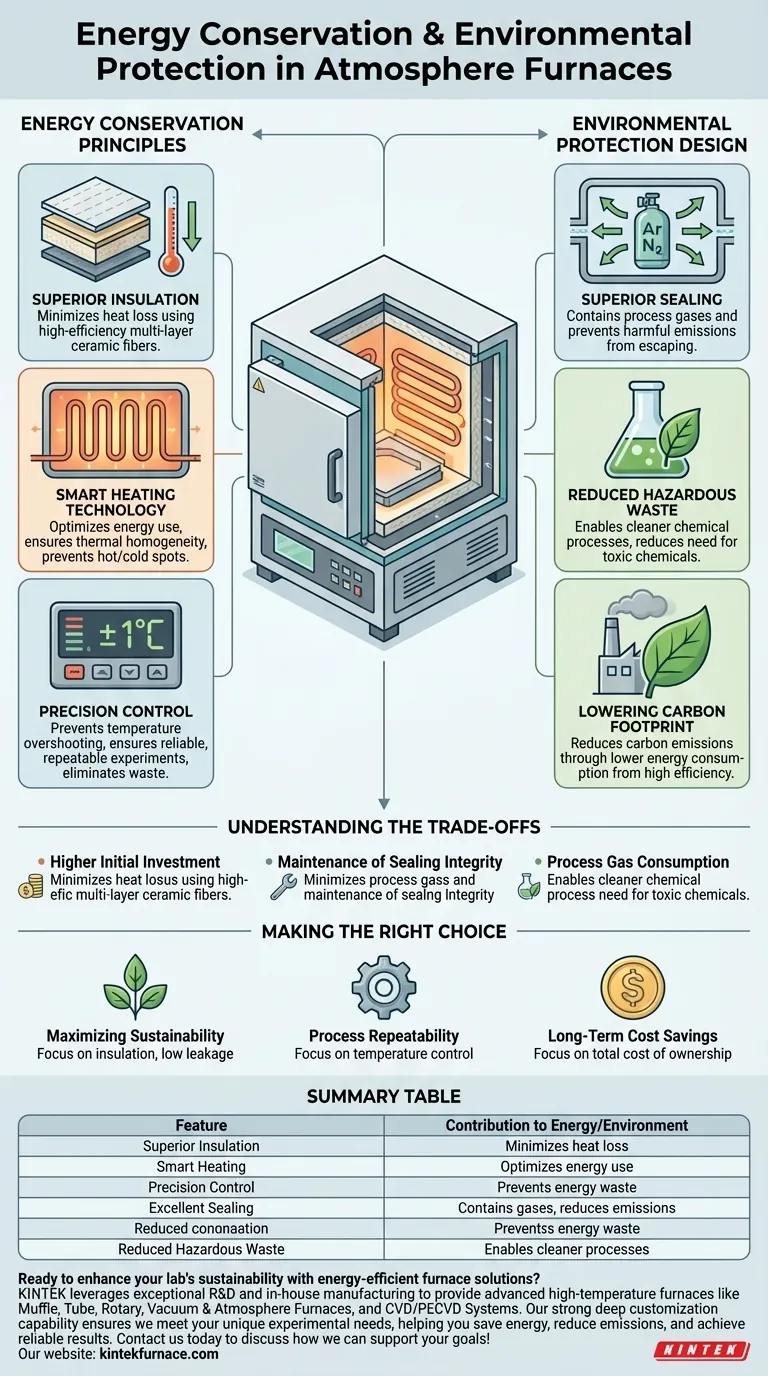
At its core, an experimental box type atmosphere furnace contributes to energy conservation and environmental protection through three primary design features: superior insulation materials that minimize heat loss, advanced heating technologies that optimize energy use, and excellent sealing that prevents the emission of process gases. These elements work together to reduce energy consumption and lessen the furnace's overall environmental impact.
The defining characteristic of a modern atmosphere furnace is its holistic approach to efficiency. By integrating thermal management, precise control, and gas containment, it transforms from a simple heating device into a sustainable tool for advanced material processing.

The Core Principles of Energy Conservation
An atmosphere furnace's energy efficiency is not an accident; it is the result of deliberate engineering choices designed to minimize waste at every stage of the thermal process.
Minimizing Heat Loss with Advanced Insulation
Modern furnaces utilize high-efficiency insulation materials, such as multi-layer ceramic fibers, to create a highly effective thermal barrier.
This superior insulation drastically reduces heat loss to the surrounding environment, ensuring that the energy consumed is used for the primary task of heating the chamber, not the laboratory.
Optimizing Energy Use with Smart Heating
These furnaces employ advanced heating technologies and optimized layouts for their heating elements.
This ensures uniform heat distribution—or thermal homogeneity—throughout the chamber. By heating the target material evenly, the system avoids "hot spots" and "cold spots," which waste energy and can ruin experimental outcomes.
Eliminating Waste Through Precision Control
Advanced temperature control systems are a key feature, with some models maintaining stability as tight as ±1°C.
This level of precision prevents temperature overshooting and fluctuations, which consume excess energy. More importantly, it ensures that experiments are reliable and repeatable, eliminating the significant energy and material waste associated with failed process runs.
How Design Mitigates Environmental Impact
Beyond saving energy, the fundamental design of an atmosphere furnace is built around containment and control, which directly translates to environmental protection.
Containing Emissions with Superior Sealing
The defining feature of an atmosphere furnace is its ability to maintain a controlled atmosphere, which requires excellent sealing performance.
This robust sealing serves a dual purpose: it keeps the controlled gas (e.g., argon, nitrogen) in, and it prevents any potentially harmful byproducts of the high-temperature reaction from escaping into the environment.
Reducing Hazardous Material Use
By providing precise atmospheric control, these furnaces can enable cleaner chemical processes that reduce the need for certain toxic chemicals.
This leads to a direct reduction in the generation of hazardous waste, making the entire manufacturing or research workflow more sustainable.
Lowering the Carbon Footprint
The most direct environmental benefit is a reduced carbon footprint. Since the furnace consumes less energy due to its high efficiency, it is responsible for fewer carbon emissions from electricity generation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, it is important to understand the context and potential considerations when adopting this technology. Objectivity requires acknowledging these points.
Higher Initial Investment
The advanced materials, precision control systems, and robust construction used in high-efficiency atmosphere furnaces typically result in a higher upfront cost compared to simpler, less efficient models.
Maintenance of Sealing Integrity
The energy and environmental benefits are heavily dependent on the integrity of the furnace's seals. These components may require periodic inspection and maintenance to prevent leaks and ensure continued high performance.
Process Gas Consumption
While the furnace contains the atmosphere, it still consumes process gases like nitrogen or argon. The production and transportation of these gases carry their own environmental footprint, which should be considered as part of the total lifecycle impact.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace involves aligning its specific features with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing sustainability: Prioritize models with the highest-grade insulation and documented low gas-leakage rates to minimize both energy use and emissions.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Concentrate on the sophistication of the temperature control system, seeking furnaces that guarantee exceptional thermal stability and uniformity.
- If your primary focus is long-term cost savings: Look beyond the initial purchase price and calculate the total cost of ownership, factoring in the reduced energy and gas consumption over the furnace's lifespan.
Ultimately, adopting an advanced atmosphere furnace is a strategic decision that aligns the demands of modern materials science with the principles of responsible operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Contribution to Energy/Environment |
|---|---|
| Superior Insulation | Minimizes heat loss, cutting energy consumption |
| Smart Heating | Optimizes energy use with uniform heat distribution |
| Precision Control | Prevents energy waste from temperature fluctuations |
| Excellent Sealing | Contains gases, reducing harmful emissions |
| Reduced Hazardous Waste | Enables cleaner processes, lowering environmental impact |
Ready to enhance your lab's sustainability with energy-efficient furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, helping you save energy, reduce emissions, and achieve reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance



















