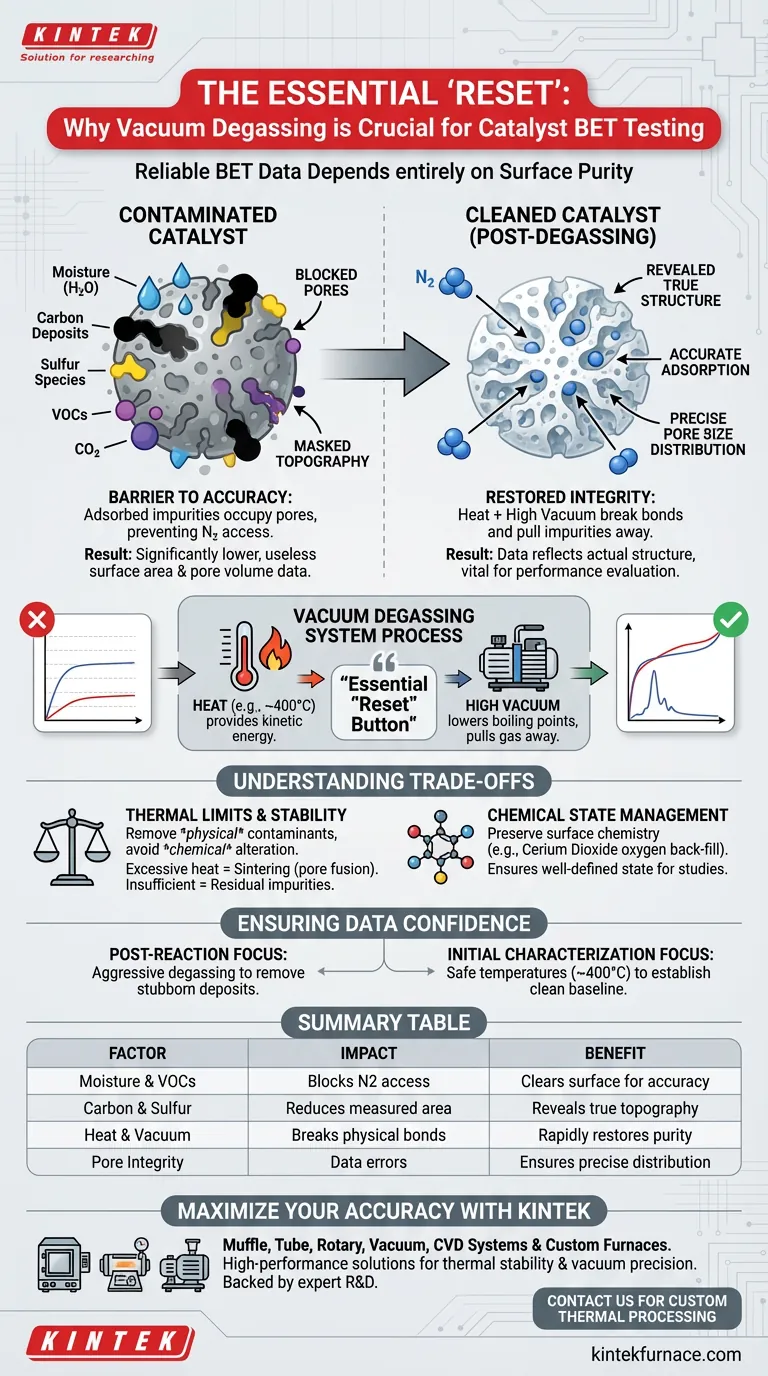
Reliable BET data depends entirely on surface purity. A vacuum degassing system is required to strip away contaminants—such as residual moisture, carbon deposits, and sulfur species—that accumulate on catalyst surfaces, particularly after high-temperature reactions. By applying heat under a high vacuum, this process removes these physically adsorbed barriers, ensuring that the subsequent nitrogen adsorption test measures the catalyst's actual structure rather than the impurities covering it.
Vacuum degassing is the essential "reset" button for catalyst characterization. It clears blocked pores and surface sites of foreign molecules, preventing severe errors in specific surface area, pore volume, and pore size distribution measurements.

The Barrier to Accuracy: Surface Contamination
The Nature of Adsorbed Impurities
Catalysts are highly reactive materials that naturally accumulate "debris" from their environment or previous reactions.
According to standard protocols, these surfaces are frequently covered with adsorbed sulfur species, carbon deposits, and moisture. Additionally, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and carbon dioxide can physically bind to the powder surface, effectively masking the material's true topography.
The Consequences of skipped Degassing
If these impurities remain, they occupy the microscopic pores of the catalyst.
When you attempt a Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) test on a contaminated sample, the nitrogen gas cannot access these blocked pores. This results in calculated surface areas and pore volumes that are significantly lower than reality, rendering the data useless for evaluating catalyst performance.
How the Degassing System Restores Integrity
Combining Heat and Vacuum
The degassing system operates by subjecting the sample to high temperatures—often around 400°C—while simultaneously pulling a high vacuum.
This dual approach is critical. The heat provides the kinetic energy required to break the weak bonds holding physically adsorbed impurities to the surface, while the vacuum lowers the boiling point of liquids and physically pulls the liberated gas molecules away from the sample.
Revealing the True Pore Structure
The primary goal of this pretreatment is the restoration of the catalyst's "true" physical state.
By thoroughly removing the blockage caused by sulfur, carbon, and water, the system exposes the underlying pore structure. This allows the low-temperature nitrogen adsorption test to accurately reflect changes in pore size distribution and specific surface area, which is vital for understanding how a reaction may have altered the catalyst.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Limits and Material Stability
While heat is necessary for cleaning, it must be applied judiciously.
The goal is to remove physically adsorbed contaminants without altering the chemical nature or structure of the catalyst itself. Excessive heat during degassing can accidentally sinter (melt/fuse) the pores you are trying to measure. Conversely, insufficient heat or vacuum time will leave contaminants behind, skewing the data.
Chemical State Management
In specific advanced applications, simply stripping the surface isn't enough; the surface chemistry must be preserved.
For example, materials like cerium dioxide may require an oxygen back-fill process after degassing. This ensures that surface oxygen vacancies are controlled and the material is in a well-defined state for subsequent chemical studies, rather than just physical mapping.
Ensuring Data Confidence for Your Project
To ensure your BET results drive the right decisions, align your degassing strategy with your analytical goals:
- If your primary focus is analyzing post-reaction catalysts: You must ensure the degassing conditions are aggressive enough to remove stubborn carbon deposits and sulfur species to see how the reaction changed the pore structure.
- If your primary focus is initial material characterization: Focus on removing moisture and VOCs at temperatures that are safe for the material stability (often ~400°C) to establish a clean baseline.
Accurate surface area analysis is not just about the measurement tool; it is about the purity of the sample you put into it.
Summary Table:
| Degassing Factor | Impact on BET Analysis | Benefit of Pretreatment |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture & VOCs | Blocks nitrogen access to pores | Clears surface for accurate adsorption |
| Carbon & Sulfur | Reduces measured surface area | Reveals true topography post-reaction |
| Heat & Vacuum | Breaks physical bonds of impurities | Rapidly restores catalyst surface purity |
| Pore Integrity | Blocked pores lead to data errors | Ensures precise pore size distribution |
Maximize Your Material Analysis Accuracy with KINTEK
Don't let surface impurities compromise your BET data. KINTEK provides high-performance vacuum degassing and thermal treatment solutions designed to restore your catalyst's true structure.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces that are fully customizable for your unique characterization needs. Whether you are analyzing post-reaction catalysts or establishing a material baseline, our equipment ensures the thermal stability and vacuum precision required for reliable results.
Ready to optimize your lab's testing efficiency? Contact us today to discuss your custom thermal processing requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Hengchang Ni, Ping Li. Promotion Effect of H2S at High Concentrations on Catalytic Dry Reforming of Methane in Sour Natural Gas. DOI: 10.3390/catal14060352
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing between argon and nitrogen for vacuum furnace applications? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- Why is vacuum oven processing required before the curing of resin-impregnated carbon nanotube composites?
- How does high-temperature sintering furnace setting influence BaTiO3 microstructure? Optimize Sputtering Performance
- How do inert gas technology, airflow, and air pressure work together in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- How does an industrial-grade high-temperature vertical furnace contribute to the homogenization annealing of magnetocaloric materials?
- What is a vacuum furnace and what processes can it perform? Unlock Precision Heat Treatment Solutions
- What are the core technical advantages of LD-FZ systems? Precision Crystal Growth with Laser Diode Technology
- What are the advantages of using a Vacuum Reactor for bio-oil? Maximize Yield and Quality Through Pressure Control


















