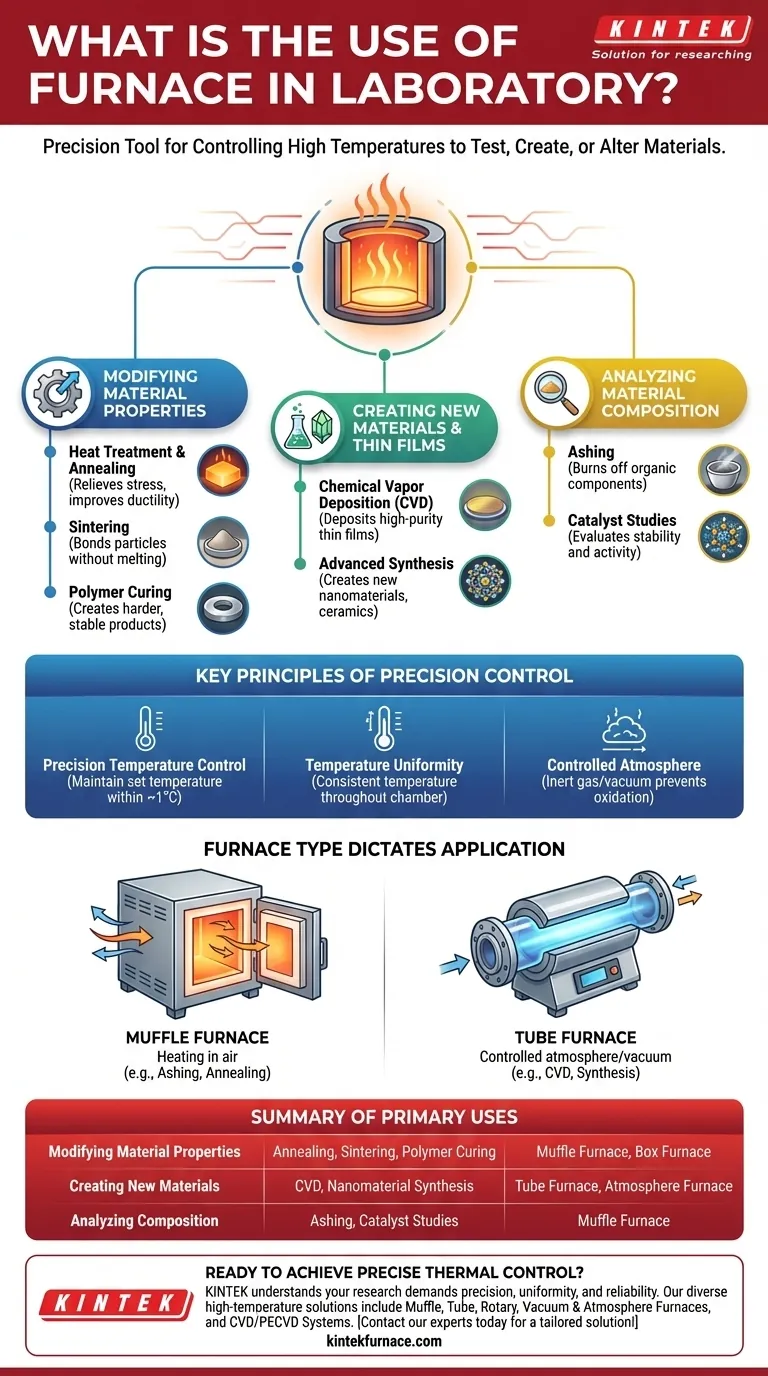
At its core, a laboratory furnace is a tool for precisely controlling high temperatures to test, create, or fundamentally alter the physical and chemical properties of materials. Unlike a simple oven, a lab furnace provides a highly uniform and stable thermal environment, which is essential for obtaining repeatable and reliable results in research, development, and quality control.
A laboratory furnace is not just a heat source; it is a precision instrument. Its primary use is to enable specific, repeatable material transformations—from creating new nanomaterials to analyzing composition—that are only possible within a tightly controlled thermal environment.

Modifying Material Properties
One of the most common uses for a laboratory furnace is to intentionally change the intrinsic properties of a material through carefully managed heat. This process, known as heat treatment, is fundamental in materials science and metallurgy.
Heat Treatment and Annealing
This process involves heating a material (often metal or glass) to a specific temperature and then cooling it at a controlled rate. The goal is to relieve internal stresses, improve ductility, and reduce hardness, making the material easier to work with.
Sintering for Material Creation
In powder metallurgy and ceramics, fine powders are heated to a temperature just below their melting point. This causes the particles to bond together, forming a solid, dense object without liquefying the material.
Polymer Curing and Baking
Specialized furnaces are used to cure polymers or bake materials like polyimide. The precise application of heat initiates a chemical reaction that creates a harder, more stable, and durable final product.
Creating New Materials and Thin Films
Beyond modifying existing materials, furnaces are critical tools for synthesizing entirely new substances, often with unique and valuable properties. These processes typically occur within specialized tube furnaces that allow for a controlled atmosphere.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a process where a furnace is used to heat a substrate (like a silicon wafer). Gaseous chemicals react in the hot zone and deposit a high-purity, high-performance thin film onto the substrate's surface.
Synthesis of Advanced Materials
Furnaces are used for thermal decomposition studies to create new oxide, nitride, or carbide materials. They are also central to the synthesis of nanomaterials and advanced ceramics, where temperature dictates the final structure and properties.
Analyzing Material Composition
Furnaces are also indispensable analytical tools used to determine what a sample is made of. By observing how a material behaves under extreme heat, researchers can deduce its composition.
Ashing for Content Analysis
A muffle furnace, which heats a sample in the presence of air, is used to burn off all organic and volatile components. The remaining non-combustible material, or ash, is weighed to determine the proportion of inorganic content in the original sample.
Catalyst and Decomposition Studies
By heating a material in a controlled environment, researchers can evaluate the stability and activity of catalysts or study the exact temperatures at which a compound breaks down, providing critical data for chemical research.
Understanding the Key Principles
The reason a laboratory furnace is used over a simpler heat source like a Bunsen burner comes down to one word: control. The value of a furnace lies in its ability to manage the heating environment with extreme precision.
Precision Temperature Control
A laboratory furnace can maintain a set temperature, often within a single degree, for extended periods. This precision is non-negotiable for experiments where slight temperature variations could ruin the outcome.
Temperature Uniformity
High-quality furnaces ensure that the temperature is consistent throughout the entire heating chamber. This guarantees that every part of the sample receives the exact same thermal treatment, leading to uniform results.
Controlled Atmosphere
Many advanced applications, especially in a tube furnace, require the removal of air to prevent oxidation. These systems can be filled with an inert gas (like argon) or put under a vacuum, creating an ideal environment for sensitive chemical reactions.
Furnace Type Dictates Application
The choice between a muffle furnace and a tube furnace is critical. Muffle furnaces are perfect for heating in air, such as for ashing. Tube furnaces excel when a controlled atmosphere or vacuum is necessary, as in CVD or advanced material synthesis.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, match the furnace's capability to your specific scientific or industrial objective.
- If your primary focus is analyzing composition: You will use a muffle furnace for ashing to determine the non-combustible content of a sample.
- If your primary focus is improving a material: You will use a furnace for heat treatment processes like annealing to make a material stronger or more ductile.
- If your primary focus is creating something new: You will use a tube furnace for sintering powders or synthesizing advanced materials and thin films via CVD.
- If your primary focus is electronics manufacturing: You will use a furnace for diffusion, doping, and oxidation to create functional semiconductor components.
Ultimately, the laboratory furnace provides the controlled thermal energy required to unlock the potential hidden within materials.
Summary Table:
| Primary Use | Key Processes | Typical Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| Modifying Material Properties | Annealing, Sintering, Polymer Curing | Muffle Furnace, Box Furnace |
| Creating New Materials | CVD, Nanomaterial Synthesis | Tube Furnace, Atmosphere Furnace |
| Analyzing Composition | Ashing, Catalyst Studies | Muffle Furnace |
Ready to achieve precise thermal control for your lab?
At KINTEK, we understand that your research demands more than just heat—it requires precision, uniformity, and reliability. Whether you are modifying materials through annealing, synthesizing new substances with CVD, or analyzing composition via ashing, the right furnace is critical to your success.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Let's discuss how a KINTEK furnace can be the precision instrument your lab needs. Contact our experts today for a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is the thermal stability of KBaBi compounds evaluated? Discover Precise XRD & Heat Treatment Limits
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace contribute to the thermal treatment process of chalcopyrite ore?
- What is the core function of a muffle furnace in biomass activation? Optimize Carbonization & Pore Development



















