Choosing between vacuum casting and injection molding comes down to a fundamental trade-off between upfront investment and per-part cost at scale. Vacuum casting is an exceptional process for producing small quantities of high-fidelity parts quickly and affordably. Injection molding, by contrast, requires a significant initial investment in tooling but delivers an extremely low cost-per-part for mass production.
The decision is not about which process is technically superior, but which one aligns with your specific goal and production volume. Vacuum casting is for speed and low-volume fidelity, while injection molding is for scaling to mass production economically.
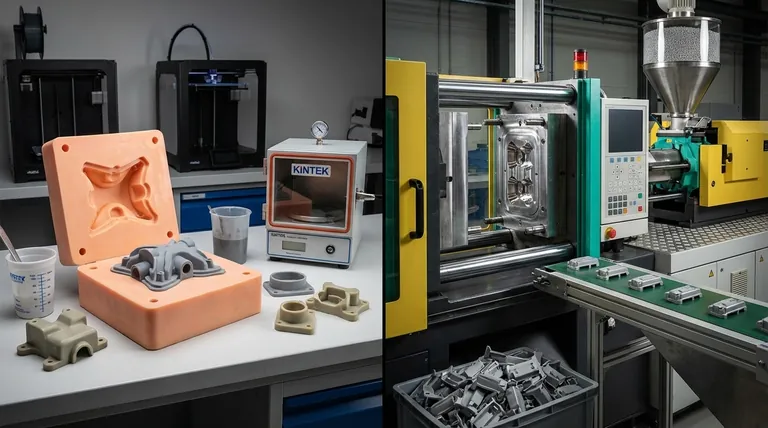

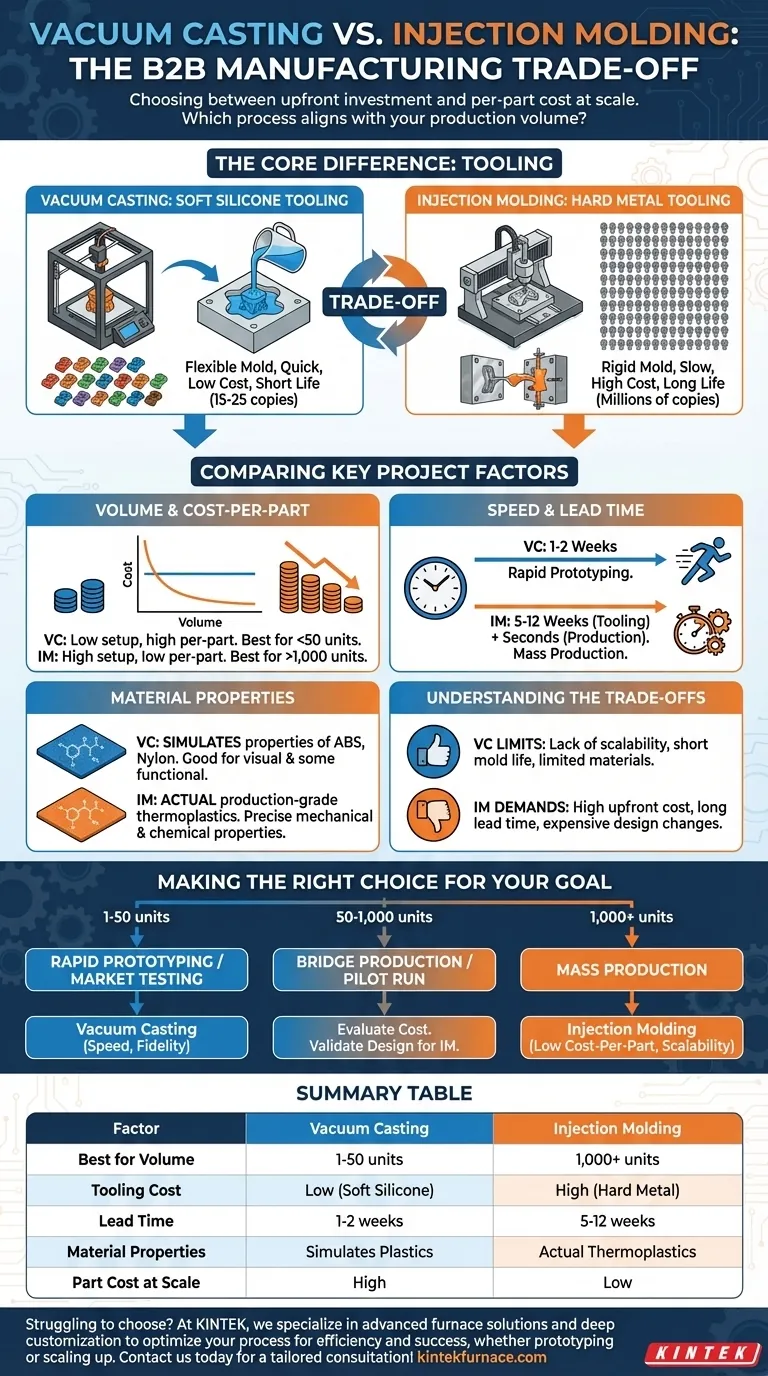
The Core Difference: Tooling
The defining factor that separates these two processes is the mold, often referred to as "tooling." This single element dictates the cost, speed, and viable volume of your project.
Vacuum Casting: Soft Silicone Tooling
Vacuum casting uses a master model, often 3D printed, to create a soft silicone mold. This mold is relatively inexpensive and can be produced in a matter of days.
Because the mold is flexible, it can accommodate complex geometries, including undercuts, without requiring complex and expensive tooling mechanisms. However, this softness is also its limitation; a silicone mold degrades quickly and can typically only produce 15-25 high-quality copies before it needs to be replaced.
Injection Molding: Hard Metal Tooling
Injection molding relies on a robust, two-part mold machined from metal, usually aluminum or steel. Creating this "hard tool" is a precise and time-consuming engineering process that can take weeks or months and cost tens of thousands of dollars.
This rigid tool is built for durability and can withstand immense pressure and heat, enabling it to produce hundreds of thousands, or even millions, of identical parts. Its rigidity, however, demands strict adherence to Design for Manufacturability (DFM) principles to ensure parts can be ejected without damage.
Comparing Key Project Factors
Understanding the tooling difference helps clarify how each process performs against key manufacturing metrics.
Volume and Cost-Per-Part
Vacuum casting has a very low setup cost but a relatively high cost-per-part that remains fairly constant. It is the most economical choice for runs under 50 units.
Injection molding has a very high setup cost due to the tool, but the material and cycle cost for each part is exceptionally low. The tooling cost is amortized over the production run, making it the only viable option for achieving a low price point at volumes of 1,000 units or more.
Speed and Lead Time
For producing a small batch of parts, vacuum casting is significantly faster. You can go from a final design to physical parts in hand within 1-2 weeks.
For injection molding, the longest lead time is in creating the tool, which often takes 5-12 weeks. Once the tool is complete, however, parts can be produced in seconds, allowing for rapid mass production.
Material Properties
Vacuum casting uses two-part polyurethane resins that are formulated to simulate the properties of common production plastics like ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon. While these simulants are excellent for visual prototypes and some functional testing, they are not the actual thermoplastic material.
Injection molding uses the actual production-grade thermoplastic pellets. This means the parts have the precise mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties required for a final, market-ready product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is a perfect solution for every scenario. Being aware of their inherent limitations is critical for making an informed decision.
The Limits of Vacuum Casting
The primary drawback is its lack of scalability. The process is manual, and the molds have a very short lifespan, making it completely unsuitable for mass production. Furthermore, the material selection is limited to polyurethane simulants, which may not be appropriate for rigorous functional or regulatory testing.
The Demands of Injection Molding
The most significant barrier to injection molding is the high upfront cost and long lead time for tooling. Any design changes after the tool is made are extremely expensive and time-consuming to implement. This makes it a poor choice for early-stage prototyping where designs are still likely to change.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your manufacturing process based on the current stage and objective of your project.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or market testing (1-50 units): Vacuum casting offers production-quality aesthetics and good functional stand-ins with unmatched speed for low volumes.
- If your primary focus is bridge production or an initial pilot run (50-1,000 units): This is the crossover point where you must evaluate the cost. Multiple silicone molds may still be cheaper than a simple aluminum injection mold, but you should be validating your design for an eventual move to injection molding.
- If your primary focus is mass production (1,000+ units): Injection molding is the definitive standard, offering the low per-part cost necessary to be commercially viable at scale.
By aligning your manufacturing process with your production volume and project goals, you ensure both financial efficiency and product success.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Vacuum Casting | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Best for Volume | 1-50 units | 1,000+ units |
| Tooling Cost | Low (soft silicone) | High (hard metal) |
| Lead Time | 1-2 weeks | 5-12 weeks for tooling |
| Material Properties | Simulates plastics (e.g., ABS, nylon) | Actual production-grade thermoplastics |
| Part Cost at Scale | High per-part cost | Low per-part cost |
Struggling to choose between vacuum casting and injection molding for your project? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs—whether you're prototyping or scaling up. Let us help you optimize your process for efficiency and success. Contact us today for a tailored consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing between hot pressing and cold compacting and sintering? Optimize Your Material Manufacturing
- How does tailored heat and pressure control benefit hot pressing? Achieve Superior Material Density and Strength
- How does hot pressing work? Achieve Maximum Density and Strength for Advanced Materials
- How does automation enhance the hot pressing process? Boost Precision, Efficiency, and Quality
- What is a vacuum press and why is it important in modern manufacturing? Unlock Flawless Bonding and Precision



















