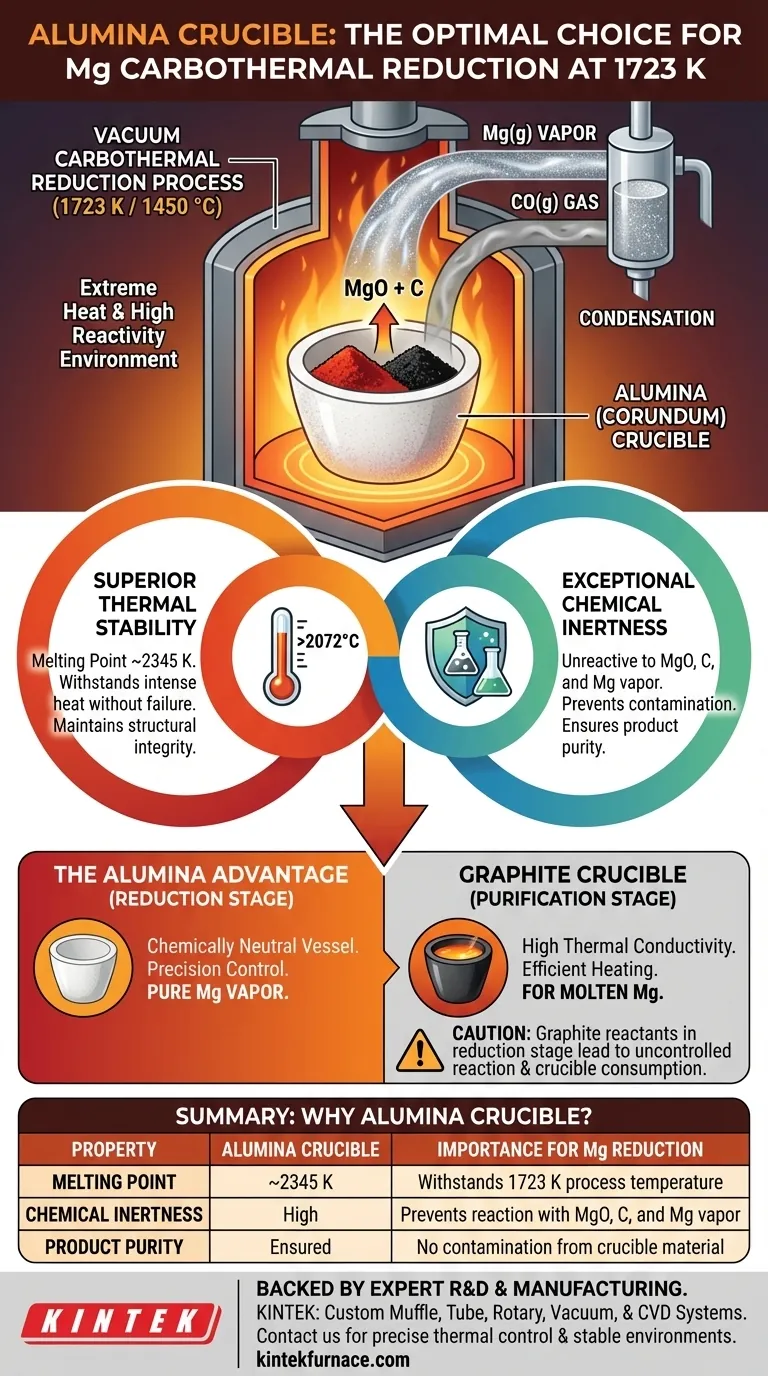
An alumina (corundum) crucible is selected for the vacuum carbothermal reduction of magnesium at extreme temperatures like 1723 K primarily for two reasons: its exceptional thermal stability and its chemical inertness. It can withstand the intense heat without melting or deforming, and critically, it does not react with the magnesium oxide, carbon, or the resulting highly reactive magnesium vapor, thereby preventing contamination of the final product.
The success of any high-temperature metallurgical process is fundamentally tied to the choice of its reaction vessel. Selecting an alumina crucible is a strategic decision to create a chemically neutral and structurally sound environment, ensuring the reaction proceeds cleanly and the resulting product is pure.

The Critical Demands of the Process
To understand the material choice, we must first appreciate the harshness of the operating environment. The carbothermal reduction of magnesium oxide is not a gentle process.
Extreme Temperature
At 1723 K (1450 °C), most common materials would melt, soften, or fail. The reaction vessel must possess a very high melting point and maintain its structural integrity under these demanding thermal loads.
Highly Reactive Environment
The process involves magnesium oxide (MgO), carbon (C), and the product, magnesium vapor (Mg). At this temperature, magnesium vapor is extremely reactive. The crucible must act as an inert container, resisting chemical attack from all components.
Vacuum Conditions
The reaction is performed under vacuum to facilitate the removal of the magnesium vapor as it forms. The crucible material must be stable under these low-pressure conditions and not degrade or release gases that could interfere with the process.
Why Alumina Is the Optimal Choice
Alumina (Al₂O₃), in its crystalline form corundum, possesses a unique combination of properties that makes it ideally suited for this specific application.
Superior Thermal Stability
Alumina has a melting point of approximately 2345 K (2072 °C), well above the operating temperature. This ensures it remains a solid, stable vessel throughout the entire reduction process.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
This is the most critical factor. Alumina is a very stable oxide. It has very little thermodynamic incentive to react with the magnesium oxide reactant or the carbon reducing agent.
Most importantly, it is inert to the magnesium vapor product. Any reaction between the crucible and the magnesium would introduce impurities (like aluminum) into the final product, defeating the goal of producing pure magnesium.
Ensuring Product Purity
By serving as a chemically invisible bystander, the alumina crucible ensures that the reaction MgO + C → Mg(g) + CO(g) proceeds without side reactions involving the container. This is vital for achieving high-purity magnesium.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Alumina vs. Graphite
While alumina is ideal for the reduction step, it's insightful to compare it with another high-temperature material often used in magnesium processing: graphite.
The Case for an Inert Vessel (Alumina)
For the initial carbothermal reduction, an inert vessel is paramount. The goal is to control the precise ratio of magnesium oxide to carbon. Using a crucible that does not participate in the reaction, like alumina, allows for this precise control.
When Graphite Becomes the Choice
Graphite crucibles are frequently used in the next step: the vacuum distillation or purification of crude magnesium. In this context, the reactant is molten magnesium, not magnesium oxide.
Graphite does not react with molten magnesium and offers the key advantage of high thermal conductivity. This allows for more efficient and uniform heating, which is critical for a stable distillation process.
The Risk of Using Graphite for Reduction
Using a graphite crucible for the initial MgO + C reduction would be problematic. The crucible itself is made of carbon, one of the reactants. This would make it impossible to control the reaction stoichiometry precisely and would lead to the degradation and consumption of the crucible itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The selection of a crucible material is dictated entirely by the specific chemical and thermal demands of the process stage.
- If your primary focus is a clean carbothermal reduction of an oxide: Alumina is the superior choice because its chemical inertness prevents product contamination and ensures precise reaction control.
- If your primary focus is the subsequent purification of molten metal via distillation: Graphite is often preferred for its excellent thermal conductivity and its stability with the molten metal.
- If your primary focus is maximizing thermal efficiency: Graphite's superior heat transfer is a significant advantage, but it can only be leveraged in processes where it is chemically compatible with all reactants and products.
Ultimately, choosing the right material is a foundational step that dictates the purity of the product and the success of the entire operation.
Summary Table:
| Property | Alumina Crucible | Importance for Mg Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | ~2345 K | Withstands 1723 K process temperature |
| Chemical Inertness | High | Prevents reaction with MgO, C, and Mg vapor |
| Product Purity | Ensured | No contamination from crucible material |
Need a high-temperature furnace for demanding processes like carbothermal reduction?
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique needs. Our lab furnaces provide the precise thermal control and stable environment required for critical applications.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your process efficiency and product purity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















