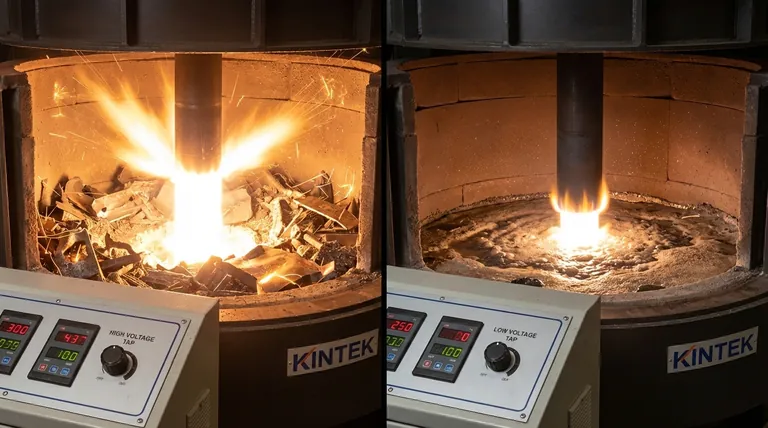
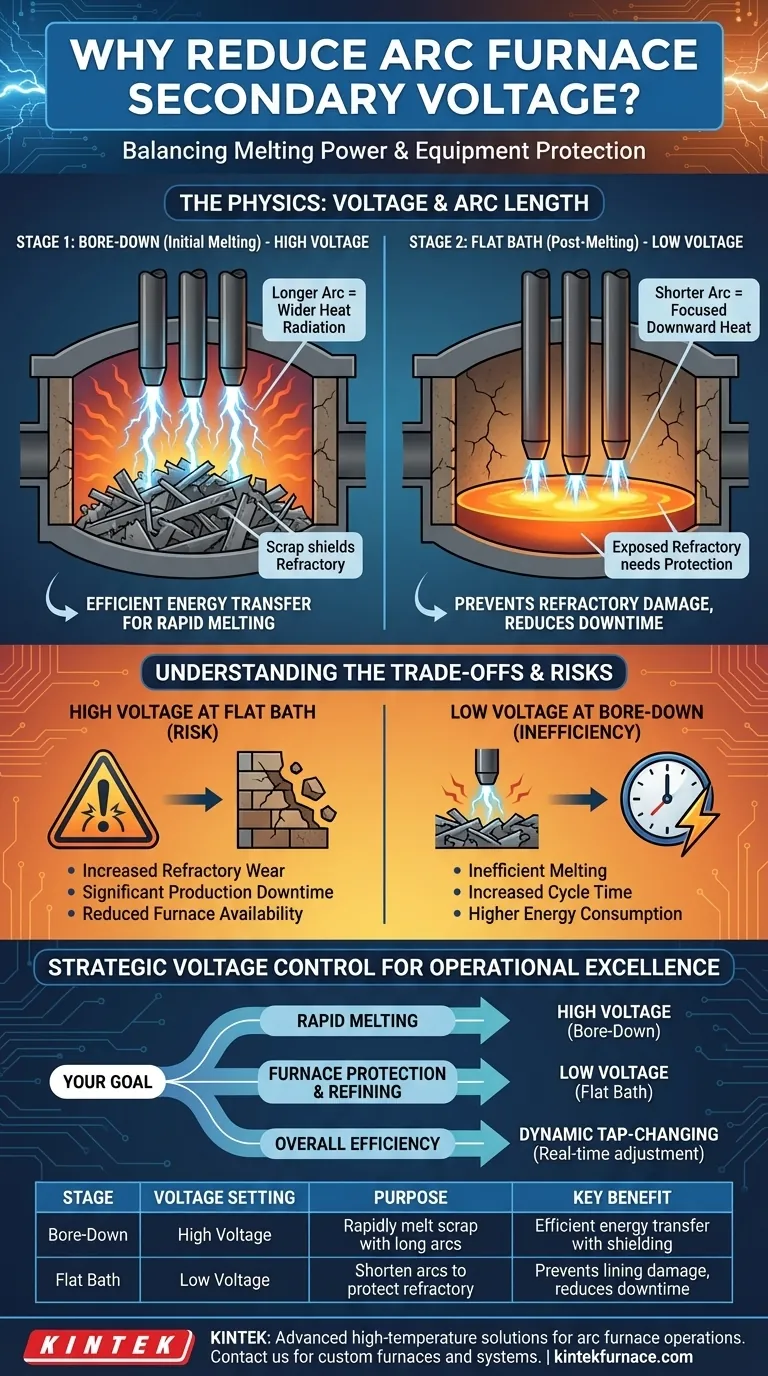
In an electric arc furnace, reducing the applied secondary voltage is a critical operational step taken after the initial scrap metal has been melted. This is done to shorten the length of the electrical arcs, which prevents them from radiating excessive heat sideways and damaging the furnace's heat-resistant refractory lining on the walls and roof.
The core challenge in arc furnace operation is balancing maximum melting power with the physical integrity of the furnace itself. Voltage reduction is the primary method for controlling arc geometry to protect the equipment, especially once the initial scrap pile no longer shields the walls.

The Physics of Arc Length and Heat
An electric arc furnace melts steel by passing an immense current through graphite electrodes, creating powerful arcs that jump to the metal scrap charge. The properties of this arc are directly tied to the applied voltage.
The Direct Link: Voltage and Arc Length
A higher secondary voltage creates the potential for a longer, more stable electrical arc. Think of it as the electrical "pressure" pushing the arc across a greater distance.
Conversely, reducing the voltage shortens the maximum possible length of the arc. To maintain the arc and the required current, the control system must physically lower the electrodes closer to the molten bath.
The Consequence: Heat Radiation Pattern
A long arc is a powerful radiator of energy. Crucially, a significant portion of this energy radiates horizontally and vertically.
A shorter arc, burrowed into the molten bath, directs the majority of its energy downwards into the liquid steel. This is far more efficient and protects the furnace structure.
Voltage Control Throughout the Melting Cycle
The need for high or low voltage is not static; it changes dramatically based on the stage of the melting process.
Stage 1: Bore-Down (High Voltage)
At the beginning of the process, the electrodes are surrounded by a tall pile of solid scrap metal.
During this "bore-down" phase, a long, powerful arc is desirable. The high voltage allows the arc to transfer energy efficiently over a large area, rapidly melting the scrap. The surrounding scrap acts as a natural shield, absorbing the horizontal heat radiation and protecting the furnace walls and roof.
Stage 2: Flat Bath (Low Voltage)
Once the scrap pile has melted down into a liquid pool, the situation changes completely. This is known as the "flat bath" condition.
With no scrap to shield them, the furnace walls and roof are now directly exposed to the arc's radiation. A long, high-voltage arc at this stage would be catastrophic, rapidly eroding the expensive refractory lining.
Therefore, operators reduce the voltage by switching to a lower secondary tap. This forces the electrodes closer to the bath, creating a shorter arc that is "foamy" or submerged in the slag, directing heat downward where it is needed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right voltage is about managing competing operational priorities. There are clear costs to making the wrong choice at the wrong time.
The Risk of High Voltage at the Wrong Time
Operating with a long arc during the flat-bath stage is the primary cause of premature refractory wear. This leads directly to:
- Increased maintenance costs for refractory repairs.
- Significant production downtime while repairs are made.
- Reduced furnace availability and overall plant throughput.
The Inefficiency of Low Voltage at the Wrong Time
Using a low voltage and short arc during the initial bore-down would be inefficient. The arc would not be powerful enough to effectively melt the large scrap pile, significantly increasing the time and energy required to complete the cycle.
The control system automatically manages electrode position to maintain a target current, but the voltage tap selection is the strategic decision that dictates the fundamental behavior of the arc.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your voltage strategy must align with the specific phase of the furnace cycle to maximize both efficiency and equipment life.
- If your primary focus is rapid initial melting: Use a high-voltage tap during the bore-down phase to leverage long, powerful arcs while the scrap shields the furnace walls.
- If your primary focus is furnace protection and final refining: Switch to a lower-voltage tap as soon as a flat bath is achieved to create a short, focused arc that protects the refractory.
- If your primary focus is overall operational excellence: Implement a dynamic tap-changing profile that automatically adjusts voltage based on the real-time conditions and melting stage.
Ultimately, mastering voltage control is fundamental to running a safe, efficient, and profitable arc furnace operation.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Voltage Setting | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bore-Down (Initial Melting) | High Voltage | Rapidly melt scrap with long arcs | Efficient energy transfer with scrap shielding |
| Flat Bath (Post-Melting) | Low Voltage | Shorten arcs to protect refractory | Prevents damage to furnace lining, reduces downtime |
Upgrade your arc furnace operations with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems tailored to your needs. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise performance for your unique requirements. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and protect your equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity



















