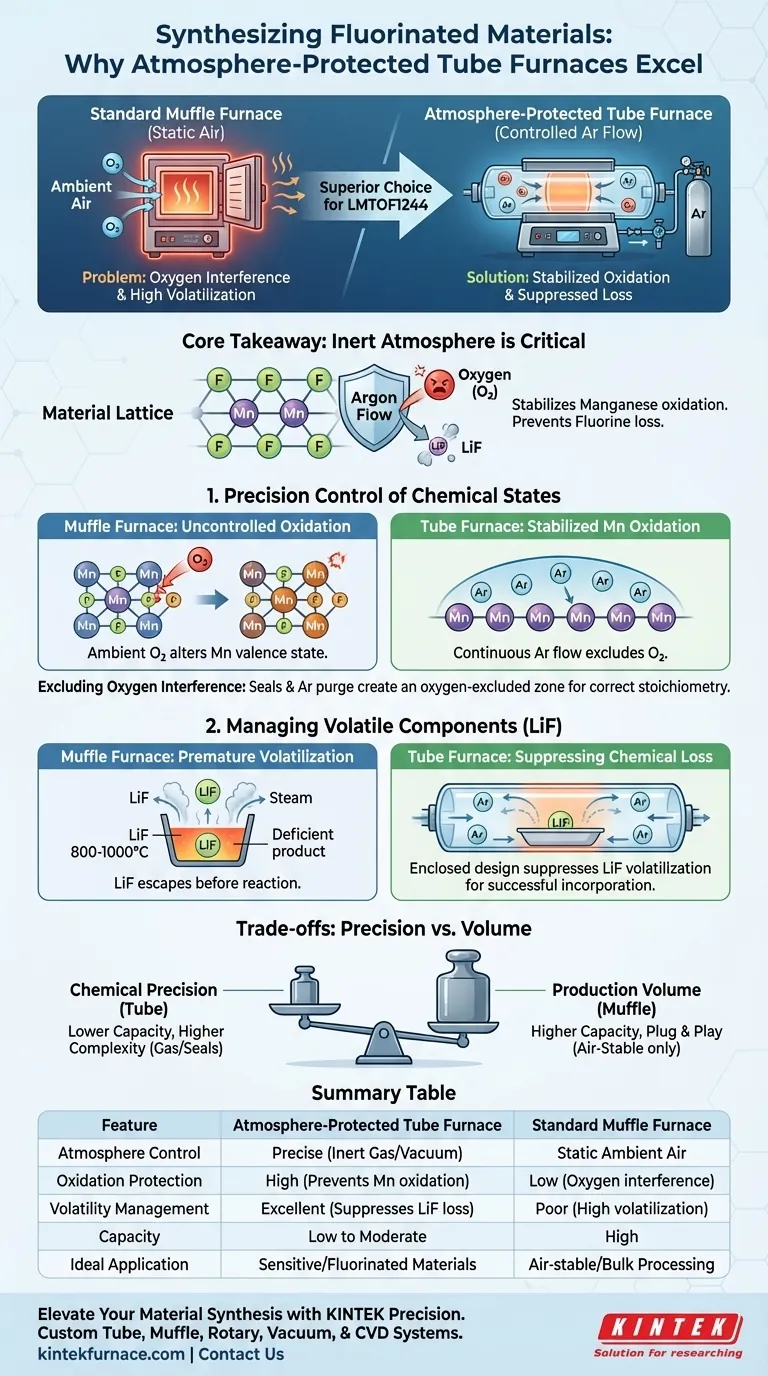
An atmosphere-protected tube furnace is the superior choice for synthesizing fluorinated materials like LMTOF1244 because it allows for precise control over the reaction environment via gas flow. Unlike a standard muffle furnace, which operates in static air, a tube furnace maintains an inert atmosphere that is critical for stabilizing specific metal oxidation states and retaining volatile components.
Core Takeaway The successful synthesis of LMTOF1244 relies on stabilizing the oxidation state of Manganese and preventing the loss of Fluorine. An atmosphere-protected tube furnace achieves this by utilizing a continuous flow of Argon to exclude oxygen and suppress the premature volatilization of Lithium Fluoride.

Precision Control of Chemical States
Stabilizing Manganese Oxidation
The synthesis of LMTOF1244 is highly sensitive to the oxidation state of manganese (Mn). In a standard muffle furnace, ambient oxygen would react with the manganese, altering its valence state uncontrollably.
A tube furnace mitigates this by maintaining a continuous flow of Argon (Ar) gas. This inert environment protects the manganese, ensuring it remains in the specific oxidation state required for the material's performance.
Excluding Oxygen Interference
Beyond the metal center, the overall crystal structure is vulnerable to oxygen interference. The presence of excess oxygen can disrupt the formation of the intended disordered rocksalt structure.
By sealing the reaction area and purging it with Argon, the tube furnace creates an oxygen-excluded zone. This ensures that the stoichiometry of the final product matches the intended design without oxidative impurities.
Managing Volatile Components
The Challenge of Lithium Fluoride (LiF)
Introduction of fluorides is a critical step in synthesizing this material, typically involving Lithium Fluoride (LiF). However, LiF is prone to premature volatilization at the required reaction temperatures of 800 °C to 1000 °C.
In an open atmosphere or standard muffle furnace, the LiF would likely vaporize and escape before it could react with the other precursors. This results in a fluorine-deficient product.
Suppressing Chemical Loss
The atmosphere-protected tube furnace addresses this volatility through its enclosed design and gas flow dynamics. The controlled environment suppresses the rate at which LiF volatilizes.
This suppression keeps the lithium and fluorine available in the reaction zone long enough to be incorporated into the lattice. This is the deciding factor in ensuring successful fluorine incorporation into the disordered rocksalt structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Capacity Constraints
While the tube furnace offers superior chemical control, it generally has a significantly smaller sample capacity than a box or muffle furnace. You are trading production volume for chemical precision.
Operational Complexity
A standard muffle furnace is often "plug and play." Conversely, an atmosphere-protected tube furnace requires the management of gas cylinders, flow regulators, and vacuum seals. Any leak in the system can reintroduce oxygen, negating the furnace's benefits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the successful synthesis of complex fluorinated materials, match your equipment to your chemical requirements:
- If your primary focus is Compositional Accuracy: Use the atmosphere-protected tube furnace to strictly control manganese oxidation and ensure correct fluorine stoichiometry.
- If your primary focus is High Throughput: A standard muffle furnace may be used only if the material chemistry is air-stable and non-volatile, which is not the case for LMTOF1244.
For sensitive fluorinated cathodes, the inert environment of a tube furnace is not a luxury—it is a chemical necessity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Atmosphere-Protected Tube Furnace | Standard Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Precise (Inert Gas/Vacuum) | Static Ambient Air |
| Oxidation Protection | High (Prevents Mn oxidation) | Low (Oxygen interference) |
| Volatility Management | Excellent (Suppresses LiF loss) | Poor (High volatilization) |
| Capacity | Low to Moderate | High |
| Ideal Application | Sensitive/Fluorinated Materials | Air-stable/Bulk Processing |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Don’t let oxidative impurities or chemical loss compromise your research. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet the unique thermal processing needs of your laboratory.
Whether you are synthesizing sensitive disordered rocksalt cathodes or advanced fluorinated materials, our atmosphere-protected systems ensure the chemical precision you require. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
References
- Venkata Sai Avvaru, Haegyeom Kim. Alternative Solid‐State Synthesis Route for Highly Fluorinated Disordered Rock‐Salt Cathode Materials for High‐Energy Lithium‐Ion Batteries. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202500492
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the uniform length of a tube furnace and what factors affect it? Maximize Your Lab's Thermal Precision
- What are the features of more elaborate tube furnaces? Precision Control for Advanced Thermal Processing
- Why is it critical to precisely control the heating rate at 3°C/min for Ni/NiO@GF electrodes? Achieve Structural Integrity
- At what pressures can gases be introduced into the 3-Zone tube furnace? Optimize Your Thermal Process Control
- What is the purpose of using a tube furnace during the reduction phase of graphite flake surface treatment?
- Why is a tube furnace required during the synthesis of phosphorus-doped nickel catalysts using high-purity nitrogen?
- What is a tube furnace and its main characteristics? Discover Precision Heating for Your Lab
- What factors affect the price of a vacuum tube furnace? Key Drivers and Smart Investment Tips



















