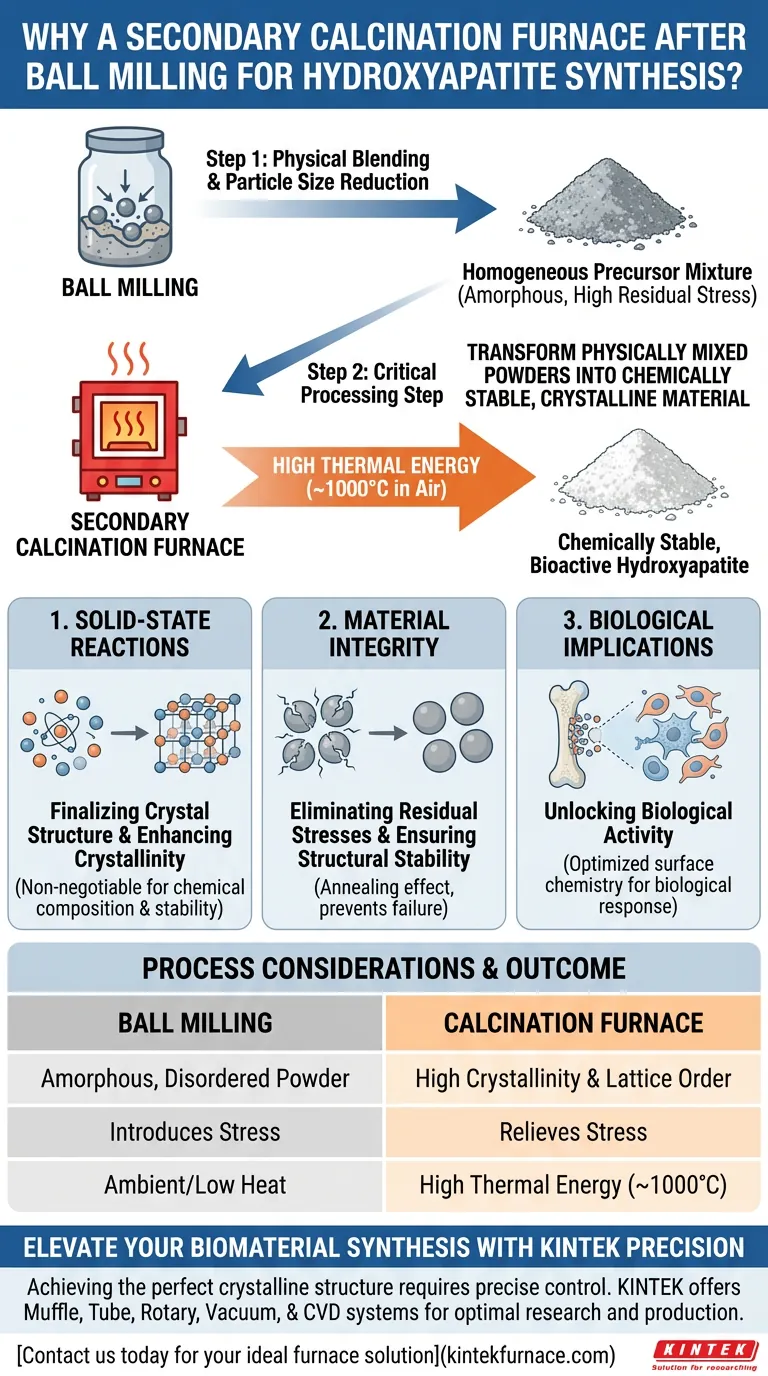
The secondary calcination furnace is the critical processing step required to transform physically mixed powders into a chemically stable, crystalline material. While ball milling blends the precursors, the furnace provides the high thermal energy—typically around 1000°C in an air atmosphere—needed to drive solid-state reactions and finalize the hydroxyapatite crystal structure.
This thermal treatment acts as the definitive phase transformation stage. It converts a raw ground mixture into a usable material by driving crystallization, relieving mechanical stress, and ensuring the final powder possesses the necessary biological and structural integrity.
The Role of Solid-State Reactions
Finalizing the Crystal Structure
Ball milling effectively creates a homogeneous mixture, but it does not fully complete the chemical bonding process. The secondary calcination furnace induces solid-state reactions at high temperatures.
These reactions allow atoms to diffuse and arrange themselves into the correct lattice structure. This step is non-negotiable for achieving the actual chemical composition of hydroxyapatite.
Enhancing Crystallinity
The thermal energy provided by the furnace significantly enhances the crystallinity of the product.
Without this high-temperature treatment, the material may remain partially amorphous or disordered. High crystallinity is directly linked to the material's stability and performance in end-use applications.
Improving Material Integrity
Eliminating Residual Stresses
Mechanical processing, such as ball milling, introduces significant mechanical energy into the powder, leading to residual stresses within the particles.
The calcination process acts as an annealing stage. The heat creates a relaxation effect, effectively eliminating these internal stresses and preventing future mechanical failure or unpredictability in the material.
Ensuring Structural Stability
To function correctly as a biomaterial, the hydroxyapatite powder must have structural stability.
The furnace treatment consolidates the powder particles and stabilizes the phases. This ensures the powder maintains its integrity during subsequent handling or forming processes.
Biological Implications
Unlocking Biological Activity
The primary reference highlights that this thermal treatment ensures the powder possesses the necessary biological activity.
The interaction between hydroxyapatite and biological tissue depends heavily on the surface chemistry and crystal phase. Calcination ensures the material properties are optimized to elicit the correct biological response.
Understanding Process Considerations
Balancing Temperature and Energy
Achieving the necessary phase transformation requires reaching temperatures as high as 1000°C in an air atmosphere.
This implies a trade-off regarding energy consumption and processing time. Skimping on this thermal budget can result in incomplete reactions, while precise control is required to prevent overheating or phase decomposition.
The Necessity of Atmosphere Control
The process specifies an air atmosphere, indicating that the presence of oxygen or ambient air components is relevant to the reaction or stability of the material.
Incorrect atmospheric conditions during this high-temperature phase could potentially alter the stoichiometry or color of the final hydroxyapatite product.
Optimizing the Synthesis Process
To ensure you produce high-quality hydroxyapatite, consider your specific end-goals when configuring your calcination parameters.
- If your primary focus is biological performance: Ensure the temperature is sufficient to maximize crystallinity, as this dictates the material's bioactive potential.
- If your primary focus is mechanical reliability: Prioritize the thermal soak time to fully eliminate residual stresses introduced during the milling phase.
By strictly controlling the secondary calcination environment, you guarantee a product that is both chemically stable and biologically effective.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role of Ball Milling | Role of Calcination Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Physical blending & particle size reduction | Chemical bonding & phase transformation |
| Crystallinity | Often results in amorphous/disordered powder | Induces high crystallinity and lattice order |
| Internal Stress | Introduces mechanical residual stress | Relieves stress through thermal annealing |
| Temperature | Ambient/Low heat from friction | High thermal energy (approx. 1000°C) |
| Outcome | Homogeneous precursor mixture | Chemically stable, bioactive hydroxyapatite |
Elevate Your Biomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect crystalline structure in hydroxyapatite requires more than just heat—it requires precise atmospheric control and thermal uniformity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as other lab high-temperature furnaces.
Whether you need to optimize bioactivity or ensure mechanical stability, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique research and production needs. Don't settle for incomplete phase transformations.
Contact us today to find your ideal furnace solution and take the first step toward superior material integrity.
Visual Guide
References
- Aseel Majid Habeeb, Nihad Abdul-Ameer Salih. Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite from Egg Shell Bio-Waste for Use in Functionally Graded NiTi/HA Bone Implants. DOI: 10.18280/acsm.480107
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a top-blown oxygen-nitrogen system? Precision Control for High-Yield Smelting
- What is the necessity of baking electrode sheets in a vacuum oven? Ensure Battery Stability and Peak Performance
- What is the purpose of post-treating Nitrogen-doped Carbide-Derived Carbon (N-CDC)? Optimize Purity & Performance
- What is the use of furnace in laboratory? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Control for Material Transformations
- How do industrial molds and 10 MPa pressure impact PEEK quality? Unlock Superior Density & Structural Integrity
- How does a PID intelligent segmented temperature control system impact diamond tools? Precision Sintering Explained
- What is the role of high-precision furnaces in Inconel 718 heat treatment? Master Microstructural Engineering
- What advantages does a vacuum drying oven offer for Fe-N-BC catalysts? Protect Integrity and Improve Uniformity



















