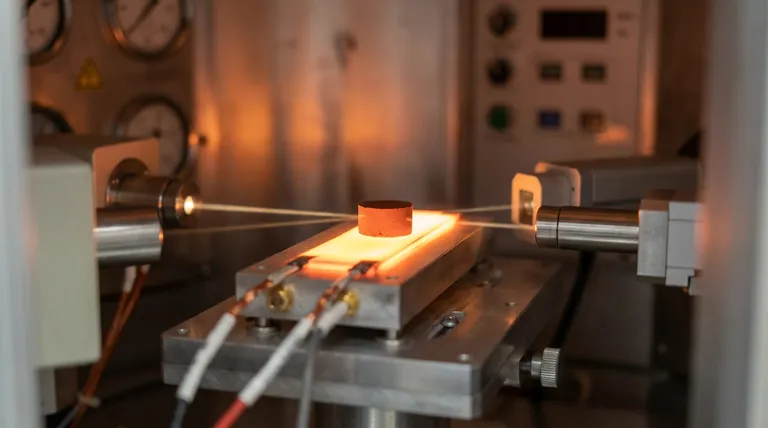
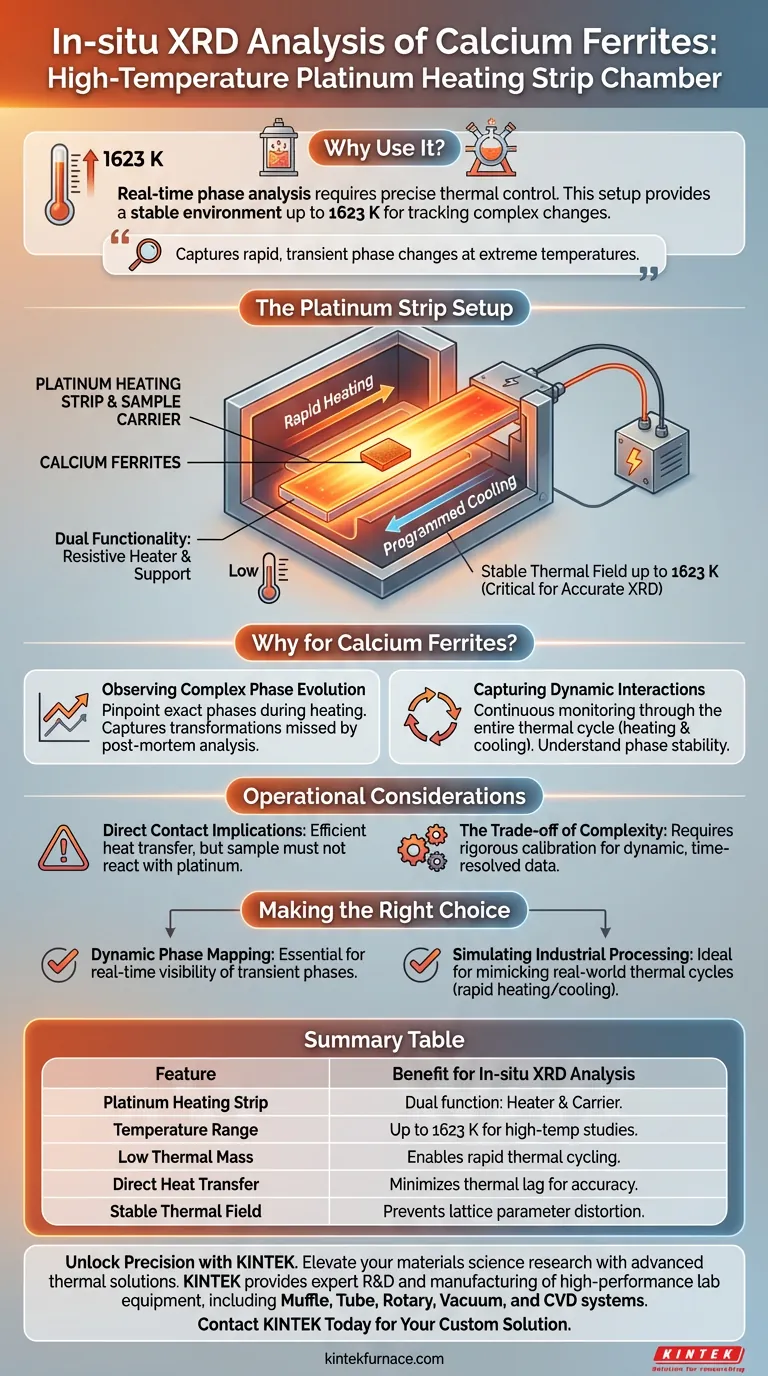
Real-time phase analysis requires precise thermal control. A high-temperature reaction chamber with a platinum heating strip is utilized to create a stable environment capable of reaching temperatures as high as 1623 K. This setup is essential for observing calcium ferrites because the platinum strip functions as both the heating element and the sample carrier, enabling the rapid heating and programmed cooling necessary to track complex structural changes as they occur.
The study of calcium ferrites involves capturing rapid, transient phase changes at extreme temperatures. By utilizing a platinum strip for both support and heat generation, researchers ensure the direct thermal transfer and stability required to visualize this evolution in real-time.
The Mechanics of the Platinum Strip Setup
Dual Functionality for Efficiency
In this specialized configuration, the platinum heating strip serves a dual purpose.
It acts as the physical support carrier for the sample while simultaneously functioning as the resistive heating element. This integration eliminates the need for external furnaces, allowing for a more compact and responsive system.
Achieving High-Temperature Stability
The primary advantage of this chamber is its ability to generate a stable thermal field up to 1623 K.
Maintained stability at these extremes is critical for X-ray diffraction (XRD), as even minor fluctuations can distort lattice parameter measurements. The platinum strip provides the consistency required for accurate high-temperature data collection.
Precision Control of Thermal Cycles
The low thermal mass of the strip allows for rapid heating and programmed cooling.
Researchers are not limited to static temperatures; they can simulate specific thermal histories. This control allows for the precise replication of reaction conditions relevant to the formation of calcium ferrites.
Why This Matters for Calcium Ferrites
Observing Complex Phase Evolution
Calcium ferrites undergo intricate structural transformations that are often missed by post-mortem (room temperature) analysis.
Using this in-situ method allows researchers to observe complex phase evolution as it happens. You can pinpoint exactly when specific phases appear or disappear during the heating process.
Capturing Dynamic Interactions
The setup captures data throughout the entire thermal cycle, including the cooling phase.
This continuous monitoring is vital for understanding how high-temperature phases stabilize or degrade as the material cools. It provides a complete picture of the material's lifecycle rather than just a snapshot of the end product.
Understanding the Operational Considerations
Direct Contact Implications
Because the platinum strip acts as the sample carrier, the sample is in direct contact with the heating source.
This ensures efficient heat transfer, minimizing the lag between the programmed temperature and the actual sample temperature. However, it requires that the sample material does not chemically react with the platinum at high temperatures.
The Trade-off of Complexity
Implementing in-situ analysis is inherently more complex than standard ex-situ XRD.
It requires rigorous calibration of the thermal field and precise control of environmental conditions. This complexity is the "cost" of obtaining dynamic, time-resolved data that standard methods cannot provide.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
To determine if this experimental setup aligns with your objectives, consider the specific nature of your investigation into calcium ferrites.
- If your primary focus is dynamic phase mapping: This setup is essential. It provides the real-time visibility needed to document transient phases and transition temperatures up to 1623 K.
- If your primary focus is simulating industrial processing: The ability to execute rapid heating and programmed cooling makes this the ideal choice for mimicking real-world thermal cycles.
This approach transforms XRD from a static characterization tool into a dynamic window into material synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for In-situ XRD Analysis |
|---|---|
| Platinum Heating Strip | Functions as both resistive heating element and sample carrier. |
| Temperature Range | Reaches up to 1623 K for high-temperature material studies. |
| Low Thermal Mass | Enables rapid heating and programmed cooling for thermal history simulation. |
| Direct Heat Transfer | Minimizes thermal lag for accurate real-time phase mapping. |
| Stable Thermal Field | Prevents lattice parameter distortion for high-precision data. |
Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Research with KINTEK
Elevate your materials science research with advanced thermal solutions designed for the most demanding applications. KINTEK provides expert R&D and manufacturing of high-performance lab equipment, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are conducting in-situ XRD analysis or complex material synthesis, our customizable high-temperature furnaces deliver the stability and control your data requires.
Ready to optimize your lab’s heating capabilities? Contact KINTEK Today to Discuss Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- <i>In-Situ</i> X-ray Diffraction Analysis Reveals Complex Calcium Ferrite Phase Formation during Heating and Cooling of Silico-Ferrite of Calcium (SFC) Compositions. DOI: 10.2355/isijinternational.isijint-2025-121
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why use 10% Carbon Monoxide in black liquor pyrolysis? Prevent sodium volatilization for superior char quality.
- What problem does a fluidized bed address in ceramic molds? Ensure Uniform Shells for High-Temp Casting
- What role does an ultrafast Joule heating device play in the synthesis of heterostructure nanocatalysts?
- What is the primary purpose of operating a laboratory oven at 383 K for 24 hours? Precision Drying for Carbon Prep
- How does temperature control in carbonization furnaces affect structural battery anodes? Optimize Fiber Performance
- What type of furnace was chosen for annealing silicon-based materials and what were the key requirements? Discover the Ideal Solution for Precise Heat Treatment
- What is the significance of the vacuum oven drying process in the preparation of MnO@WAC electrode sheets? Expert Guide
- What are the typical applications of drying ovens? Essential Uses in Labs and Industry



















