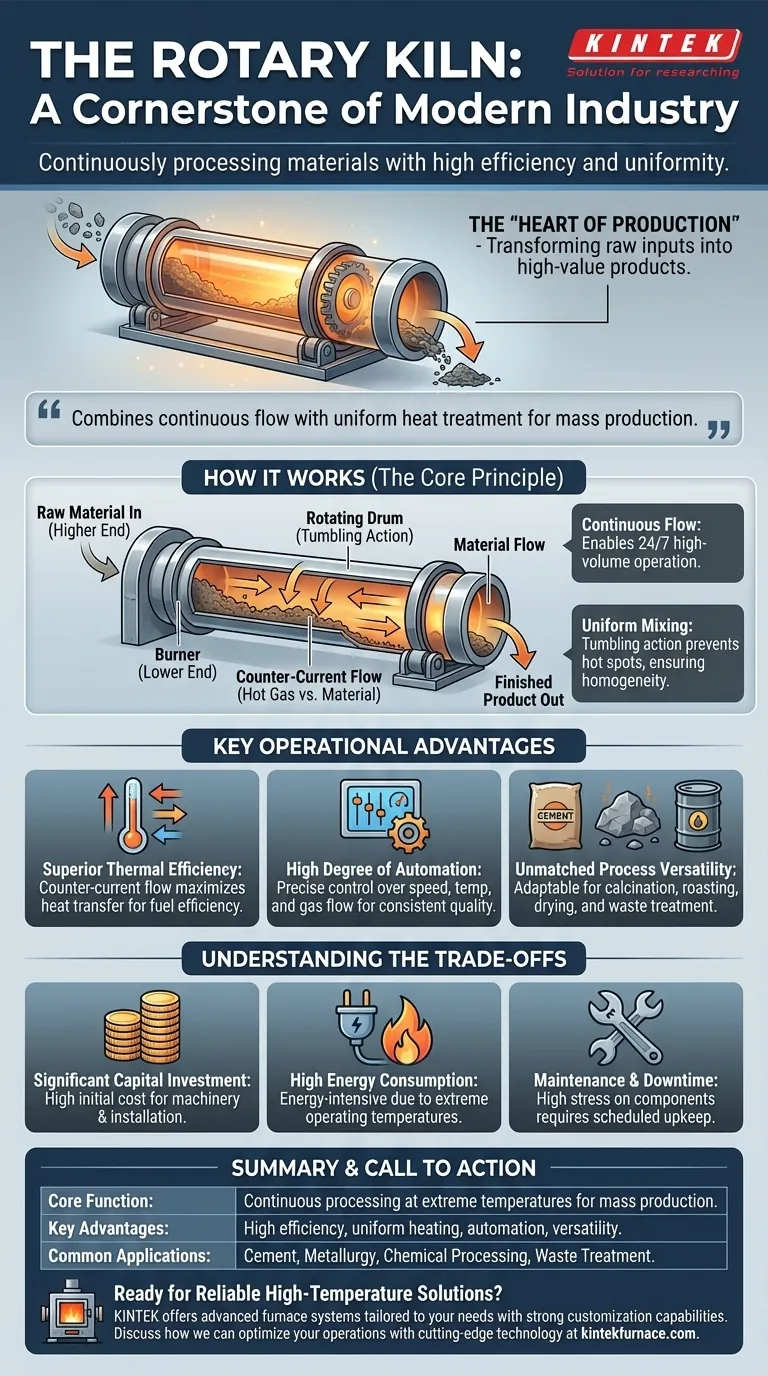
The Core Principle: How It Achieves Industrial Scale
At its core, a rotary kiln is a simple and robust machine. Understanding its fundamental mechanics reveals why it is so effective.
How a Rotary Kiln Works
A rotary kiln is a large, rotating cylindrical drum, mounted at a slight incline. Raw material is fed into the higher end.
As the kiln slowly rotates, the material tumbles and cascades its way down toward the lower end due to gravity. This tumbling motion is the secret to its effectiveness.
The Power of Continuous Flow
Unlike batch ovens that process one load at a time, a rotary kiln operates continuously. Material is constantly fed in one end and discharged from the other.
This uninterrupted flow is the foundation of modern, high-volume manufacturing, enabling plants to operate 24/7 and achieve massive production outputs. It is the engine that drives industrial-scale economics.
Ensuring Product Homogeneity
The constant tumbling action ensures that the material is thoroughly mixed as it travels through the drum. This prevents hot spots and guarantees that every particle is exposed to a uniform temperature.
This level of consistency is critical for producing high-quality cement, calcined minerals, and other chemical products where precise material properties are required.
Key Operational Advantages
The kiln's design gives rise to several technical and economic advantages that have solidified its role in industry for over a century.
Superior Thermal Efficiency
Most rotary kilns operate on a counter-current flow principle. Hot gas from a burner at the lower end flows up the kiln, directly against the flow of the material moving down.
This design maximizes heat transfer, ensuring that the hottest gases meet the most processed material, while cooler gases preheat the incoming raw feed. This, combined with the enclosed drum, minimizes heat loss and boosts overall fuel efficiency.
High Degree of Automation and Control
Modern kilns are highly automated systems. Operators can precisely control rotation speed, temperature profile, and gas flow, which reduces the need for manual labor.
This high degree of control directly impacts the quality, output, and cost of the final product. Innovations like electric heating offer even finer temperature adjustments and can lower maintenance costs compared to traditional fuel-fired systems.
Unmatched Process Versatility
The fundamental design of the rotary kiln can be adapted for a wide variety of thermal processes and materials.
It is used for calcination in cement production, roasting ores in metallurgy, drying bulk solids, and thermally destroying hazardous materials in waste treatment, showcasing its incredible flexibility across diverse industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While immensely powerful, the rotary kiln is not without its challenges. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Significant Capital Investment
Rotary kilns are massive, complex pieces of industrial machinery. The initial cost of procurement, installation, and commissioning represents a substantial capital expenditure.
High Energy Consumption
By their very nature, these are energy-intensive systems. While designed for thermal efficiency, the absolute amount of fuel or electricity required to maintain operating temperatures of 800-1450°C (1470-2640°F) or higher constitutes a major operational cost.
Maintenance and Downtime
The combination of high temperatures, abrasive materials, and continuous mechanical rotation places immense stress on the kiln's components, particularly the refractory lining and drive system.
Scheduled maintenance is critical, and unplanned downtime can halt the entire production line, leading to significant financial losses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary kiln is based on balancing its powerful advantages against its operational demands. Its suitability depends entirely on your primary industrial objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum production throughput: The kiln's continuous operation is its most valuable feature for achieving high-volume, uninterrupted output.
- If your primary focus is product quality and consistency: The uniform heating and mixing from its tumbling action are non-negotiable for ensuring product homogeneity at scale.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility and environmental compliance: Modern kiln designs with advanced automation and integrated emission controls offer the adaptability needed for diverse materials and strict regulations.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln remains a dominant force in industry because it provides a reliable and scalable solution to the fundamental challenge of transforming raw materials with heat.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Continuous processing at extreme temperatures for mass production |
| Key Advantages | High efficiency, uniform heating, automation, process versatility |
| Common Applications | Cement manufacturing, metallurgy, chemical processing, waste treatment |
| Limitations | High capital investment, energy consumption, maintenance requirements |
Ready to enhance your industrial processes with reliable high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how we can optimize your operations with cutting-edge technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials



















