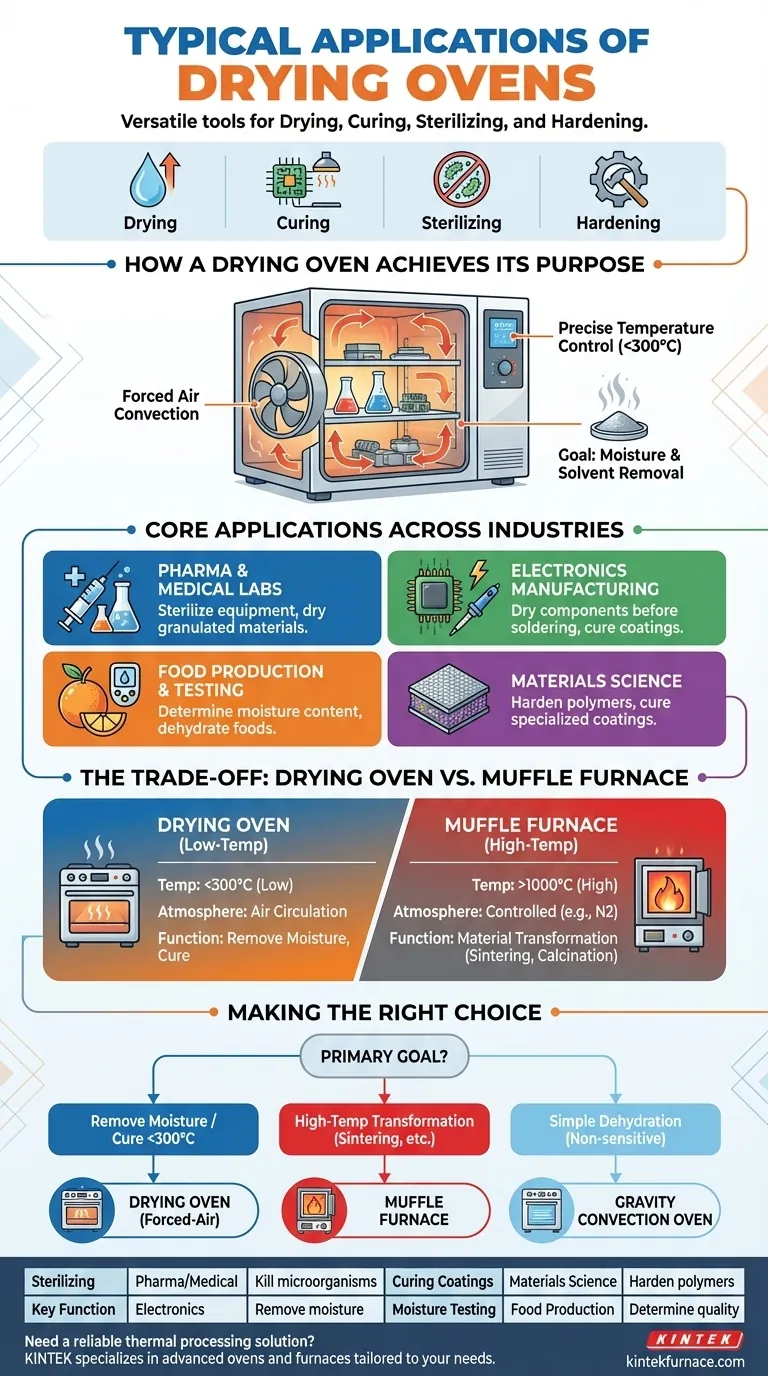
In short, a drying oven is a versatile laboratory and industrial tool used for four primary functions: drying, curing, sterilizing, and hardening materials. These ovens are essential in fields ranging from pharmaceuticals and medical labs to electronics manufacturing and food production, where precise thermal processing is required to remove moisture or trigger chemical changes.
The core purpose of a drying oven is to use heated, circulating air to achieve uniform temperature for removing moisture or curing materials. This makes it fundamentally different from a high-temperature furnace, which is designed for material transformation processes like sintering or calcination.

How a Drying Oven Achieves Its Purpose
Understanding the mechanism of a drying oven clarifies its applications. The design is not simply about generating heat, but about controlling it to achieve a specific outcome.
The Principle of Forced Convection
Most modern drying ovens use forced air convection. A fan actively circulates heated air throughout the chamber, ensuring a highly uniform temperature and eliminating "hot spots."
This constant airflow is critical for efficiently carrying moisture away from the surface of the items being dried.
Precise and Moderate Temperature Control
Drying ovens are engineered for stability and precision within a moderate temperature range, typically from slightly above ambient up to around 300°C (572°F).
This control is vital for processes where overheating could damage the sample, such as when working with sensitive electronics, biological materials, or specific polymers.
The Goal is Moisture and Solvent Removal
The fundamental goal is to drive out volatile substances, primarily water, from a sample. This could be for sterilizing lab equipment, preparing a pharmaceutical powder, or curing a coating by evaporating its solvent base.
Core Applications Across Industries
The combination of uniform heat and moisture removal makes drying ovens indispensable in a variety of technical settings.
In Pharmaceutical and Medical Labs
Ovens are used to sterilize glass- and metalware, which requires holding them at a specific temperature for a set time to kill all microorganisms. They are also used for drying granulated materials or powders during drug formulation.
In Electronics Manufacturing
Moisture is a critical enemy of electronic components. Ovens are used to dry components before soldering to prevent damage and to cure adhesives, epoxies, and coatings used to protect circuit boards.
In Food Production and Testing
In a quality control lab, ovens are used to determine the moisture content of food products, a key quality parameter. They are also used on a larger scale for dehydrating foods like fruits and vegetables for preservation.
In Materials Science and Engineering
Engineers use drying ovens to harden polymers or cure specialized coatings on material samples. This allows them to test the properties of materials after undergoing a controlled thermal process.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Drying Oven vs. Muffle Furnace
A common point of confusion is the difference between a drying oven and a furnace. Choosing the wrong tool can lead to failed processes or damaged equipment.
Temperature Range Defines the Tool
A drying oven is a low-temperature device. A muffle furnace is a high-temperature device, capable of reaching 1000°C and beyond.
If your process involves melting metals, sintering ceramics, or performing ash content analysis, a furnace is the necessary tool.
Atmosphere Makes the Difference
A drying oven almost always operates in a standard air atmosphere. Its goal is to circulate that air.
A muffle furnace is often used for processes that require a controlled atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation at extreme temperatures. Its design is focused on insulating the sample and containing that atmosphere.
Function: Drying vs. Transforming
Use a drying oven to remove moisture or cure a coating. Its purpose is to prepare a sample.
Use a muffle furnace to fundamentally transform a material's chemical or physical state, such as in calcination, annealing, or sintering processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct equipment, you must be clear about your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture, sterilizing equipment, or curing coatings below 300°C: A standard forced-air drying oven is the correct and most efficient tool.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material transformation like sintering, annealing, or ashing: You require a muffle furnace, as a drying oven cannot reach the necessary temperatures.
- If your primary focus is simply dehydrating a non-sensitive sample without a strict need for temperature uniformity: A less expensive gravity convection oven may be sufficient.
Ultimately, choosing the right thermal processing tool is about matching its core function to your specific scientific or industrial objective.
Summary Table:
| Application | Industry | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilizing | Pharmaceutical/Medical | Kill microorganisms on equipment |
| Drying Components | Electronics | Remove moisture before soldering |
| Curing Coatings | Materials Science | Harden polymers and adhesives |
| Moisture Content Testing | Food Production | Determine quality parameters |
Need a reliable thermal processing solution? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnaces and drying ovens tailored to your needs. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique requirements in pharmaceuticals, electronics, food, and materials science. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a box-type high-temperature furnace contribute to 6Mo stainless steel? Optimize Solution Treatment Now
- How are a muffle furnace and ceramic crucible used for MoO3? Master High-Purity Synthesis Today
- Why is it necessary to dry glassware in a 140 °C oven overnight before GTP? Ensure Precise Anhydrous Polymerization
- What role do high-precision laboratory ovens play in assessing the energy potential of MSW? Enhancing Biomass Accuracy
- Why is dual heat treatment required for SnO2 nanoparticles? Optimize Oxidation for Superior Performance



















