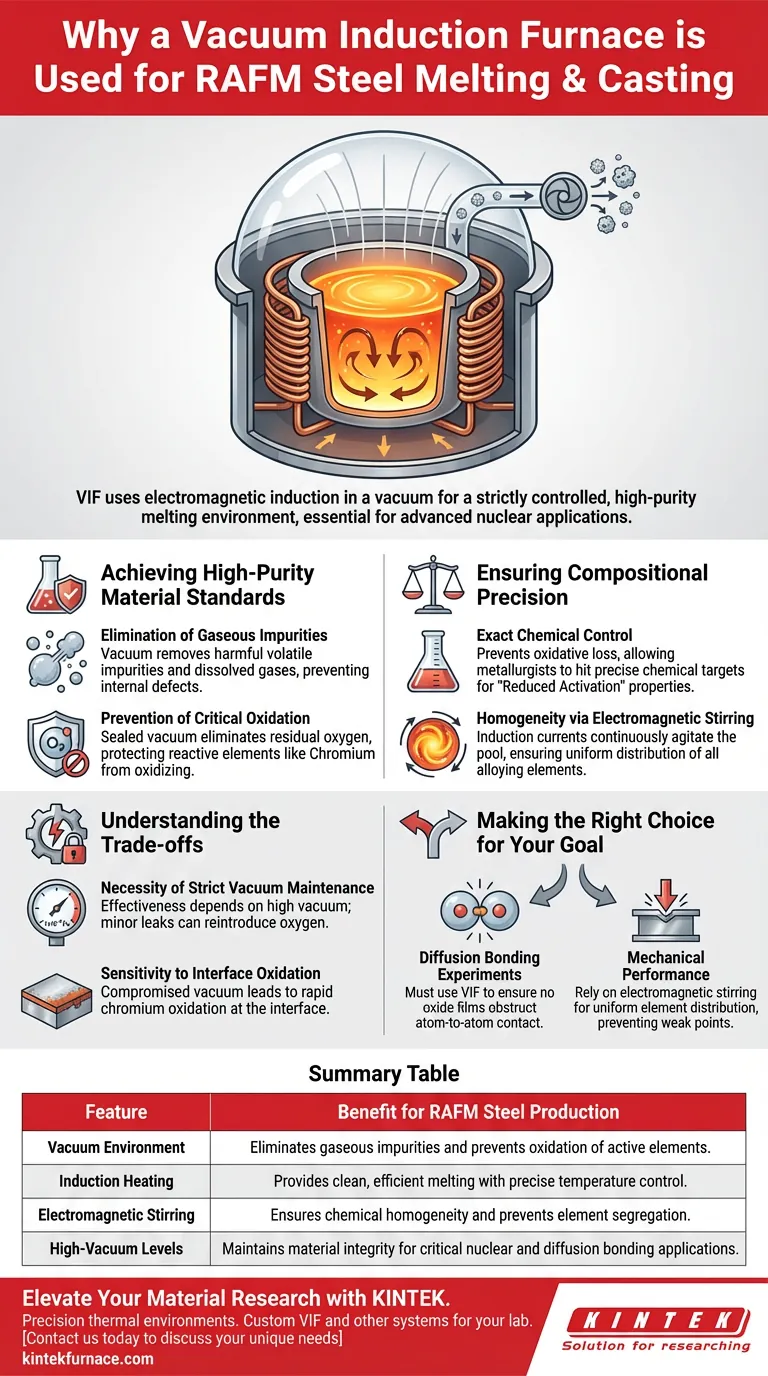
A vacuum induction furnace is the primary tool for processing RAFM steel because it utilizes electromagnetic induction heating within a vacuum to create a strictly controlled, high-purity melting environment. This specific isolation effectively removes gaseous impurities and prevents the oxidation of the molten steel, ensuring the precise chemical composition required for advanced nuclear applications.
By eliminating atmospheric contamination and leveraging electromagnetic stirring, this process produces RAFM steel ingots with the exceptional purity and homogeneity necessary to serve as a reliable foundation for critical downstream processes like diffusion bonding.

Achieving High-Purity Material Standards
Elimination of Gaseous Impurities
RAFM (Reduced Activation Ferritic/Martensitic) steel requires an extremely clean microstructure to function correctly. The vacuum environment within the furnace allows for the effective removal of harmful volatile impurities and dissolved gases from the molten metal.
Eliminating these gases is not merely about cleanliness; it is a structural necessity. By degassing the melt, the furnace prevents the formation of internal defects that would compromise the material's mechanical integrity.
Prevention of Critical Oxidation
The alloying elements within RAFM steel, particularly Chromium, are highly reactive to oxygen. Without the protection of a vacuum, these elements would rapidly oxidize, leading to material loss and the formation of oxide inclusions.
The vacuum induction furnace maintains a sealed environment that virtually eliminates residual oxygen. This preserves the active alloying elements, ensuring they remain in the solution rather than turning into brittle impurities.
Ensuring Compositional Precision
Exact Chemical Control
Producing RAFM steel is a chemistry challenge as much as a metallurgical one. The vacuum process prevents the oxidative loss of active elements, allowing metallurgists to hit precise chemical targets.
This control is vital for maintaining the "Reduced Activation" properties of the steel. It ensures that the final ingot matches the strict compositional specifications required for high-performance material designs.
Homogeneity via Electromagnetic Stirring
Beyond simple melting, the induction mechanism provides a physical advantage: electromagnetic stirring. The induction currents naturally agitate the molten pool.
This continuous stirring effect ensures that all alloying components—such as iron, manganese, and chromium—are distributed uniformly throughout the mixture. The result is a chemically homogeneous ingot free from segregation issues.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Strict Vacuum Maintenance
While the vacuum induction furnace offers superior purity, its effectiveness is entirely dependent on maintaining high vacuum levels (e.g., 1x10^-4 Pa). Even minor leaks or fluctuations in pressure can reintroduce oxygen.
Sensitivity to Interface Oxidation
Despite the furnace's capabilities, the material remains sensitive. If the vacuum environment is compromised, the high affinity of Chromium for oxygen can lead to rapid oxidation at the interface. This highlights that the equipment is only as effective as the rigor of the process control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating the production of RAFM steel, the choice of melting technology dictates the success of downstream applications.
- If your primary focus is diffusion bonding experiments: You must use vacuum induction melting to ensure the material is free of oxide films that would physically obstruct atom-to-atom contact during bonding.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance: You rely on the electromagnetic stirring of the VIF to guarantee the uniform distribution of alloying elements, preventing weak points in the cast ingot.
The vacuum induction furnace is not just a melting tool; it is a purification system that transforms raw inputs into a chemically precise, research-grade alloy.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for RAFM Steel Production |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Eliminates gaseous impurities and prevents oxidation of active elements. |
| Induction Heating | Provides clean, efficient melting with precise temperature control. |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Ensures chemical homogeneity and prevents element segregation. |
| High-Vacuum Levels | Maintains material integrity for critical nuclear and diffusion bonding applications. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision in RAFM steel production begins with the right thermal environment. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Vacuum Induction Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD systems, all customizable to meet your most demanding laboratory and industrial specifications.
Whether you are focusing on diffusion bonding or high-performance mechanical testing, our equipment delivers the strict compositional control and purity your research requires. Contact us today to discuss your unique needs and see how our advanced high-temperature solutions can empower your next breakthrough.
Visual Guide
References
- Jin‐Gui Chen, Yushun Wei. Diffusion bonding of RAFM steels: Evolution of interfacial oxide layer with pressure and microstructure and mechanical property after post bonding heat treatment. DOI: 10.2298/jmmb231011007c
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does an industrial-grade arc melting furnace play in the preparation of Mn–Ni–Fe–Si alloys?
- How does vacuum casting compare to injection moulding? Choose the Right Process for Your Production Volume
- What are some common operational issues with induction-heated vacuum furnaces and how can they be addressed? Boost Reliability and Efficiency
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in the modification of W18Cr4V steel? Enhance Alloy Purity
- Why is it necessary to reduce the applied secondary voltage during the arc furnace process? Protect Your Furnace and Boost Efficiency
- What are the energy efficiency advantages of induction melting furnaces? Achieve 30-80% Greater Energy Savings
- What is the historical background of induction furnace development? From Faraday to Modern Metallurgy
- What is the role of a vacuum induction melting furnace in Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloys? Achieve High Purity and Homogeneity



















