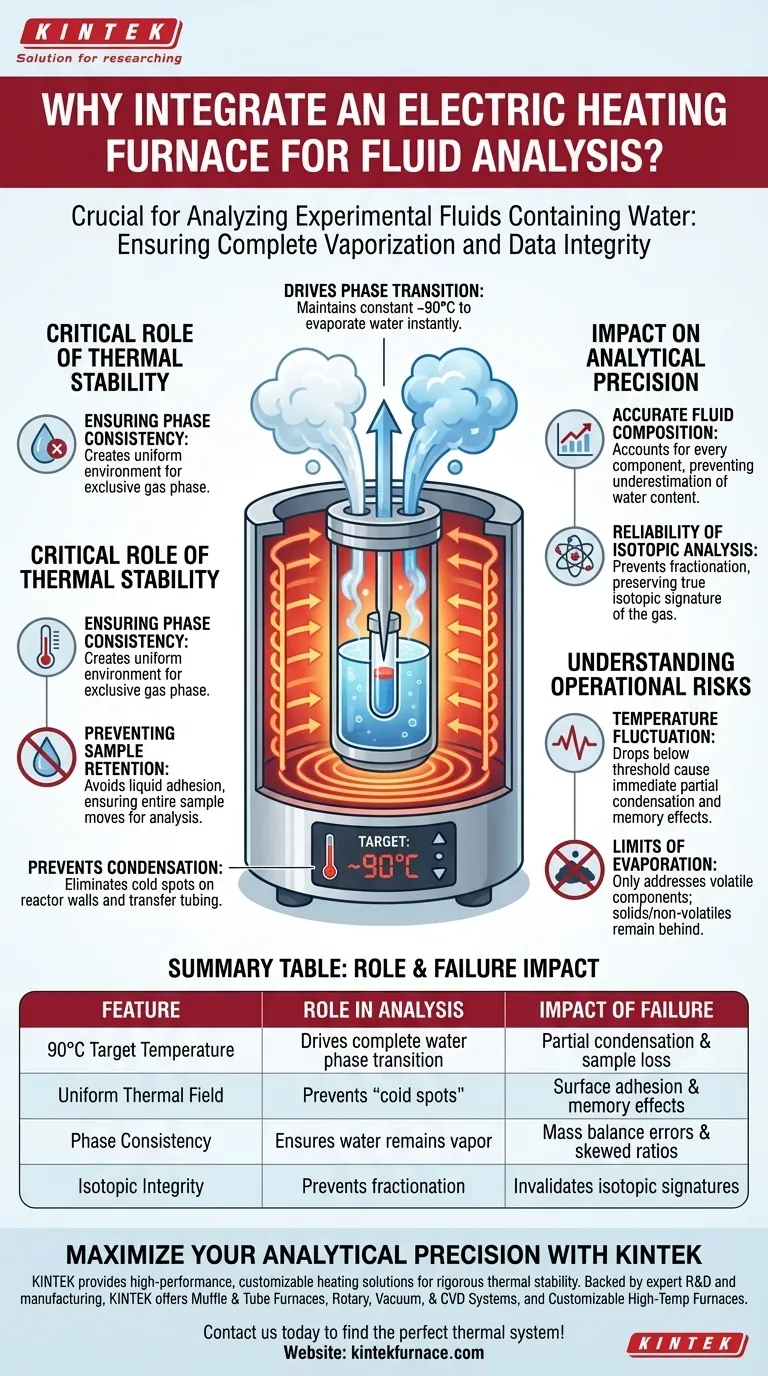
The integration of an electric heating furnace serves a vital thermodynamic purpose: it maintains the capsule-piercing reactor at a constant temperature, typically around 90°C, to drive the phase transition of water.
This thermal control ensures that any water contained within the extracted fluid is instantly and completely evaporated into a gaseous state. By maintaining this temperature, the system prevents water vapor from cooling and condensing back into liquid form on the reactor walls or within the transfer tubing.
The core objective of the heating furnace is to guarantee complete vaporization, eliminating condensation "cold spots" that would distort fluid composition calculations and ruin isotopic analysis.

The Critical Role of Thermal Stability
Ensuring Phase Consistency
When analyzing experimental fluids, water is a particularly challenging component due to its high boiling point relative to other gases.
The electric furnace surrounds the reactor to create a uniform thermal environment. By holding the temperature at approximately 90°C, the system ensures that the physical conditions favor the gas phase exclusively.
Preventing Sample Retention
Without this external heat source, extracting fluid from a capsule would lead to immediate cooling.
This cooling would cause water vapor to condense into liquid droplets, adhering to the internal surfaces of the reactor or the connecting tubes. The furnace effectively eliminates this surface adhesion, ensuring the entire sample moves through the system for analysis.
Impact on Analytical Precision
Accurate Fluid Composition
To calculate the true composition of a fluid, every component extracted must be accounted for by the analyzer.
If water condenses and stays trapped inside the reactor or tubing, it is effectively removed from the measurement. This results in an erroneous calculation where the water content is underestimated, skewing the reported ratios of all other components.
Reliability of Isotopic Analysis
Isotopic analysis relies heavily on the principle of mass balance.
If condensation occurs, heavier isotopes tend to preferentially condense into the liquid phase (fractionation), while lighter isotopes remain in the vapor. This separation alters the isotopic signature of the gas reaching the analyzer, rendering the data scientifically invalid.
Understanding the Operational Risks
The Consequence of Temperature Fluctuation
While the furnace is essential, it must be precise. If the temperature drops below the target threshold (e.g., significantly below 90°C), partial condensation will occur immediately.
This creates a "memory effect" in the system, where residual water from one experiment contaminates the next, or simply fails to reach the detector.
The Limits of Evaporation
It is important to note that the furnace is designed specifically for volatile components like water.
It does not address solids or non-volatile solutes that may be dissolved in the water. These residues will remain in the capsule or reactor, requiring separate handling protocols if they are part of the analysis.
Ensuring Data Integrity in Fluid Analysis
To ensure your experimental results remain valid, consider how thermal management impacts your specific analytical goals:
- If your primary focus is fluid composition: Verify that the furnace temperature is stabilized at 90°C before piercing the capsule to prevent any initial loss of water mass.
- If your primary focus is isotopic precision: Ensure the heating extends through the transfer lines (if applicable) to prevent fractionation caused by condensation during transport.
Controlled heating is not merely an operational step; it is the baseline requirement for capturing the true chemical reality of your sample.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Analysis | Impact of Failure |
|---|---|---|
| 90°C Target Temperature | Drives complete water phase transition to gas | Partial condensation and sample loss |
| Uniform Thermal Field | Prevents "cold spots" in reactor/tubing | Surface adhesion and memory effects |
| Phase Consistency | Ensures water remains as vapor during transport | Mass balance errors & skewed ratios |
| Isotopic Integrity | Prevents fractionation of heavy/light isotopes | Invalidates isotopic signatures |
Maximize Your Analytical Precision with KINTEK
Don’t let condensation compromise your research data. KINTEK provides high-performance, customizable heating solutions designed to maintain the rigorous thermal stability required for complex fluid analysis.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of laboratory equipment including:
- Muffle & Tube Furnaces for precise thermal control.
- Rotary, Vacuum, & CVD Systems for specialized materials research.
- Customizable High-Temp Furnaces tailored to your unique reactor integration needs.
Ensure complete vaporization and data integrity in every experiment. Contact us today to find the perfect thermal system for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
References
- Luca Toffolo, Simone Tumiati. A reliable analytical procedure to determine the carbon isotopic signature of CO<sub>2</sub>-bearing COH fluids generated in petrological experiments. DOI: 10.5194/ejm-37-25-2025
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is vacuum distillation preferred for biodiesel ethanol removal? Protect Fuel Quality with Low-Temp Processing
- Why is a high-precision furnace critical for refractory castables? Ensure Structural Integrity & Mineral Stability
- What core processing conditions does a laboratory high-temperature oven provide? Optimize Geopolymer Curing Results
- What is the significance of using a laboratory electric furnace for the quenching and tempering of hull steel? Achieve Precise Microstructure Control
- Why must (MnFeNiCo)3O4 materials undergo a secondary calcination? Key Steps to Optimizing FCC Spinel Structure
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of microwave drying for iron ore briquettes? Expert Process Insights
- How does the applicability of materials change with advancements in cracking technology? Unlock New Material Processing Possibilities
- What is the significance of using high-temperature heating equipment to reach 1250°C for alloys? Stress Test Excellence



















