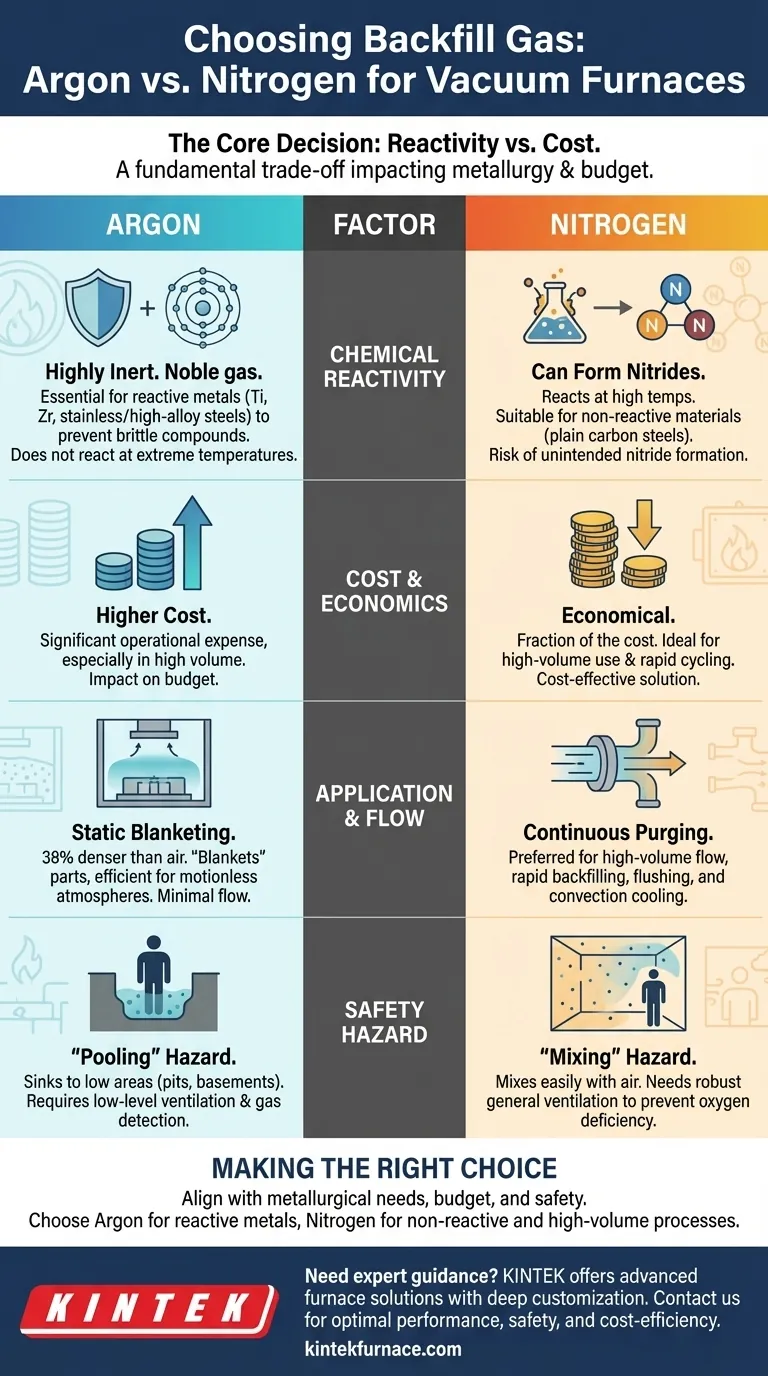
When selecting a backfill gas for a vacuum furnace, the primary factors to consider are the chemical reactivity of the material being processed, the operational temperature, overall cost, and specific safety protocols for your facility. Argon provides superior inertness for sensitive metals at a higher price, while nitrogen offers a cost-effective solution for materials where nitride formation is not a concern.
The choice between argon and nitrogen is fundamentally a trade-off. Argon offers near-total chemical inertness, which is critical for reactive materials at high temperatures. Nitrogen provides a significant cost advantage but carries the risk of forming unintended nitrides with certain metals.

The Core Decision: Reactivity vs. Cost
The most critical factor in your decision is how the gas will interact with your materials at process temperatures. This interaction directly impacts metallurgical properties and final product quality.
Argon: The Inert Safeguard
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is chemically inert and will not react with other elements, even at extreme temperatures. This makes it the essential choice for heat-treating highly reactive metals.
Materials like titanium, zirconium, and certain stainless or high-alloy steels require argon. Using a less inert gas would result in the formation of brittle compounds on the material's surface, compromising its integrity.
The primary drawback of argon is its higher cost compared to nitrogen, which can significantly impact operational expenses, especially in high-volume operations.
Nitrogen: The Economical Workhorse
Nitrogen is significantly less expensive than argon and is suitable for a wide range of heat-treating applications where material reactivity is not a concern.
It provides excellent protection against oxidation for materials like plain carbon steels and some tool steels. However, at high temperatures, nitrogen can react with certain elements to form nitrides.
While sometimes intentional (in nitriding processes), this unintended nitride formation is often detrimental, making nitrogen unsuitable for the reactive metals mentioned previously.
Practical Application: Gas Behavior and Flow
The physical properties of each gas influence how they are best used within the furnace chamber and how they behave in the surrounding facility.
Static Blanketing with Argon
Argon is approximately 38% denser than air. This density allows it to effectively "blanket" parts within the furnace, creating a stable, protective layer that displaces lighter gases with minimal flow.
This makes argon highly efficient for processes requiring a static, motionless protective atmosphere.
Continuous Purging with Nitrogen
Due to its lower cost, nitrogen is the preferred gas for applications requiring high-volume flow.
This includes rapid backfilling, continuous purging to flush out contaminants, or convection-assisted rapid cooling cycles where large quantities of gas are circulated to remove heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Safety and Handling
Both gases are non-toxic but are simple asphyxiants, meaning they can displace oxygen in a confined space and cause suffocation. Their different densities create distinct safety hazards that require different mitigation strategies.
The Asphyxiation Risk of Both Gases
Neither argon nor nitrogen can be detected by smell, which makes gas monitoring and proper ventilation absolutely critical. A leak in an enclosed area can quickly create an oxygen-deficient atmosphere.
Argon's "Pooling" Hazard
Because argon is denser than air, it will sink and accumulate in low-lying areas. Leaked argon can fill up maintenance pits, trenches, or basements, creating a hidden and deadly trap. Facilities using argon must consider low-level ventilation and gas detection.
Nitrogen's "Mixing" Hazard
Nitrogen has a density very similar to air, so it mixes easily and disperses throughout a room. This can make it more dangerous in poorly ventilated spaces, as it will reduce the oxygen concentration of the entire atmosphere rather than settling in one area. Robust general ventilation is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your final decision must be aligned with your specific metallurgical requirements, budget, and safety infrastructure.
- If you are processing reactive materials (like titanium or certain refractory metals): You must use argon to prevent unwanted nitride formation and ensure the final product's metallurgical integrity.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency on non-reactive materials (like plain carbon steels): Nitrogen provides effective protection from oxidation at a fraction of the cost, making it the clear economic choice.
- If you are performing high-volume purges or rapid cooling: Nitrogen's low cost makes it the only practical option for processes that consume large amounts of gas.
- If your facility has enclosed low-lying areas or inspection pits: Be especially cautious with argon and ensure you have dedicated low-level ventilation and gas monitoring in place to mitigate its "pooling" risk.
Ultimately, selecting the right gas is not just an operational choice; it's a strategic decision that directly impacts your product quality, safety, and bottom line.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Argon | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Reactivity | Highly inert, ideal for reactive metals like titanium | Can form nitrides, suitable for non-reactive materials like carbon steels |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost, economical for high-volume use |
| Safety Hazard | Pools in low areas, requires low-level ventilation | Mixes with air, needs robust general ventilation |
| Application | Static blanketing for sensitive processes | Continuous purging and rapid cooling |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right gas for your vacuum furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements to ensure optimal performance, safety, and cost-efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- What is the mechanism of a vacuum sintering furnace for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 + Y2O3? Optimize Your High-Entropy Alloy Processing



















