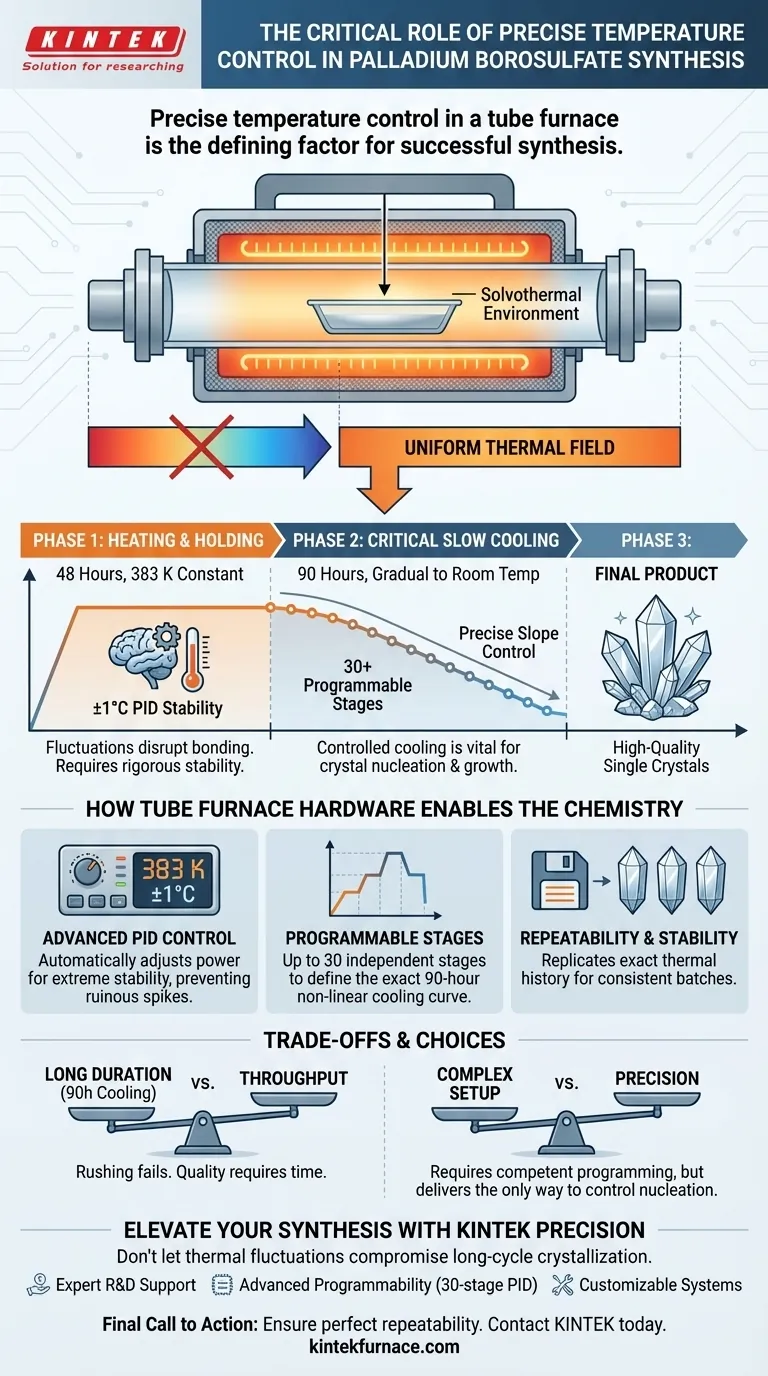
Precise temperature control in a tube furnace is the defining factor in the successful synthesis of Palladium Borosulfates. To achieve the specific crystal structure required, you must maintain a strictly uniform thermal field within a solvothermal environment and execute a complex, automated cooling protocol that spans several days.
The synthesis relies on a delicate balance of maintaining steady heat for 48 hours followed by a 90-hour cooling phase; without the programmable precision of a tube furnace, managing the crystal nucleation and growth required for this material is virtually impossible.

The Solvothermal Synthesis Challenge
Requirement for Thermal Uniformity
The preparation of Palladium Borosulfates is a complex solvothermal reaction. This process requires a highly uniform thermal field to ensure the reaction proceeds evenly throughout the sample. A tube furnace provides this consistency, eliminating thermal gradients that could lead to uneven material properties or failed synthesis.
The Long-Cycle Heating Protocol
Success depends on a rigorous heating schedule that is difficult to manage manually. The standard protocol involves maintaining a constant temperature of 383 K for 48 hours. Fluctuations during this holding period can disrupt the chemical bonding process.
Criticality of Slow Cooling
The most challenging aspect of this synthesis is the cooling phase. After the initial heating, the material requires a controlled slow cooling process lasting 90 hours. This gradual reduction in temperature is vital for controlling crystal nucleation and growth, directly determining the quality of the final product.
How the Hardware Enables the Chemistry
Advanced PID Control
To handle these long durations without deviation, tube furnaces utilize PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) algorithms. This technology automatically adjusts heating power to maintain stability, often achieving accuracy within ±1°C. This prevents temperature spikes or drops that would ruin the crystalline structure.
Programmable Temperature Stages
The 90-hour cooling phase requires a non-linear or strictly linear temperature slope that manual controls cannot achieve. Modern tube furnaces allow for up to 30 independent temperature control stages. This allows researchers to pre-program the exact cooling rate, ensuring the transition from 383 K to room temperature follows the precise curve needed for optimal crystallization.
Repeatability and Stability
In materials science, reproducibility is as important as the initial success. High-precision control systems allow you to save specific sintering curves. This ensures that the exact thermal history—heating rate, holding time, and cooling slope—can be replicated perfectly for every batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Duration vs. Throughput
The strict requirement for a 90-hour cooling cycle creates a significant bottleneck. While the tube furnace ensures quality, the long occupancy time of the equipment severely limits throughput. You cannot rush this process; accelerating the cooling to save time will result in poor crystal quality or synthesis failure.
Complexity of Setup
Achieving this level of precision requires advanced configuration. Users must be competent in programming multi-stage PID controllers. Incorrectly setting the "fuzzy control" or self-tuning parameters can lead to oscillations in temperature, defeating the purpose of the high-end hardware.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure you select the correct equipment for Palladium Borosulfate preparation, consider your specific end-goals:
- If your primary focus is High-Quality Single Crystals: Prioritize a furnace with multi-stage programmability to strictly enforce the 90-hour slow-cooling curve without deviation.
- If your primary focus is Batch Consistency: Ensure the furnace features advanced PID self-tuning to guarantee that the thermal field remains uniform (±1°C) across repeated 48-hour heating cycles.
Precision in your thermal equipment is not a luxury here; it is the only variable that allows you to control the physics of nucleation over a multi-day timeline.
Summary Table:
| Synthesis Phase | Duration | Temperature Requirement | Critical Success Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heating/Holding | 48 Hours | 383 K (Constant) | Thermal uniformity & ±1°C PID stability |
| Cooling Phase | 90 Hours | Gradual to Room Temp | Precise programmable slopes for nucleation |
| Synthesis Type | Multi-day | Solvothermal | Automated multi-stage thermal programming |
Elevate Your Materials Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Don't let thermal fluctuations compromise your long-cycle crystallization. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all engineered for the extreme stability required by Palladium Borosulfate synthesis.
Our Value to You:
- Expert R&D Support: Our systems are backed by deep technical expertise in materials science.
- Advanced Programmability: Achieve perfect 90-hour cooling curves with our 30-stage PID controllers.
- Customizable Systems: We tailor furnace dimensions and heating elements to your unique lab requirements.
Ready to ensure perfect repeatability for your next research breakthrough? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project.
Visual Guide
References
- Stefan Sutorius, Jörn Bruns. Pd[B(S <sub>2</sub> O <sub>7</sub> ) <sub>2</sub> ] <sub>2</sub> and Pd[B(SO <sub>4</sub> ) (S <sub>2</sub> O <sub>7</sub> )] <sub>2</sub> : Two Borosulfates with Pd <sup>2+</sup> in Octahedral and One with Pd <sup>2+</sup> in Square Planar Oxygen Coordin. DOI: 10.1002/chem.202501515
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to use a tube furnace for air oxidation of the 3D copper framework? Master Lithiophilic Interfaces
- What are some advanced features of more elaborate tube furnaces? Unlock Precision Control for High-Temp Processes
- What is the temperature of a tube furnace? Selecting the Right High-Temp Solution for Your Lab
- What role does a tubular furnace play in walnut shell carbonization? Master the Art of Stable Carbon Skeleton Creation
- How does a tube furnace ensure uniform temperature distribution? Discover Key Mechanisms for Precise Heating
- What are the primary benefits of using a split tube furnace? Enhance Lab Efficiency with Unmatched Flexibility
- What is the function of autoclaves and tube reactors in hydrometallurgical leaching? Unlock Refractory Ore Potential
- What are the main applications of horizontal tube furnaces? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment and Synthesis



















