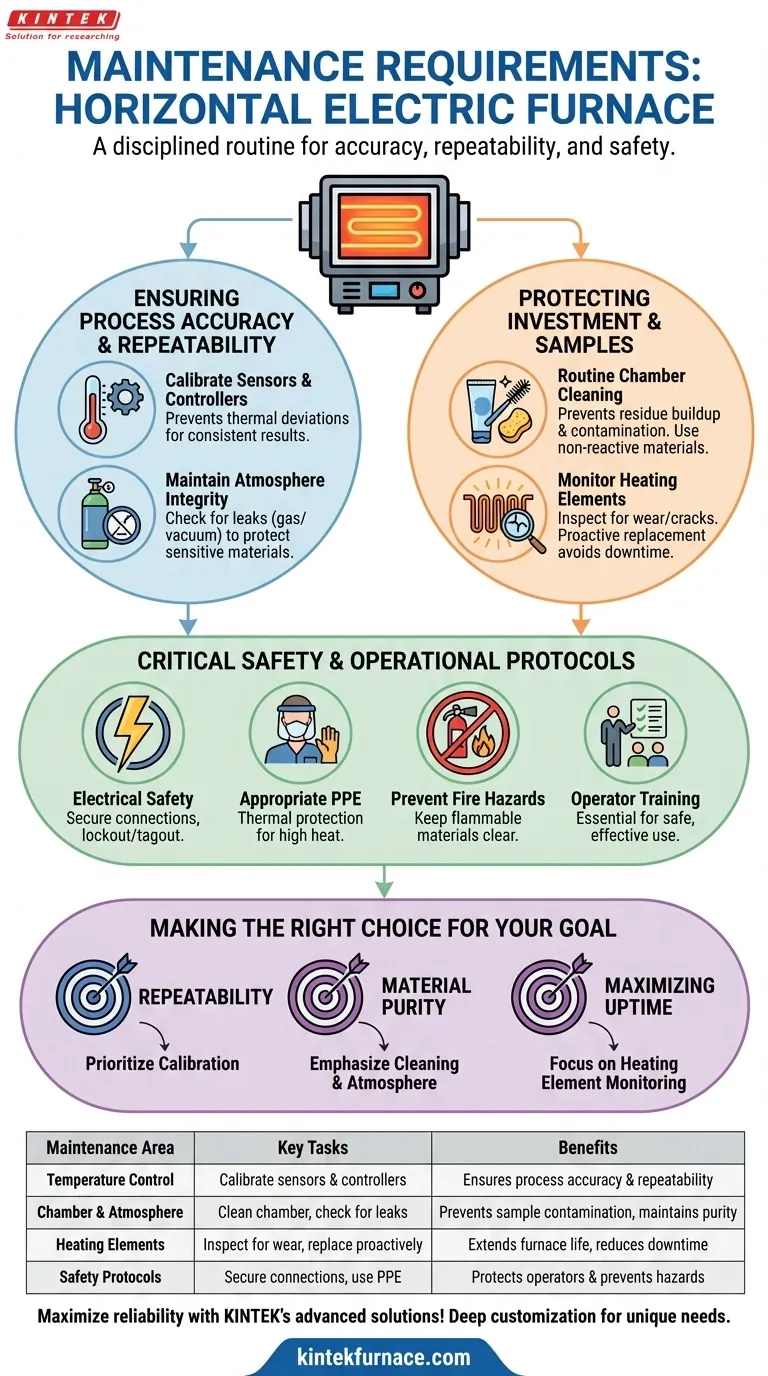
At its core, maintaining a horizontal electric furnace involves a disciplined routine focused on four key areas. These include the regular calibration of temperature sensors, thorough cleaning to prevent sample contamination, proactive monitoring of heating element wear, and verification of the processing atmosphere, whether it be gas or vacuum.
The goal of furnace maintenance is not simply to prevent failure, but to guarantee the accuracy, repeatability, and safety of your thermal processes. It transforms the furnace from a piece of hardware into a reliable and precise scientific instrument.

Ensuring Process Accuracy and Repeatability
The primary function of your furnace is to deliver precise thermal control. Maintenance is what ensures that precision is not compromised over time.
Calibrating Temperature Sensors
Periodic calibration of temperature sensors and their associated controllers is non-negotiable. Even minor thermal deviations can significantly alter the properties of your materials, compromising your results.
Regular calibration ensures that the temperature you set is the temperature your sample experiences, maintaining accuracy across countless processing cycles.
Maintaining Atmosphere Integrity
For furnaces using controlled atmospheres, atmosphere integrity is paramount. This involves checking for leaks in gas delivery lines or vacuum pump systems.
This step is especially critical when processing oxidation-sensitive materials, as even a small leak can introduce contaminants and ruin the sample.
Protecting Your Investment and Samples
Proper maintenance directly extends the operational life of the furnace and prevents the loss of valuable materials and time.
Routine Chamber Cleaning
Operators must clean the furnace chamber regularly. Over time, residue from previous cycles can build up inside the tube.
This residue can vaporize during subsequent runs, creating an unintended and uncontrolled atmosphere that contaminates your samples. Always use non-reactive cleaning materials to avoid introducing new contaminants.
Monitoring Heating Element Wear
Heating elements are consumable components that degrade with use. Visually inspect the elements for signs of wear, cracking, or discoloration.
Proactive monitoring allows you to replace elements before they fail catastrophically, preventing costly emergency repairs and unscheduled downtime.
Critical Safety and Operational Protocols
A well-maintained furnace is a safe furnace. Integrating safety checks into your maintenance routine is essential for protecting operators and your facility.
Adhering to Electrical Safety
These are high-power systems. Always ensure all electrical connections are secure and panels are properly closed. Follow standard lockout/tagout procedures during any internal maintenance.
Using Appropriate Protective Gear
Operators must use personal protective equipment (PPE) suitable for high-heat environments. This includes thermal gloves and face shields, especially when loading or unloading the furnace.
Preventing Fire Hazards
Keep the area surrounding the furnace clear of all flammable materials. This simple housekeeping rule is a critical fire prevention measure.
The Importance of Operator Training
The best maintenance plan can be undermined by improper use. Ensure all operators are thoroughly trained on the furnace's specific operating procedures, safety features, and emergency protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance schedule should reflect your most critical objectives.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Prioritize rigorous calibration of temperature sensors and controllers.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Emphasize meticulous chamber cleaning and verification of atmosphere integrity.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime: Implement a proactive schedule for monitoring and replacing heating elements.
Consistent maintenance empowers you to have full confidence in your equipment and the results it produces.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Area | Key Tasks | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Calibrate sensors and controllers | Ensures process accuracy and repeatability |
| Chamber and Atmosphere | Clean chamber, check for leaks | Prevents sample contamination, maintains purity |
| Heating Elements | Inspect for wear and replace proactively | Extends furnace life, reduces downtime |
| Safety Protocols | Secure electrical connections, use PPE | Protects operators and prevents hazards |
Maximize your furnace's reliability with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















