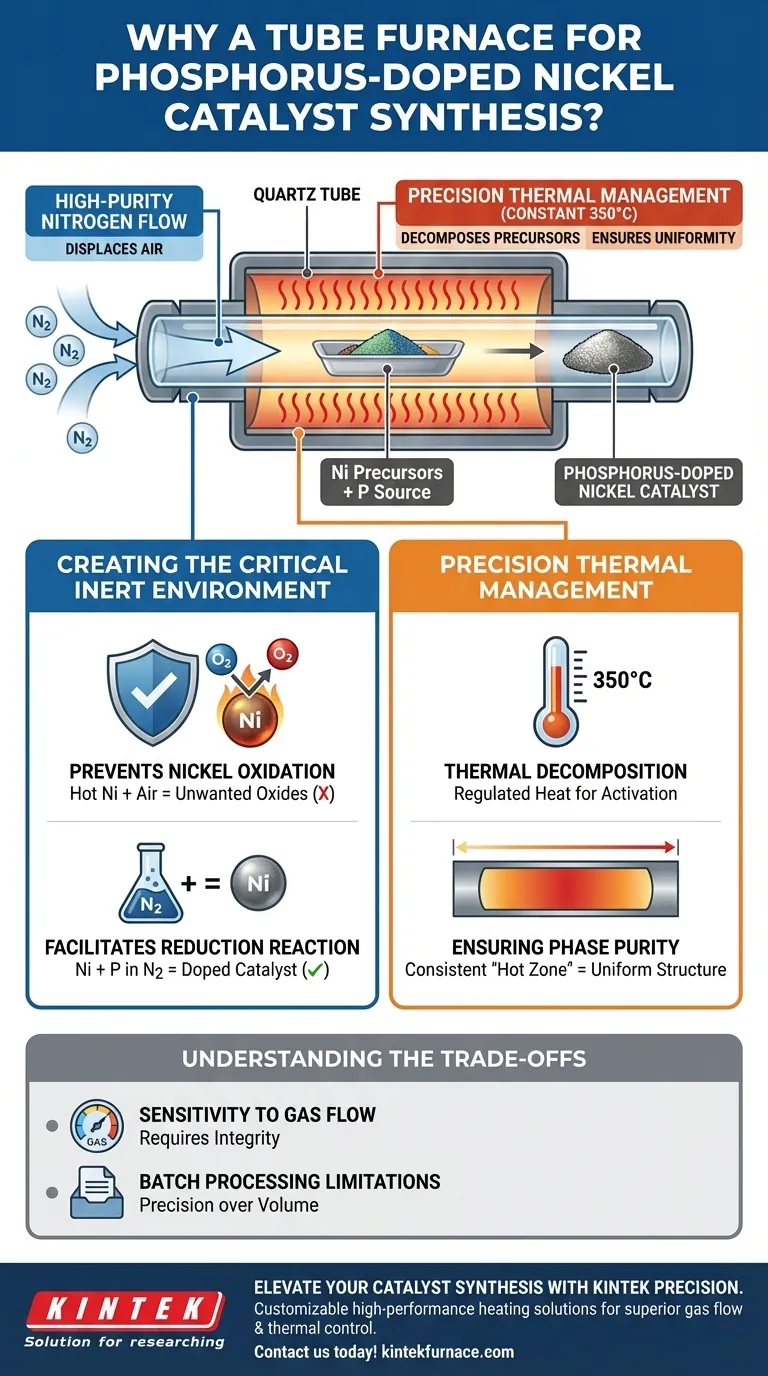
The tube furnace serves as a dual-purpose isolation chamber, essential for synthesizing phosphorus-doped nickel catalysts. It provides the specific thermal energy required to decompose precursor mixtures—typically at a constant temperature around 350°C—while simultaneously encasing the reaction in high-purity nitrogen. This isolation is strictly required because exposing hot nickel to ambient air would immediately cause oxidation, ruining the catalytic properties; the furnace allows for a precise reduction reaction in an oxygen-free environment.
The core function of the tube furnace in this process is to decouple thermal activation from chemical oxidation. By maintaining a nitrogen-rich, oxygen-deficient atmosphere, it forces the phosphorus and nickel to undergo a specific doping reaction that produces high-purity metal rather than metal oxides.
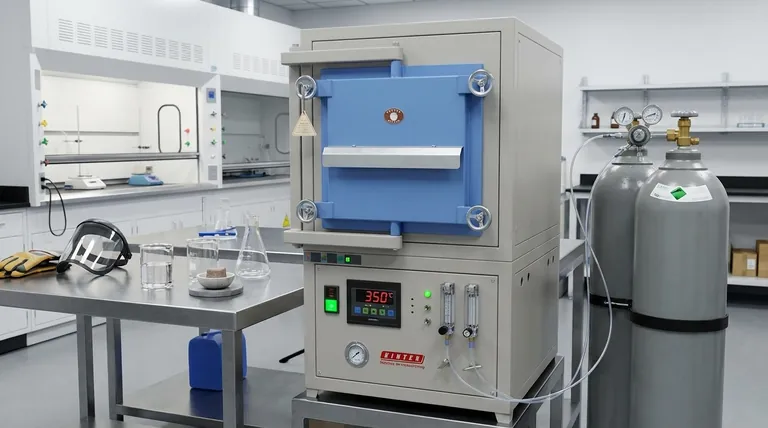

Creating the Critical Inert Environment
Preventing Nickel Oxidation
The primary danger in synthesizing metal catalysts is the presence of oxygen during the heating phase.
When nickel precursors are heated to 350°C in standard air, they react rapidly with oxygen to form unwanted oxides.
The tube furnace allows you to continuously flush the reaction zone with high-purity nitrogen, displacing the air and ensuring the nickel remains in its metallic state throughout the process.
Facilitating the Reduction Reaction
The synthesis requires a chemical reduction, where the phosphorus source modifies the nickel structure.
This doping process relies on a stable, inert background to proceed correctly.
By eliminating competitive reactions (like combustion or oxidation), the nitrogen atmosphere ensures that the chemical interaction occurs exclusively between the phosphorus and the nickel.
Precision Thermal Management
Thermal Decomposition of Precursors
The synthesis relies on decomposing a specific mixture of raw materials to release the active elements.
The tube furnace provides the constant, regulated heat needed to break down these precursors effectively.
Typically maintained at 350°C, this thermal environment provides the activation energy necessary to initiate the decomposition without overheating the material.
Ensuring Phase Purity
Achieving a high-quality catalyst requires uniformity across the entire material sample.
Tube furnaces are designed to create a consistent "hot zone" where the temperature is uniform.
This uniformity ensures that the crystal structure of the phosphorus-doped nickel is consistent, resulting in high phase purity and predictable catalytic performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Gas Flow
The effectiveness of the tube furnace is entirely dependent on the integrity of the nitrogen flow.
If the gas flow is interrupted or the seals leak, the protective atmosphere is lost immediately.
Even a momentary exposure to oxygen at these temperatures can irreversibly degrade the catalyst, turning a reduction process into an oxidation failure.
Batch Processing Limitations
Tube furnaces are generally designed for batch or semi-continuous processing rather than high-volume throughput.
While excellent for precise control and research, they may become a bottleneck if you attempt to scale up production significantly.
You must balance the need for high purity and control against the limited volume of material a tube can process at one time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your phosphorus-doped nickel catalysts, consider your specific priorities:
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Prioritize the integrity of your gas delivery system to ensure the nitrogen atmosphere remains completely oxygen-deficient throughout the entire 350°C heating cycle.
- If your primary focus is Structural Consistency: Focus on the stability of the furnace's temperature controller to ensure the thermal decomposition of precursors is uniform across the entire sample batch.
The tube furnace is a precision tool that turns a volatile thermal process into a controlled chemical synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Catalyst Synthesis | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Displaces oxygen with high-purity nitrogen | Prevents nickel oxidation & ensures metallic purity |
| Thermal Management | Constant heat (typically 350°C) | Facilitates precise precursor decomposition |
| Controlled Environment | Decouples thermal activation from oxidation | Ensures specific phosphorus doping reactions |
| Hot Zone Uniformity | Consistent temperature across the sample | High phase purity and structural consistency |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your phosphorus-doped nickel catalysts with high-performance heating solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-quality Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific research or production needs. Whether you require superior gas flow integrity for inert atmospheres or precise thermal control for precursor decomposition, our lab high-temp furnaces provide the reliability you need.
Ready to optimize your chemical processing? Contact us today to find your perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Chenyun Zhang, Jiahao Wang. Preparation of P‐Doped Ni Catalyst Using Deep Eutectic Solvents and Its Excellent Hydrogen Evolution Performance in Water Splitting. DOI: 10.1002/open.202500023
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What are the maintenance requirements for a horizontal electric furnace? Ensure Peak Performance and Longevity
- What design aspects of a split tube furnace influence its performance? Optimize for Temperature Uniformity and Efficiency
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate Fe-Nx-C electrocatalyst formation? Expert Synthesis Insights
- What option is available for frequently relocated split tube furnaces? Discover the Vertical Portable Stand Solution
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in NC framework preparation? Master Precision Carbonization
- What advantages does a continuous flow tube reactor provide for CO2 hydrogenation? Optimize Catalyst Evaluation
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature tube furnace in ZnS CVD? Master Precise Nanostructure Synthesis



















