A tube atmosphere furnace is strictly required to create a controlled, oxygen-free environment during the synthesis process. Without this specialized equipment, the high temperatures necessary for synthesis would cause the hard carbon to oxidize and disintegrate rather than integrating the sulfur. Additionally, the furnace provides the precise thermal regulation needed to force sulfur atoms into the carbon framework to form stable chemical bonds.
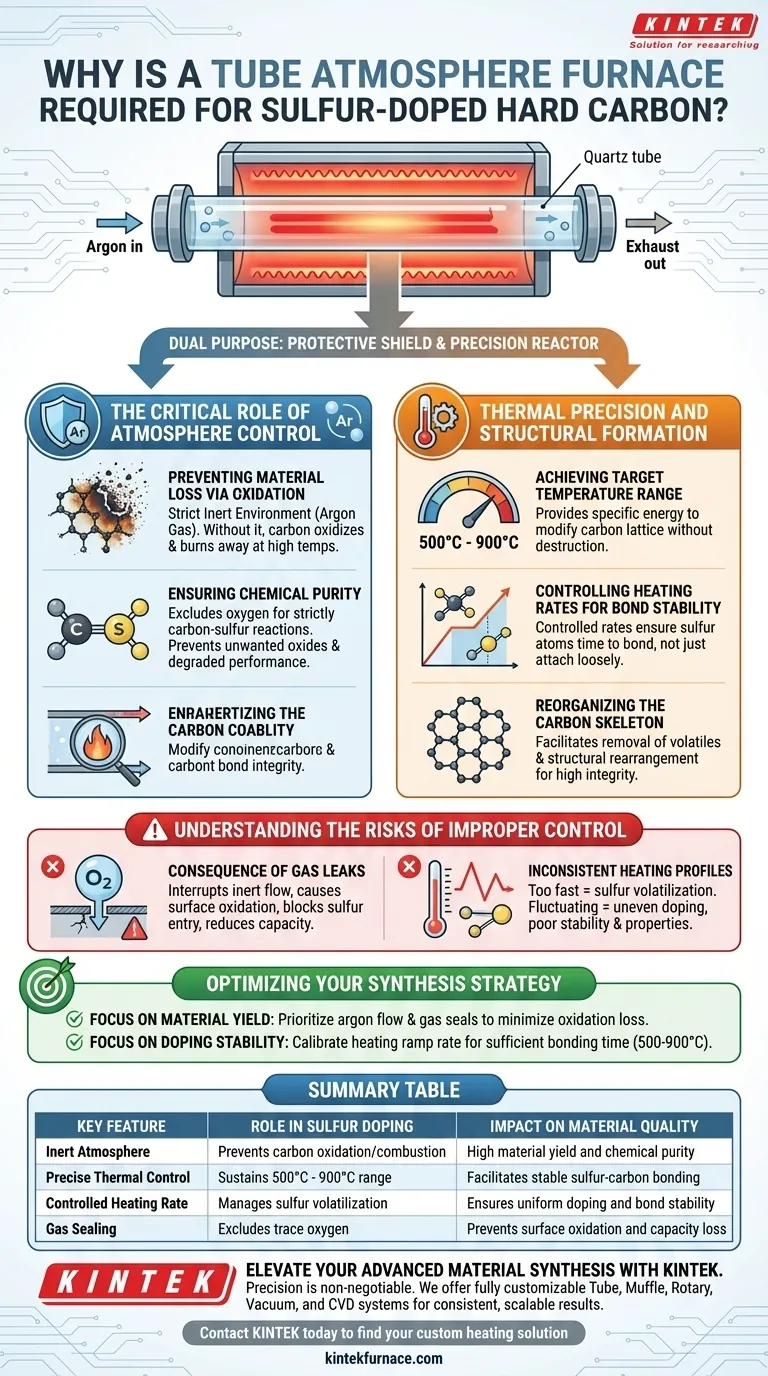
The furnace serves a dual purpose: it acts as a protective shield against oxidation using inert gas, and as a precision reactor that enables the specific thermal conditions necessary for stable sulfur doping.
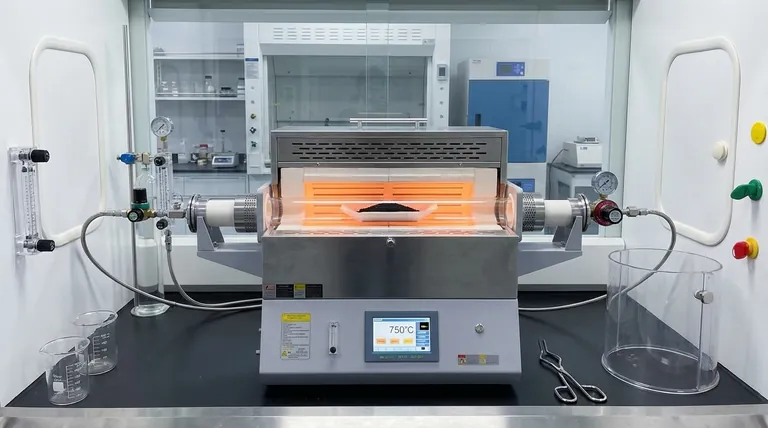

The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
Preventing Material Loss via Oxidation
The primary function of the tube atmosphere furnace is to maintain a strict inert environment, typically using argon gas.
At high processing temperatures, carbon is highly reactive with oxygen. Without the protective argon atmosphere provided by the furnace, the hard carbon materials would oxidize and essentially burn away, leading to significant material loss.
Ensuring Chemical Purity
By excluding oxygen, the furnace ensures that the chemical reactions occurring inside are strictly between the carbon and the sulfur.
This isolation is vital for preventing the formation of unwanted oxides or combustion byproducts that would degrade the material's electrochemical performance.
Thermal Precision and Structural Formation
Achieving the Target Temperature Range
Sulfur doping requires a specific high-temperature window to be effective.
The tube furnace is designed to sustain temperatures between 500 °C and 900 °C. This specific range provides the energy required to modify the carbon lattice without destroying it.
Controlling Heating Rates for Bond Stability
Simply reaching a high temperature is not enough; the rate at which the material is heated is equally critical.
The furnace allows for specific, controlled heating rates. This control ensures that sulfur atoms have the time and energy to successfully dope into the carbon framework and form stable chemical bonds, rather than loosely attaching to the surface.
Reorganizing the Carbon Skeleton
Beyond doping, the thermal process facilitates the reorganization of the carbon structure itself.
As noted in similar synthesis processes, precise heat treatment removes volatile components and rearranges the carbon skeleton. This results in a material with the structural integrity required for high-performance battery applications.
Understanding the Risks of Improper Control
The Consequence of Gas Leaks
Even with the right furnace, failure to maintain a perfect seal can render the process useless.
If the inert gas flow is interrupted or the tube is not sealed correctly, trace amounts of oxygen will enter. This leads to surface oxidation, which blocks sulfur from entering the carbon lattice and reduces the final capacity of the material.
Inconsistent Heating Profiles
If the heating rate is too fast, the sulfur may volatilize before it can bond with the carbon.
Conversely, if the temperature fluctuates or does not hold steadily at the target range, the doping will be uneven. This results in a material with poor stability and inconsistent electrochemical properties.
Optimizing Your Synthesis Strategy
To ensure high-quality sulfur-doped hard carbon, align your equipment settings with your specific experimental goals:
- If your primary focus is Material Yield: Prioritize the integrity of the argon flow and gas seals to absolutely minimize material loss through oxidation.
- If your primary focus is Doping Stability: Focus on calibrating the heating ramp rate to ensure sulfur atoms have sufficient time to chemically bond within the 500-900 °C window.
Success in this process relies not just on reaching high temperatures, but on the precise orchestration of atmosphere and heat that only a tube furnace can provide.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Role in Sulfur Doping | Impact on Material Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Prevents carbon oxidation/combustion | High material yield and chemical purity |
| Precise Thermal Control | Sustains 500°C - 900°C range | Facilitates stable sulfur-carbon bonding |
| Controlled Heating Rate | Manages sulfur volatilization | Ensures uniform doping and bond stability |
| Gas Sealing | Excludes trace oxygen | Prevents surface oxidation and capacity loss |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when preparing high-performance sulfur-doped hard carbons. At KINTEK, we understand the critical balance of atmosphere control and thermal stability. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique lab requirements.
Whether you are focusing on battery applications or structural carbon research, our high-temperature furnaces provide the reliability you need for consistent, scalable results.
Contact KINTEK today to find your custom heating solution
Visual Guide
References
- Yuanfeng Liu, Yong Wang. Shredded-Coconut-Derived Sulfur-Doped Hard Carbon via Hydrothermal Processing for High-Performance Sodium Ion Anodes. DOI: 10.3390/nano15100734
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of atmosphere control and the heating ramp rate in a reduction furnace for Ni-WOx catalysts?
- What is the function of a vertical gas mixing furnace during the annealing of orthopyroxene? Achieve Precise Stability
- What are the main components of a program-controlled atmosphere furnace? Unlock Precision in Thermal Processing
- What role does a high-temperature activation furnace perform in magnetic catalyst synthesis? Optimize Your Fe3O4 Yield
- How does the experimental box type atmosphere furnace contribute to energy conservation and environmental protection? Discover Sustainable Lab Solutions
- How does the box type annealing atmosphere furnace improve production efficiency? Boost Throughput and Cut Costs
- Why is a vacuum or inert gas environment required for the preparation of polysulfide fluxes? Ensure Material Purity
- What is the importance of a dedicated nitriding furnace? Achieve Precision Surface Hardening & Wear Resistance



















