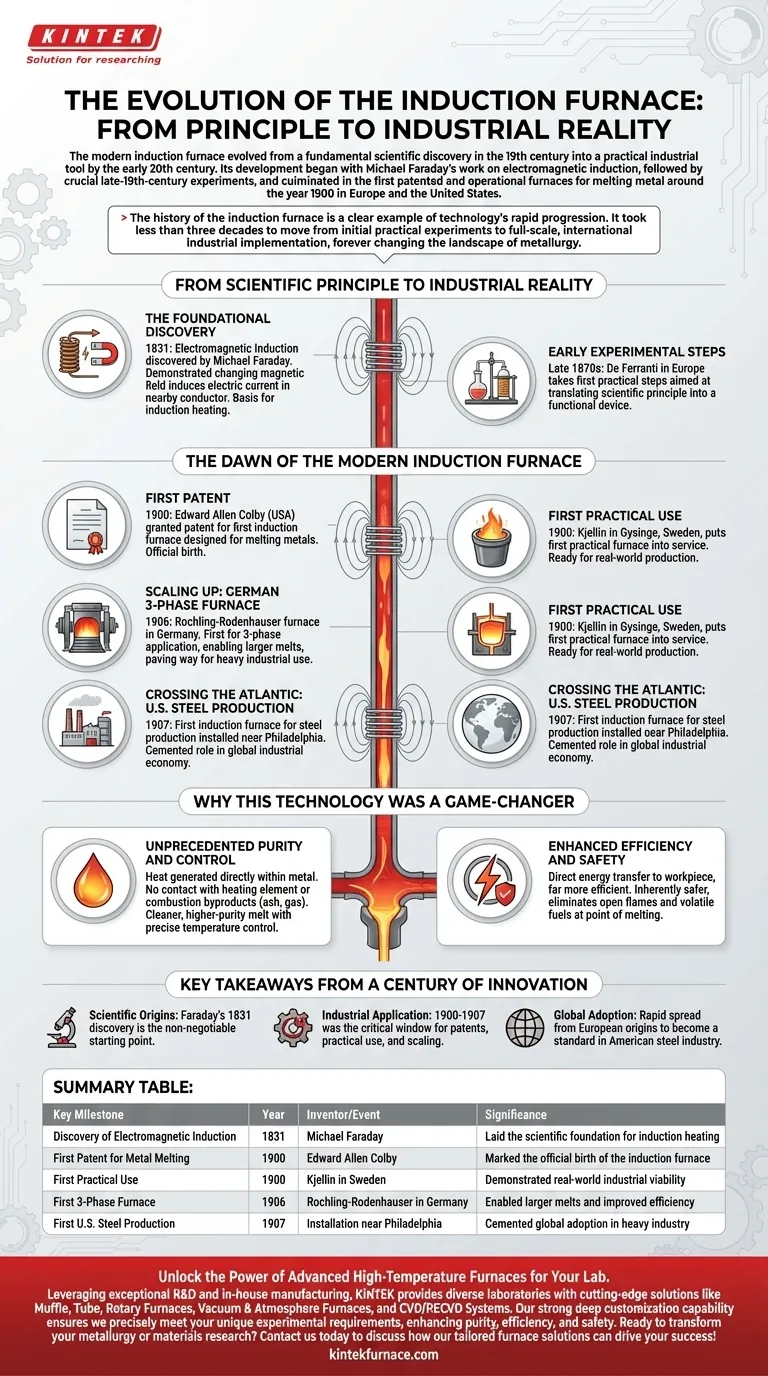
The modern induction furnace evolved from a fundamental scientific discovery in the 19th century into a practical industrial tool by the early 20th century. Its development began with Michael Faraday's work on electromagnetic induction, followed by crucial late-19th-century experiments, and culminated in the first patented and operational furnaces for melting metal around the year 1900 in Europe and the United States.
The history of the induction furnace is a clear example of technology's rapid progression. It took less than three decades to move from initial practical experiments to full-scale, international industrial implementation, forever changing the landscape of metallurgy.

From Scientific Principle to Industrial Reality
The journey to the induction furnace began not in a foundry, but in a laboratory. The core concept is one of the pillars of modern physics and electrical engineering.
The Foundational Discovery
The entire technology rests on electromagnetic induction, discovered by Michael Faraday in 1831. He demonstrated that a changing magnetic field could induce an electric current in a nearby conductor. This principle is the basis for electric motors, generators, and, critically, induction heating.
Early Experimental Steps
While Faraday laid the groundwork, the first practical steps toward an induction furnace were taken by De Ferranti in Europe during the late 1870s. These early experiments aimed to translate the scientific principle into a functional device, bridging the gap between theoretical physics and applied engineering.
The Dawn of the Modern Induction Furnace
The turn of the 20th century was the pivotal moment when experimental concepts became commercially viable industrial machines, with key developments happening nearly simultaneously across the globe.
The First Patent and Practical Use
The year 1900 marks the official birth of the induction furnace. American inventor Edward Allen Colby was granted a patent for the first induction furnace specifically designed for melting metals.
In that same year, the first truly practical induction furnace was put into service by Kjellin in Gysinge, Sweden. This demonstrated that the technology was ready for real-world production.
Scaling Up: The German 3-Phase Furnace
A significant leap in power and efficiency occurred in 1906 in Germany. The Rochling-Rodenhauser furnace was the first to be built for 3-phase electrical application, enabling larger melts and paving the way for the heavy industrial use we see today.
Crossing the Atlantic: Steel Production in the U.S.
The technology's rapid adoption was confirmed in 1907, when the first induction furnace for steel production in the United States was installed in a plant near Philadelphia. This event cemented the furnace's role as a key tool in the global industrial economy.
Why This Technology Was a Game-Changer
The rapid adoption of the induction furnace was not accidental. It offered fundamental advantages over the combustion-based and electric arc furnaces that dominated metallurgy at the time.
Unprecedented Purity and Control
Because the heat is generated directly within the metal via induced currents, there is no contact with a heating element or combustion byproducts like ash or gas. This results in a much cleaner, higher-purity melt with precise temperature control.
Enhanced Efficiency and Safety
Induction heating is far more efficient than traditional methods, as the energy is transferred directly to the workpiece. The process is also inherently safer, as it eliminates the need for open flames or volatile fuels at the point of melting, creating a better working environment.
Key Takeaways from a Century of Innovation
Understanding the historical progression provides valuable context for the technology's place in modern industry.
- If your primary focus is scientific origins: Remember that Faraday's 1831 discovery of electromagnetic induction is the non-negotiable starting point for this entire field of technology.
- If your primary focus is industrial application: The period between 1900 and 1907 was the critical window where patents, practical use, and technological scaling all occurred.
- If your primary focus is global adoption: Note how quickly the technology spread from its European origins in Sweden and Germany to become a standard in the American steel industry.
This century-old innovation, born from a simple physical principle, remains a cornerstone of modern high-purity metal production.
Summary Table:
| Key Milestone | Year | Inventor/Event | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discovery of Electromagnetic Induction | 1831 | Michael Faraday | Laid the scientific foundation for induction heating |
| First Patent for Metal Melting | 1900 | Edward Allen Colby | Marked the official birth of the induction furnace |
| First Practical Use | 1900 | Kjellin in Sweden | Demonstrated real-world industrial viability |
| First 3-Phase Furnace | 1906 | Rochling-Rodenhauser in Germany | Enabled larger melts and improved efficiency |
| First U.S. Steel Production | 1907 | Installation near Philadelphia | Cemented global adoption in heavy industry |
Unlock the Power of Advanced High-Temperature Furnaces for Your Lab
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with cutting-edge solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing purity, efficiency, and safety in your processes.
Ready to transform your metallurgy or materials research? Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















