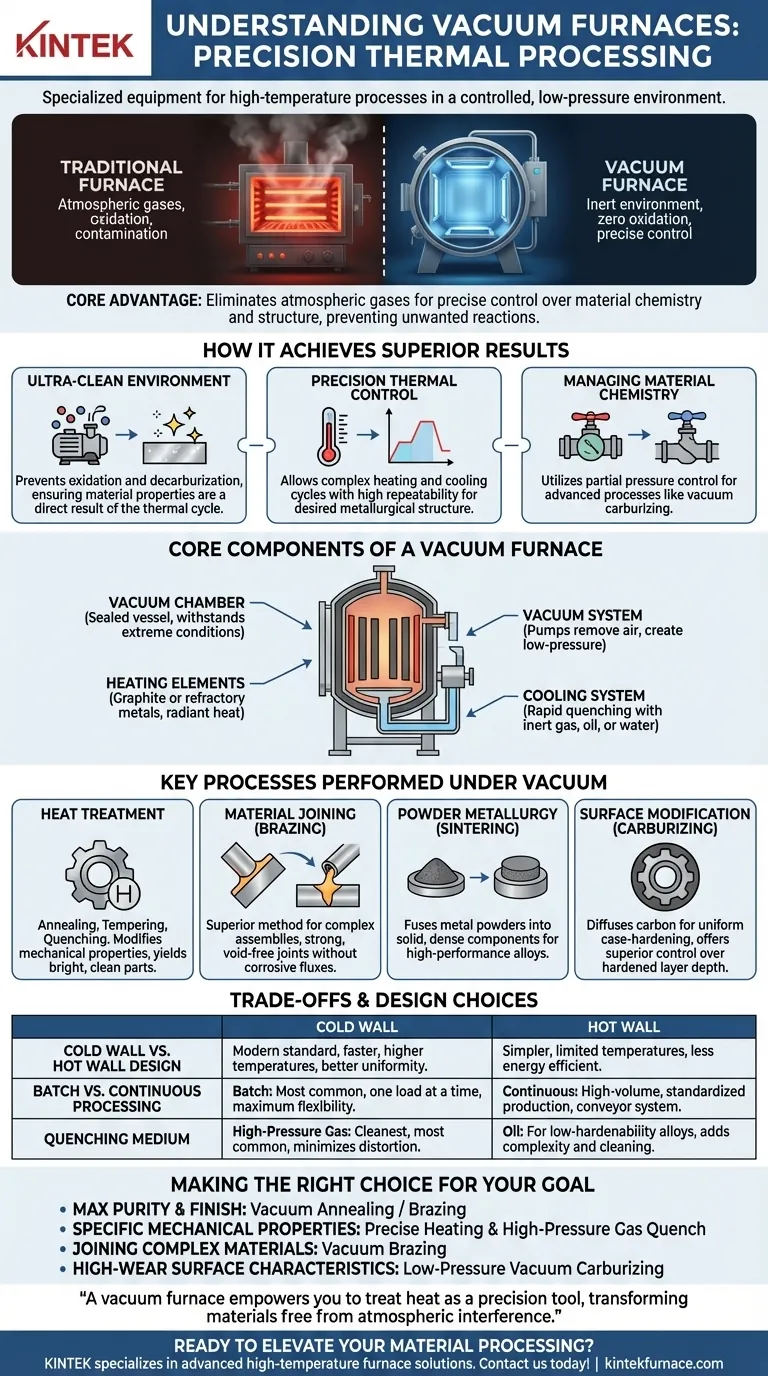
In essence, a vacuum furnace is a specialized piece of industrial equipment that heats materials to extremely high temperatures within a controlled, low-pressure environment. By removing air and other gases, it performs critical thermal processes such as heat treatment, brazing, and sintering with exceptional consistency and without the risk of oxidation or surface contamination common in traditional furnaces.
The core advantage of a vacuum furnace is not just the heat it provides, but the inert environment it creates. By eliminating atmospheric gases, it gives engineers precise control over a material's final chemistry and structural properties, preventing unwanted reactions that degrade quality.

How a Vacuum Furnace Achieves Superior Results
The function of a vacuum furnace goes far beyond simple heating. It is a precision instrument designed to manipulate material properties at a fundamental level by controlling the atmosphere, or lack thereof.
Creating an Ultra-Clean Environment
The primary role of the vacuum is to create a near-perfectly inert environment. Removing oxygen and other reactive gases prevents oxidation and decarburization, which can weaken metals and compromise their surface finish.
This ultra-clean environment ensures that the material's properties are a direct result of the thermal cycle, not a side effect of unwanted chemical reactions with the atmosphere.
Precision Thermal Control
Modern vacuum furnaces offer exceptional control over both heating and cooling rates. This allows for complex, multi-stage thermal cycles to be executed perfectly every time.
Whether performing a rapid quench to achieve maximum hardness or a slow anneal to improve ductility, the system's temperature control ensures the desired metallurgical structure is achieved with high repeatability.
Managing Material Chemistry
Advanced systems allow for the introduction of specific gases at low pressures, a technique known as partial pressure control.
This is used for sophisticated processes like vacuum carburizing (adding carbon to a steel surface) or to suppress the vaporization of certain elements, such as chromium in stainless steels, at high temperatures.
Core Components of a Vacuum Furnace System
A vacuum furnace is an integrated system where each component plays a critical role in achieving the final result.
The Vacuum Chamber
This is the sealed, typically cylindrical vessel that contains the workload. It is built to withstand both extreme temperatures and the immense external pressure when a vacuum is drawn. Chambers can be designed for vertical or horizontal loading.
The Heating Elements
These components, often made of graphite or refractory metals, generate the radiant heat inside the chamber. The "cold wall" design, where the heating elements are inside the insulated chamber, allows for much higher operating temperatures and faster heating and cooling cycles compared to older "hot wall" designs.
The Vacuum System
This is the heart of the furnace. It consists of a series of pumps, such as mechanical pumps and high-vacuum pumps (e.g., molecular or diffusion pumps), that work in stages to remove air and create the required low-pressure environment.
The Cooling System
After the heating cycle, controlled cooling is often just as critical. The cooling system facilitates quenching by rapidly introducing a medium—most commonly high-pressure inert gas (gas quenching), but also oil or water in specialized designs.
Key Processes Performed Under Vacuum
The unique environment of a vacuum furnace enables a range of high-value manufacturing processes that are difficult or impossible to perform otherwise.
Heat Treatment (Annealing, Tempering, Quenching)
This is the most common application. Vacuum heat treatment modifies the mechanical properties of metals, such as hardness, toughness, and ductility. The process yields bright, clean parts that require no subsequent cleaning.
Material Joining (Brazing)
Vacuum brazing is a superior method for joining complex assemblies, often with dissimilar metals. The clean environment ensures the braze alloy flows freely and creates strong, void-free joints without the use of corrosive fluxes.
Powder Metallurgy (Sintering)
Sintering involves heating compacted metal powders to just below their melting point. In a vacuum, this process fuses the particles together to form a solid, dense part, which is essential for creating components from high-performance alloys and ceramics.
Surface Modification (Carburizing)
Vacuum carburizing, or low-pressure carburizing, is a case-hardening process that diffuses carbon into the surface of steel. It offers superior uniformity and control over the hardened layer depth compared to traditional atmospheric carburizing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Choices
While powerful, a vacuum furnace is not a universal solution. The design and process parameters must be chosen carefully based on the application's specific requirements.
Cold Wall vs. Hot Wall Design
Cold wall furnaces are the modern standard for high-performance applications. They offer faster cycle times, higher temperature capabilities, and better temperature uniformity. Hot wall furnaces are simpler but are limited in temperature and are less energy efficient.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Most vacuum furnaces are batch furnaces, where one load is processed at a time. This offers maximum flexibility. For high-volume, standardized production, continuous vacuum furnaces exist, which move parts through heating and cooling zones on a conveyor.
Quenching Medium Selection
The choice of quenching medium is critical for achieving the desired hardness and minimizing distortion. High-pressure gas quenching is the cleanest and most common method. However, for some low-hardenability alloys, a more severe quench using oil may be necessary, which adds complexity and cleaning steps.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right vacuum process is about matching the furnace's capabilities to your desired material outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material purity and a bright, clean finish: Vacuum annealing or brazing is the ideal choice, as it completely prevents surface oxidation.
- If your primary focus is creating specific mechanical properties: A furnace with precise heating controls and a high-pressure gas quench system is essential for repeatable heat treatment results.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or dissimilar materials: Vacuum brazing provides the cleanest and strongest joints possible without the need for post-process cleaning.
- If your primary focus is creating high-wear surface characteristics: Low-pressure vacuum carburizing offers unmatched control over the case-hardening process for superior component life.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace empowers you to treat heat as a precision tool, transforming materials in an environment free from atmospheric interference.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Applications | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Tempering, Quenching | Prevents oxidation, ensures clean finish, enhances mechanical properties |
| Material Joining | Brazing | Flux-free, strong joints, ideal for complex assemblies |
| Powder Metallurgy | Sintering | Produces dense parts from metal powders and ceramics |
| Surface Modification | Carburizing | Uniform case hardening, improved wear resistance |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and purity? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored for industries like aerospace, automotive, and research. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your unique experimental needs are met with reliability and innovation. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your thermal processes and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion



















