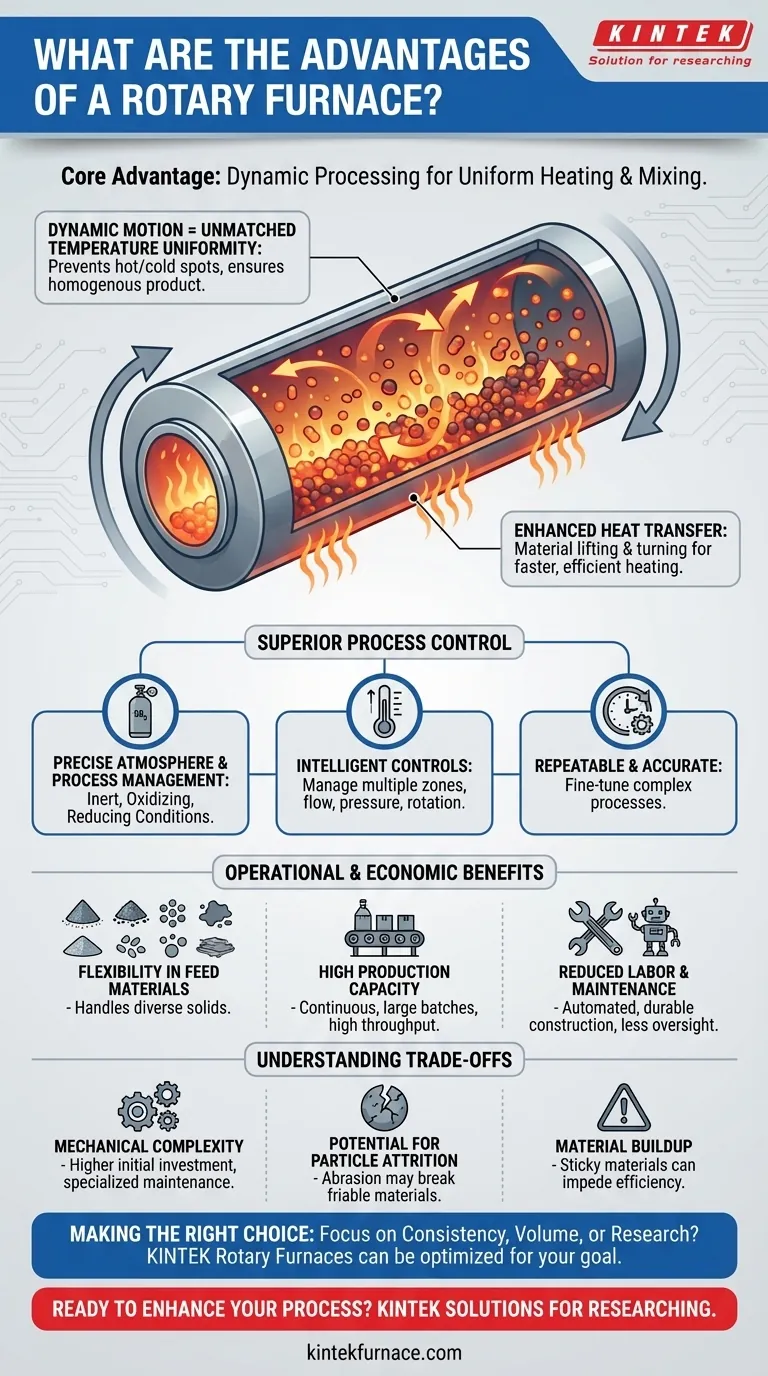
The core advantage of a rotary furnace is its ability to deliver exceptionally uniform heating and mixing simultaneously. This is achieved through the constant rotation of its cylindrical chamber, which ensures every particle of the material is processed under identical conditions. This dynamic action leads to superior energy efficiency, process control, and flexibility in handling a wide variety of feed materials.
A rotary furnace's primary value lies not just in heating, but in its dynamic processing. The rotating action is the source of its main advantages, enabling a level of material consistency and thermal efficiency that static furnaces cannot easily replicate.
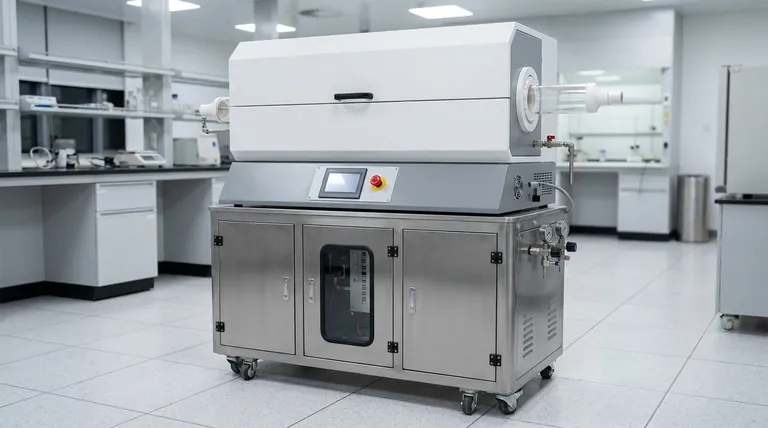

How a Rotary Furnace Achieves Superior Process Control
The defining characteristic of a rotary furnace is its rotating tube. This mechanical feature is the key to its operational benefits, fundamentally changing how heat and materials interact.
Dynamic Motion for Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The continuous tumbling of the material inside the furnace is its greatest strength. This action prevents the formation of hot or cold spots within the batch.
Every particle is consistently exposed to the heat source and the internal atmosphere. This ensures a homogenous final product, which is critical for sensitive processes like catalyst roasting or chemical synthesis where consistency is paramount.
Enhanced Heat Transfer and Efficiency
In a static furnace, heat must penetrate a stationary mass. In a rotary furnace, the material is constantly being lifted and turned over, exposing new surfaces directly to the heat source.
This dramatically increases the efficiency of heat transfer through conduction, convection, and radiation. The result is faster processing times and a higher utilization of input energy, leading to significant energy savings.
Precise Atmosphere and Process Management
Rotary furnaces are sealed systems, which allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere. This makes them adaptable for processes requiring inert, oxidizing, or reducing conditions.
Modern systems integrate intelligent controls to manage temperature profiles across multiple heating zones, gas flow, pressure, and rotation speed. This allows operators to fine-tune and repeat complex thermal processes with high accuracy.
The Operational and Economic Benefits
The unique processing environment of a rotary furnace translates into tangible benefits for both industrial production and scientific research.
Flexibility in Feed Materials
The robust mechanical design and mixing action allow rotary furnaces to handle a diverse range of materials. They are effective for processing powders, granules, sludges, and various solids that would be difficult to process uniformly in a static system.
High Production Capacity
Because of their high thermal efficiency and ability to run continuously or in large batches, rotary furnaces are capable of high throughput. This makes them a cornerstone technology for industries requiring large-scale, consistent material processing.
Reduced Labor and Maintenance
The automated nature of modern rotary furnaces reduces the need for constant manual oversight. Their durable construction, featuring heavy steel bodies and corrosion-resistant refractory linings, also minimizes long-term maintenance costs and operational downtime.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Mechanical Complexity
The drive gear, seals, and rotating tube introduce mechanical complexity not found in static furnaces. This can lead to a higher initial investment and may require specialized maintenance for the rotational components over the furnace's lifespan.
Potential for Particle Attrition
The tumbling action that ensures uniform heating can also cause abrasion and break down friable materials. For applications where preserving particle size and shape is absolutely critical, the mechanical stress may be a significant drawback.
Material Buildup
Certain sticky or agglomerating materials can build up on the furnace's inner walls. This can impede heat transfer and require periodic shutdowns for cleaning, reducing overall efficiency if the feed material is not well-suited to the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct furnace requires matching its capabilities to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and quality: The unparalleled temperature uniformity makes a rotary furnace ideal for producing high-value, homogenous materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: The thermal efficiency and high throughput capacity offer a clear economic advantage for scaling operations.
- If your primary focus is research and process development: The precise control over temperature, atmosphere, and rotation speed provides an excellent platform for experimenting with and optimizing thermal processes.
By understanding its core mechanism of dynamic heating, you can determine if a rotary furnace is the optimal tool to achieve your specific processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Uniform Heating & Mixing | Constant rotation ensures every particle is processed identically. |
| Enhanced Heat Transfer | Dynamic tumbling action leads to faster processing and energy savings. |
| Process Control | Precise management of temperature, atmosphere, and rotation speed. |
| Material Flexibility | Handles a wide range of feed materials like powders, granules, and sludges. |
| High Throughput | Ideal for large-scale, continuous, or batch industrial production. |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing with superior uniformity and efficiency?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories and industrial facilities with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK rotary furnace can optimize your process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















