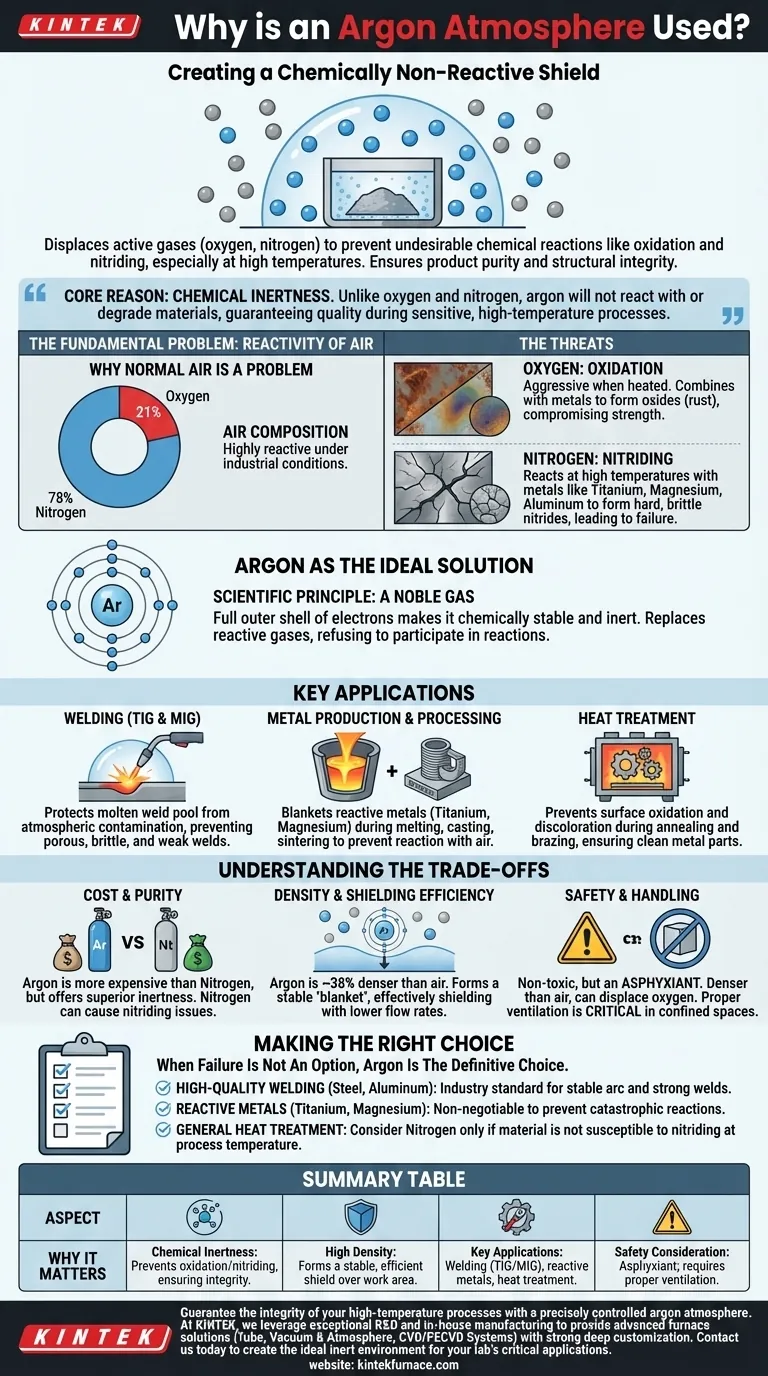
An argon atmosphere is used to create a chemically non-reactive shield around a process or material. Its purpose is to displace the active gases in normal air, primarily oxygen and nitrogen, which can cause undesirable chemical reactions like oxidation and nitriding, especially at high temperatures. This protective environment is critical in applications like welding, metal production, and heat treating to ensure the final product's purity and structural integrity.
The core reason for using an argon atmosphere is its chemical inertness. Unlike the oxygen and nitrogen in the air, argon gas will not react with or degrade materials, guaranteeing the quality and strength of the final product during sensitive, high-temperature manufacturing processes.

The Fundamental Problem: Reactivity of Air
Why Normal Air is a Problem
The air we breathe is a mixture of gases, composed of approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. While essential for life, this mixture is highly reactive under the conditions required for many industrial processes.
The Threat of Oxygen: Oxidation
Oxygen is aggressive, especially when heated. It readily combines with metals to form oxides, a process commonly known as oxidation.
This reaction can manifest as rust on iron, discoloration on other metals, or the formation of a brittle, flaky surface layer that compromises the material's strength and quality.
The Hidden Threat of Nitrogen: Nitriding
While less reactive than oxygen, nitrogen can also become a problem at the high temperatures found in welding and metal furnaces.
With certain metals like titanium, magnesium, and aluminum, nitrogen can react to form hard, brittle compounds called nitrides. This "nitriding" effect can lead to component failure.
Argon as the Ideal Solution
The Scientific Principle: A Noble Gas
Argon is a noble gas. This means it has a full outer shell of electrons, making it chemically stable and extremely unwilling to share electrons or form chemical bonds with other elements.
This inherent stability is what makes it "inert." When you flood a chamber or a workspace with argon, you are replacing reactive gases with a gas that will simply not participate in any chemical reactions.
Key Application: Welding (TIG & MIG)
In processes like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, an argon shield is used to protect the molten weld pool from the atmosphere.
Without this shield, the molten metal would rapidly oxidize and absorb nitrogen, resulting in a porous, brittle, and weak weld that would fail under stress.
Key Application: Metal Production & Processing
Manufacturing highly reactive metals like titanium or processing powdered metals for 3D printing requires a completely inert environment.
Argon is used to blanket these materials during melting, casting, or sintering to prevent them from reacting with air, which would ruin the final product.
Key Application: Heat Treatment
Processes like annealing and brazing require heating metals to high temperatures to alter their properties or join them together.
An argon atmosphere in the furnace prevents surface oxidation and discoloration, ensuring the metal parts emerge clean and with the desired material characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Cost and Purity
Argon is more expensive than nitrogen, which is sometimes used as a cheaper alternative for an inerting process.
However, nitrogen is not truly inert in all situations and can cause the nitriding issues mentioned earlier. Argon's superior inertness often justifies its higher cost for high-value or sensitive applications.
Density and Shielding Efficiency
Argon is approximately 38% denser than air. This is a significant advantage in open-air applications like welding.
Its density allows it to form a stable, heavy "blanket" of protection over the work area, effectively shielding the process with lower gas flow rates compared to lighter gases like helium.
Safety and Handling
While non-toxic, argon is an asphyxiant. Because it is denser than air, it can displace oxygen in enclosed or low-lying areas.
Proper ventilation is absolutely critical when working with argon in confined spaces to prevent the risk of suffocation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Choosing an argon atmosphere is a deliberate engineering decision to control quality by eliminating the variable of atmospheric reaction.
- If your primary focus is high-quality welding of steels or aluminum: Argon (or an argon blend) is the industry standard for creating a stable arc and a strong, clean weld pool.
- If your primary focus is working with reactive metals like titanium or magnesium: A pure argon atmosphere is non-negotiable to prevent catastrophic oxidation and nitriding.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment on a budget: You may consider nitrogen, but only after confirming your specific material is not susceptible to forming nitrides at your process temperature.
Ultimately, an argon atmosphere is the definitive choice for guaranteeing material integrity when failure is not an option.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents oxidation and nitriding, ensuring material integrity. |
| High Density | Forms a stable, efficient shield over the work area. |
| Key Applications | Welding (TIG/MIG), reactive metal processing, heat treatment. |
| Safety Consideration | An asphyxiant; requires proper ventilation in confined spaces. |
Guarantee the integrity of your high-temperature processes with a precisely controlled argon atmosphere. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace solutions—including Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems—with strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can create the ideal inert environment for your lab's critical applications. Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process



















