The most common operational issues in induction-heated vacuum furnaces fall into three categories: maintaining vacuum integrity, ensuring accurate thermal control, and preventing melt or material containment failures. Addressing these requires a systematic approach that begins with understanding their root causes, from minor seal leaks and sensor drift to improper crucible selection and degraded furnace linings.
The key to reliable furnace operation is not just reacting to failures, but understanding that most issues are symptoms of a breakdown in preventative maintenance, operational procedure, or component selection. Shifting focus from firefighting to system health is paramount.

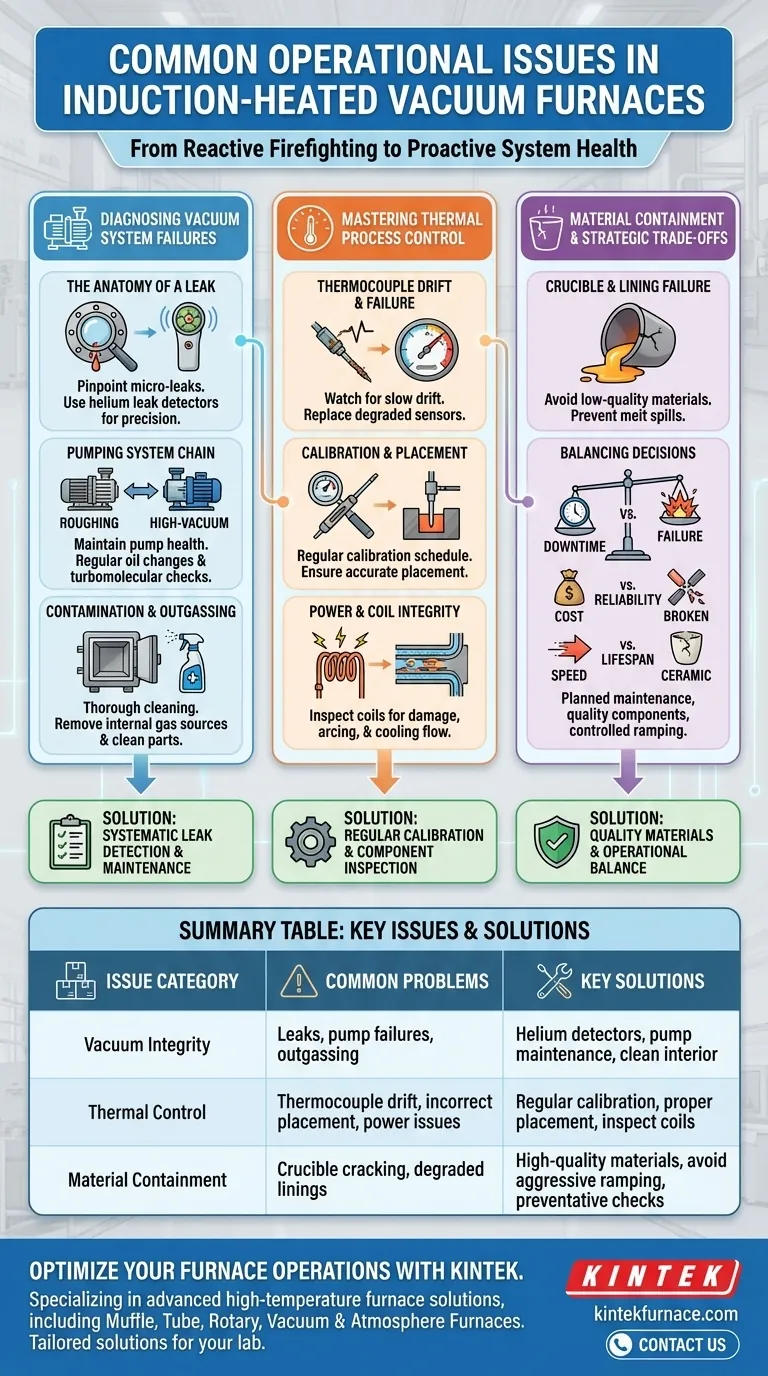
Diagnosing Vacuum System Failures
A stable, deep vacuum is the foundation of the entire process. When the target vacuum level cannot be reached or maintained, the quality of the final product—from aerospace turbine blades to medical implants—is compromised.
The Anatomy of a Leak
The most frequent cause of an insufficient vacuum is a leak. This can range from a major breach to a collection of micro-leaks that are difficult to pinpoint.
Troubleshooting must go beyond a simple visual check. It involves a systematic inspection of all potential failure points, including door seals, feedthroughs for power and water, and sensor ports. Using a helium leak detector is the professional standard for locating small, hard-to-find leaks.
The Pumping System as a Chain
The vacuum system is a sequence of pumps working together, typically a mechanical roughing pump and a high-vacuum pump (diffusion or turbomolecular). A problem in one stage will prevent the entire system from functioning correctly.
If the roughing pump fails to reach its base pressure, the high-vacuum pump cannot take over effectively. Regular maintenance, such as oil changes for mechanical pumps and monitoring the health of turbomolecular pumps, is non-negotiable.
Contamination and Outgassing
Sometimes, the problem isn't a leak but a source of gas from within the furnace. This phenomenon, known as outgassing, can come from the material being processed, contaminants on the furnace walls, or fixtures.
Materials with high vapor pressure can release significant amounts of gas when heated, potentially overwhelming the pumping system. A thorough cleaning of the furnace interior and ensuring parts are clean before loading can dramatically improve vacuum performance.
Mastering Thermal Process Control
Inaccurate temperature measurement or inconsistent heating can ruin a batch, leading to parts with incorrect material properties. Control is a function of the sensor, the controller, and the power delivery system.
The Thermocouple: Your Critical Sensor
The thermocouple is the primary sensor for temperature measurement, but it is also a common point of failure. High temperatures, chemical vapors, and mechanical vibration can cause it to degrade and provide inaccurate readings.
Thermocouple failure is often not sudden. It manifests as a slow drift in accuracy. High vapor pressure from certain materials can attack the thermocouple sheath, leading to premature failure.
The Importance of Calibration and Placement
Relying on a thermocouple without a regular calibration schedule is a significant risk. Thermocouples should be checked periodically against a calibrated reference to ensure their readings are accurate.
Equally important is placement. The thermocouple must be positioned to measure the actual temperature of the workload, not a nearby hot or cold spot. Incorrect placement leads to a process that is controlled but not controlled correctly.
Power Supply and Induction Coil Integrity
The heating itself is driven by the induction coil. Damage or degradation to this coil directly impacts performance.
Check the coil for any signs of arcing, physical damage, or clogged cooling passages. A short between coil windings or a restriction in coolant flow can lead to uneven heating and potential power supply failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving consistent, reliable furnace operation involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for making sound operational and financial decisions.
Maintenance Downtime vs. Unplanned Failure
Scheduling planned downtime for preventative maintenance may seem like a loss of production time. However, this cost is minimal compared to the cost of a catastrophic failure during a critical production run, which can result in a scrapped batch, extensive damage, and significant delays.
Component Cost vs. System Reliability
Using low-cost consumables like thermocouples or crucibles is often a false economy. A cheap crucible that cracks can lead to a melt spill, destroying the furnace lining and induction coil—a repair costing thousands of times more than the initial savings. Investing in high-quality, appropriate materials is a form of insurance.
Aggressive Ramping vs. Component Lifespan
Pushing for the fastest possible heating and cooling rates can increase throughput but puts immense thermal stress on components, especially ceramic crucibles and furnace insulation. This can drastically shorten their lifespan, leading to more frequent replacements and a higher risk of in-process failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational strategy should align directly with your primary business objectives. A robust system is built on clear procedures, rigorous maintenance, and a deep understanding of the equipment.
- If your primary focus is uptime and throughput: Prioritize a robust preventative maintenance schedule for the vacuum pumps and power systems, and standardize your operational procedures to minimize operator error.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and quality: Implement a rigorous calibration program for all thermocouples and controllers, and invest in high-quality, certified consumables like crucibles.
- If your primary focus is safety and risk mitigation: Focus on comprehensive operator training, regular inspection of furnace linings and water-cooling interlocks, and never bypass a safety feature.
Ultimately, managing an induction vacuum furnace effectively means shifting from a reactive troubleshooting mindset to a proactive system management approach.
Summary Table:
| Issue Category | Common Problems | Key Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Integrity | Leaks, pump failures, outgassing | Use helium leak detectors, regular pump maintenance, clean furnace interior |
| Thermal Control | Thermocouple drift, incorrect placement, power supply issues | Regular calibration, proper sensor positioning, inspect induction coils |
| Material Containment | Crucible cracking, degraded linings | Use high-quality materials, avoid aggressive ramping, preventative checks |
Struggling with furnace downtime or inconsistent results? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring reliable performance and enhanced productivity. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your furnace operations and deliver tailored solutions for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the use of vacuum in hot-pressing affect the material processing? Achieve Denser, Purer, and Stronger Materials
- What other types of furnaces are related to hot pressing? Explore Key Thermal Processing Technologies
- What are some specific applications of vacuum hot press furnaces? Unlock Advanced Material Fabrication
- How does induction heating ensure precision in manufacturing processes? Achieve Superior Thermal Control & Repeatability
- What are the applications of hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Performance



















