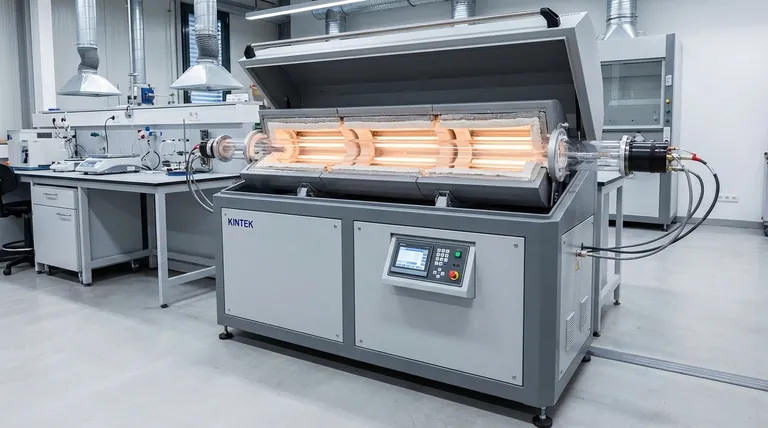
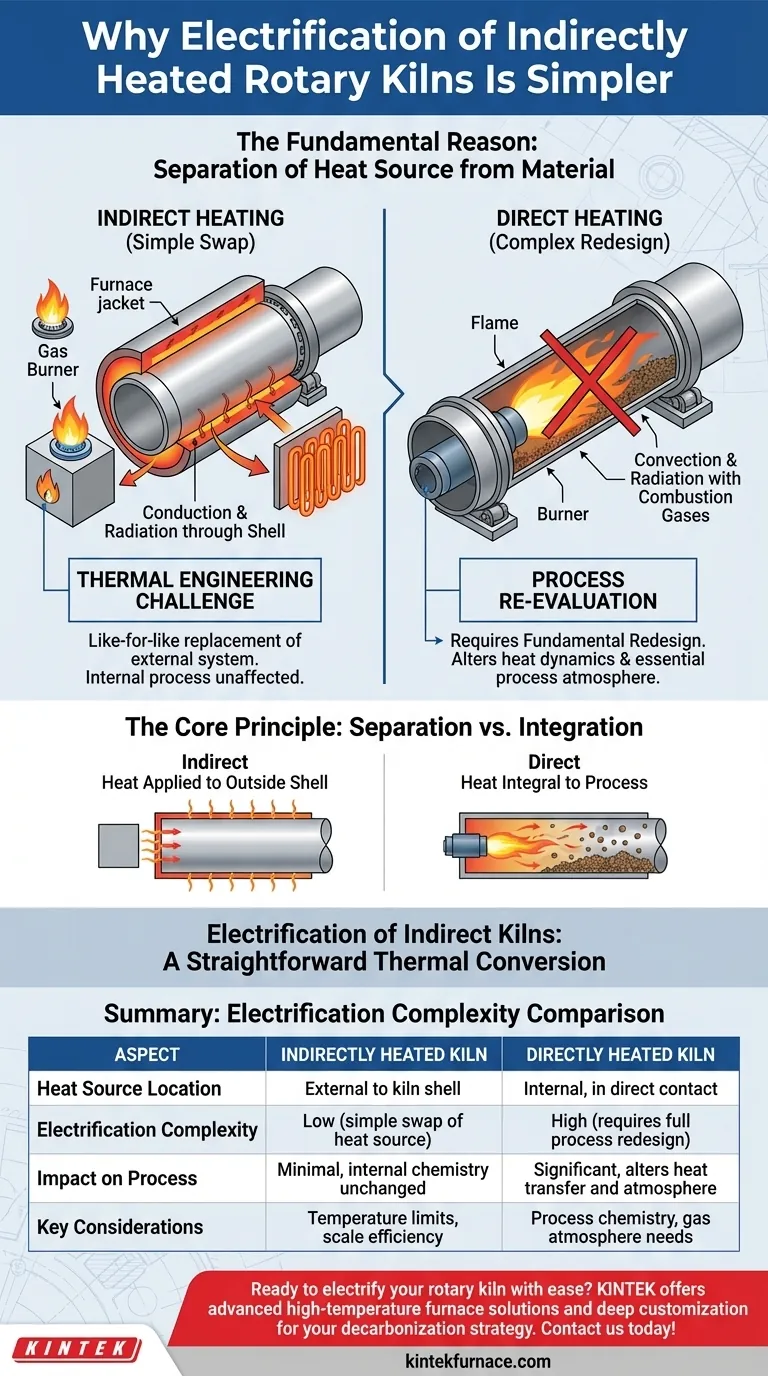
The fundamental reason electrification of indirectly heated rotary kilns is more straightforward is that it requires replacing one external heat source with another. Because the heating system is physically separate from the material being processed, the conversion is primarily a thermal engineering challenge, not a complex process redesign. The internal chemistry and mechanics of the kiln remain largely unaffected.
The core difference lies in the location of the heat source. In an indirectly heated kiln, the heat is applied to the outside of the rotating shell, much like heating a pot on a stove. Electrifying it is as simple as swapping a gas burner for an electric element, whereas electrifying a directly heated kiln requires re-engineering the entire internal process environment.

The Core Principle: Separation vs. Integration
To understand why this conversion is simpler, you must first distinguish between the two primary methods of heating a rotary kiln. The distinction dictates the entire scope of an electrification project.
How Indirect Heating Works
In an indirectly heated kiln, the material tumbles inside a rotating tube. The heat source, traditionally fossil fuel burners, is located outside this tube, often within an insulated furnace or jacket.
Heat is transferred by conduction and radiation through the metal wall of the kiln shell to the material inside. The combustion gases from the burners never come into contact with the process material.
How Direct Heating Works
In a directly heated kiln, a large burner fires a flame directly into the rotating tube. The hot combustion gases flow through the kiln, making direct contact with the process material.
Here, the heat source is an integral part of the process environment. The gases transfer heat via convection and radiation, and their chemical composition (e.g., CO2, H2O, excess oxygen) directly influences the reactions taking place inside.
The Engineering Reality of Electrification
This fundamental design difference creates two vastly different engineering challenges when considering a switch from fossil fuels to electricity.
The "Simple Swap" of Indirect Kilns
When electrifying an indirectly heated kiln, you are essentially performing a like-for-like replacement of the external heating system. The gas burners are removed, and electric resistance heating elements are installed in their place.
The internal process is agnostic to the external heat source. As long as the kiln shell reaches the same target temperature, the outcome for the material inside remains consistent.
The Complex Redesign of Direct Kilns
Electrifying a directly heated kiln is not a simple swap. You cannot simply place an electric element where the flame used to be.
Doing so would fundamentally alter the process by removing the flow of hot gases. This changes the heat transfer dynamics and, more critically, eliminates the specific chemical atmosphere created by fuel combustion, which is often essential for the desired material transformation. A successful conversion requires a complete process re-evaluation and redesign.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the path is more straightforward for indirect kilns, it is not without critical considerations.
Key Constraint: Maximum Temperature
The primary limitation is whether electric heating elements can achieve and sustain the required process temperatures. While modern elements are highly capable, very high-temperature applications (above 1100-1200°C) can be challenging and may require specialized, costly materials for the elements and the kiln shell.
Scale and Heat Transfer
Indirect heating relies on heat transfer through the kiln wall. As the diameter of a kiln increases, its volume grows faster than its surface area. This can make it difficult for indirect heating to efficiently and uniformly heat material at a very large scale, a limitation that exists regardless of whether the heat source is gas or electric.
Applying This to Your Decarbonization Strategy
Your approach to electrification depends entirely on your kiln's existing design and your process requirements.
- If you operate an existing indirect kiln: Your primary challenge will be sourcing and integrating an electric heating system that can match your current temperature profile and duty cycle.
- If your process requires a specific gas atmosphere from direct firing: Electrification is a significant undertaking that demands a fundamental redesign of your process chemistry and heat transfer methods.
- If you are designing a new process: An indirectly heated electric kiln offers a lower-risk, well-understood path for decarbonization, provided its temperature and scale limitations are suitable for your goals.
Understanding the boundary between your heat source and your process is the first step toward a successful and efficient electrification project.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Indirectly Heated Kiln | Directly Heated Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source Location | External to kiln shell | Internal, in direct contact with material |
| Electrification Complexity | Low (simple swap of heat source) | High (requires full process redesign) |
| Impact on Process | Minimal, internal chemistry unchanged | Significant, alters heat transfer and atmosphere |
| Key Considerations | Temperature limits, scale efficiency | Process chemistry, gas atmosphere needs |
Ready to electrify your rotary kiln with ease? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're upgrading an indirect kiln or tackling a complex process redesign, our expertise ensures efficient decarbonization and enhanced performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your electrification strategy!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes



















