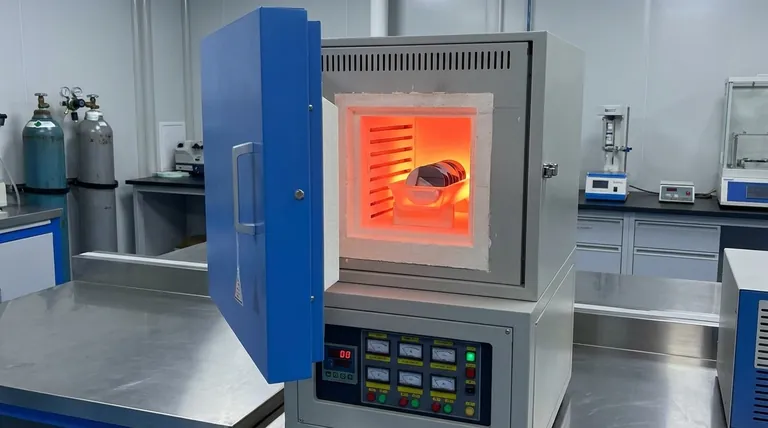
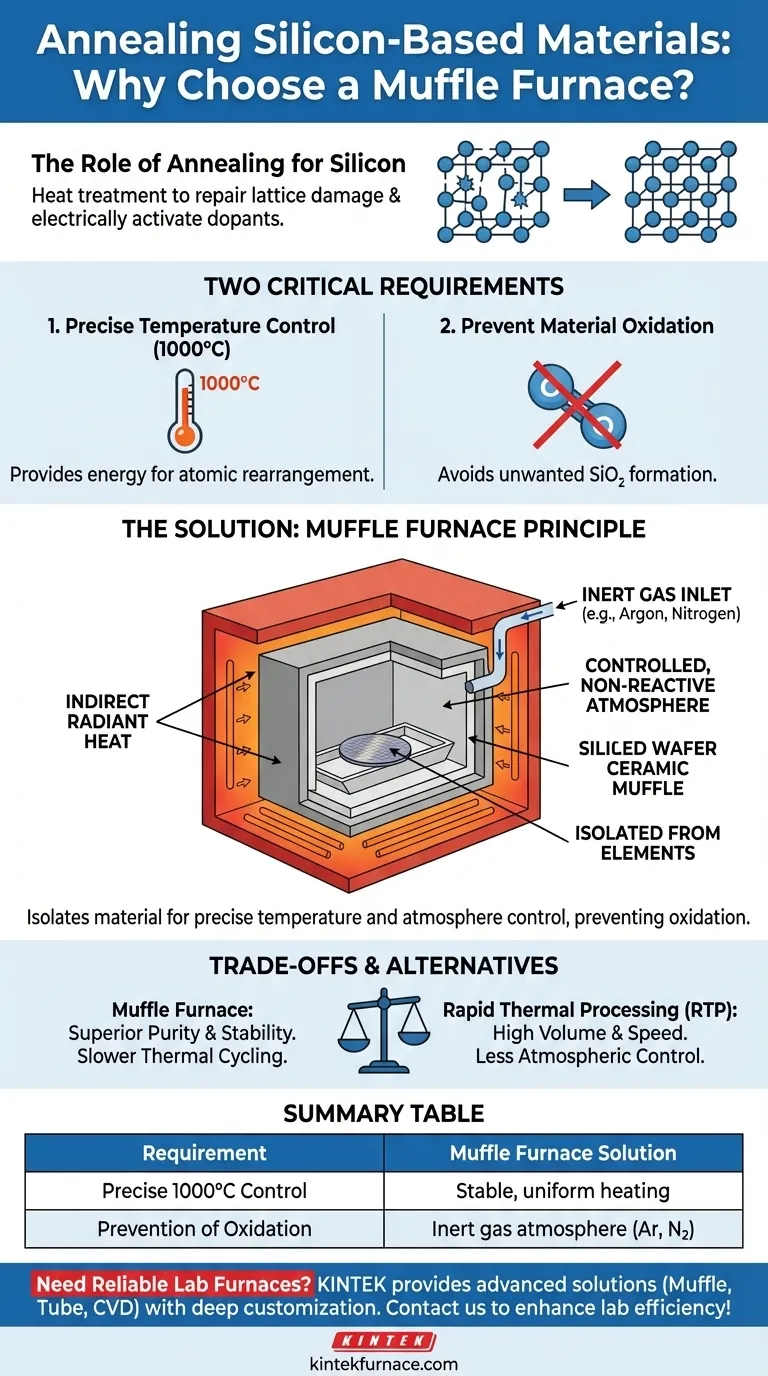
For the annealing of silicon-based materials, a muffle furnace was selected. This choice was driven by two critical operational requirements: the ability to maintain a precise and stable temperature around 1000°C and the necessity of preventing the material from oxidizing during this high-temperature process.
The core challenge in heat-treating silicon is not just reaching a high temperature, but doing so in a clean, non-reactive environment. A muffle furnace is chosen because it isolates the material from the heating elements, enabling precise control over both temperature and the surrounding atmosphere to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.

The Role of Annealing for Silicon
Annealing is a foundational heat treatment process used to alter the microstructure of a material, thereby changing its mechanical or electrical properties.
What is Annealing?
At its core, annealing involves heating a material to a specific temperature, holding it there for a period, and then cooling it in a controlled manner. This process allows the material's internal atomic structure to rearrange, relieving internal stresses and repairing microscopic defects.
Why Anneal Silicon?
In semiconductor fabrication, silicon wafers undergo processes like ion implantation that damage their crystalline structure. Annealing is critical to repair this lattice damage and to electrically "activate" the implanted dopant atoms, which is essential for creating functional transistors and integrated circuits.
Deconstructing the Core Requirements
The success of annealing silicon hinges on meeting two non-negotiable conditions.
Requirement 1: Precise Temperature Control at 1000°C
A temperature of approximately 1000°C provides enough thermal energy to allow silicon atoms and dopants in the crystal lattice to move and settle into more stable, ordered positions.
If the temperature is too low, the atomic diffusion is insufficient, and the annealing process is ineffective. If it is too high or unstable, it can cause defects or damage the delicate structures already fabricated on the wafer.
Requirement 2: Preventing Material Oxidation
Silicon reacts readily with oxygen at high temperatures to form a layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
While a controlled, high-quality SiO₂ layer is a fundamental component in microelectronics (acting as an insulator), uncontrolled oxidation during annealing is detrimental. It contaminates the material, alters its electrical properties unpredictably, and ruins device performance.
Why a Muffle Furnace Is the Solution
A muffle furnace is specifically designed to meet the dual requirements of temperature control and atmospheric purity.
The Principle of Isolation
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is its internal chamber, or "muffle," which is a separate, sealed container that holds the material being treated. The heating elements are located outside this muffle.
This design is analogous to placing food in a sealed ceramic pot and then placing that pot inside a larger oven. The heat radiates through the walls of the pot to cook the food without exposing it to the oven's direct environment.
Enabling Atmospheric Control
Because the silicon is isolated within the muffle, the atmosphere inside can be tightly controlled. Standard air can be pumped out and replaced with a high-purity inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen.
This inert atmosphere lacks the oxygen needed for oxidation, effectively protecting the silicon material even at extreme temperatures.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
The indirect heating method of a muffle furnace promotes excellent temperature stability and uniformity across the entire chamber. Radiant heat from the surrounding elements warms the muffle's walls evenly, ensuring every part of the silicon material experiences the same thermal conditions, which is vital for consistent results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, the muffle furnace is not without its operational considerations.
Slower Thermal Cycling
Because heat must transfer indirectly through the muffle walls, these furnaces typically have slower heating (ramp-up) and cooling rates compared to systems with direct heating.
Potential Throughput Limits
Muffle furnaces are often used for batch processing. For high-volume manufacturing, alternative technologies like Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) may be favored for their much faster cycle times, though they present different control challenges.
Material and Purity Concerns
In ultra-high purity applications, the material of the muffle itself (typically a ceramic) must be chosen carefully to prevent any outgassing or particle shedding that could contaminate the silicon wafer at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the appropriate heat treatment method requires aligning the technology with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is process stability and purity for research or specialized production: A muffle furnace is an excellent choice for its superior atmospheric control and temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is high-volume throughput and speed: Investigate Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) systems, which use high-intensity lamps for extremely fast heating cycles measured in seconds rather than hours.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is a direct result of understanding your material's sensitivities and your process's specific goals for purity, speed, and scale.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | Solution Provided by Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|
| Precise Temperature Control at 1000°C | Ensures stable, uniform heating for effective atomic rearrangement and defect repair in silicon. |
| Prevention of Material Oxidation | Uses inert gas atmospheres (e.g., argon, nitrogen) to isolate silicon and avoid unwanted SiO₂ formation. |
Need a reliable furnace for your silicon annealing or other high-temperature processes? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for purity, temperature control, and scalability. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve consistent results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















