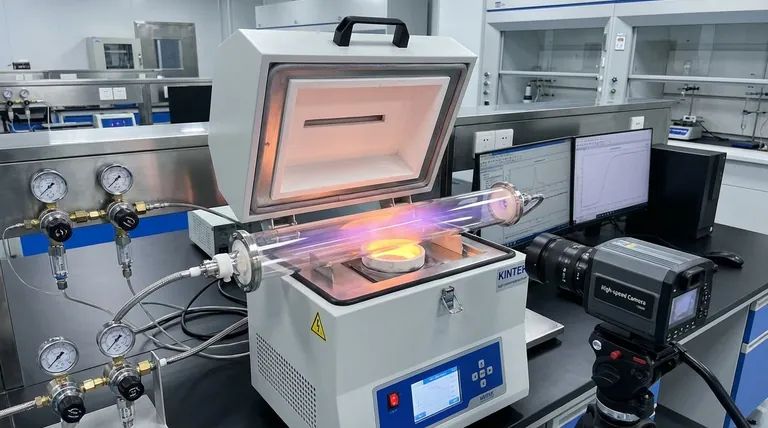
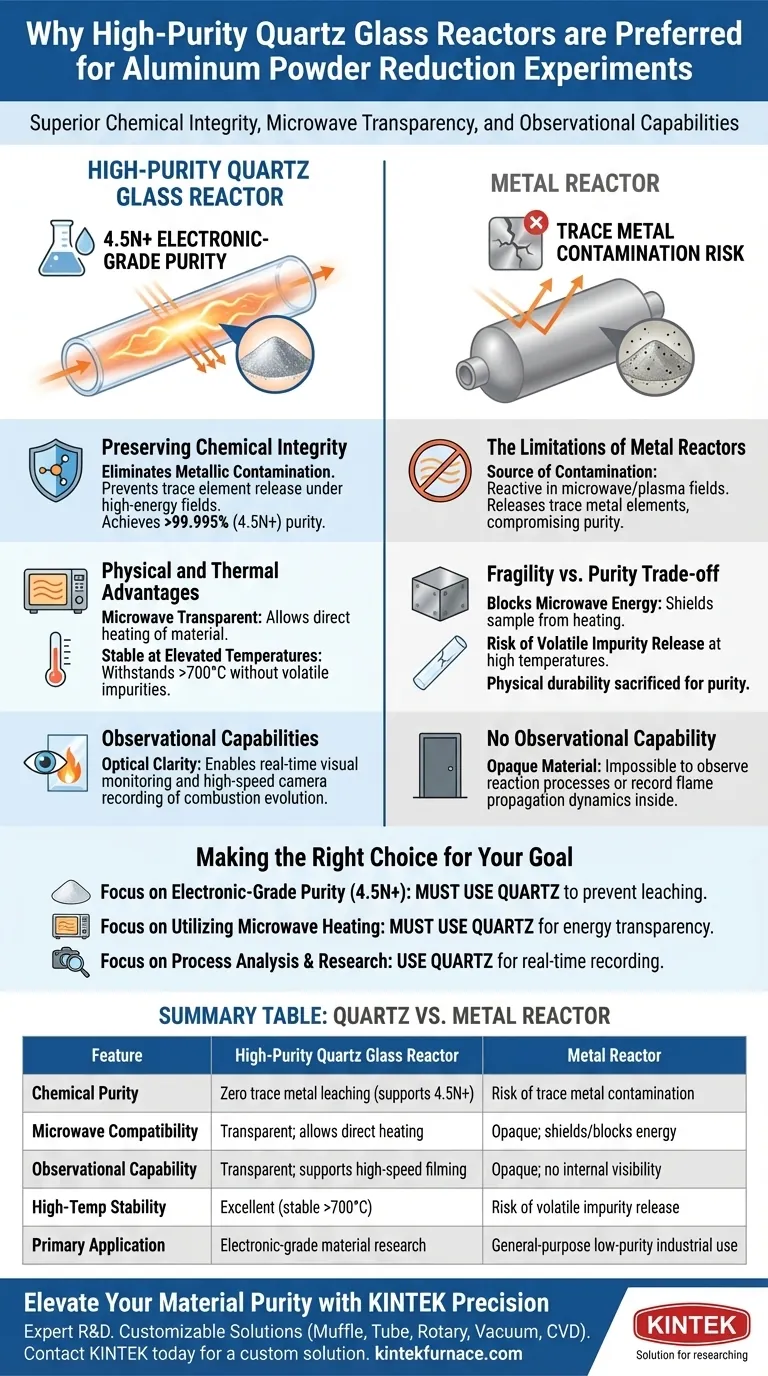
High-purity quartz glass is the preferred material for aluminum powder reduction because it eliminates the risk of metallic contamination inherent to metal reactors. It allows researchers to achieve electronic-grade purity while remaining compatible with advanced microwave and plasma heating techniques.
To achieve aluminum powder with a purity of 99.995% (4.5N) or higher, the reaction environment must be chemically inert and transparent to electromagnetic energy. Quartz satisfies these strict requirements, whereas metal reactors introduce trace impurities and interfere with microwave fields.

Preserving Chemical Integrity
Preventing Contamination in High-Energy Fields
The primary driver for choosing quartz is the need to eliminate impurities. In environments utilizing microwave energy fields or plasma discharges, metal reactors can become reactive.
The Risk of Trace Element Release
Under these high-energy conditions, a metal reactor may release trace metal elements into the aluminum powder. High-purity quartz provides excellent chemical inertness, acting as a barrier that prevents this cross-contamination.
Achieving Electronic-Grade Standards
This inertness is not merely a preference; it is a requirement for high-end applications. Using quartz ensures the reduced aluminum powder meets the rigorous electronic-grade purity standard of 4.5N or higher.
Physical and Thermal Advantages
Microwave Transparency
Beyond chemical properties, quartz allows for specific heating methods that metal cannot support. High-purity quartz is transparent to microwaves, allowing energy to pass through the reactor walls to heat the material directly.
Stability at Elevated Temperatures
Reduction experiments often require intense heat to be effective. High-purity quartz tubes possess exceptional high-temperature resistance, capable of withstanding operating temperatures exceeding 700°C.
preventing Volatile Impurities
Even at these high temperatures, high-purity quartz remains stable. Unlike lower-grade materials or certain metals, it does not release volatile impurities that could degrade the quality of the aluminum powder.
Observational Capabilities
Optical Transparency for Monitoring
A distinct advantage of quartz over metal is its optical clarity. The transparency of the glass allows researchers to observe the reduction process in real-time.
Recording Combustion Evolution
This visibility enables the use of external high-speed cameras to record critical reaction data. Researchers can study combustion evolution and flame propagation mechanisms, which is impossible inside an opaque metal vessel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Limitations of Metal Reactors
While metal reactors are typically robust, they are fundamentally unsuitable for high-purity, microwave-assisted reduction. They block microwave energy and act as a source of contamination, compromising the chemical composition of the final product.
Fragility vs. Purity
The trade-off in using quartz is physical fragility compared to metal. However, for applications requiring 4.5N purity, the mechanical durability of metal is sacrificed to gain the essential chemical inertness and electromagnetic transparency of quartz.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your experimental setup aligns with your specific objectives, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is achieving electronic-grade purity (4.5N+): You must use high-purity quartz to prevent trace metal elements from leaching into your sample during plasma or microwave exposure.
- If your primary focus is utilizing microwave heating: You must use quartz due to its microwave transparency, as metal reactors will shield the sample from the energy field.
- If your primary focus is process analysis and research: You should use quartz to leverage its optical transparency for real-time camera recording of flame spread and combustion dynamics.
Ultimately, high-purity quartz is the only viable option when the goal is combining high-temperature resilience with absolute chemical isolation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | High-Purity Quartz Glass Reactor | Metal Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Purity | Zero trace metal leaching (supports 4.5N+) | Risk of trace metal contamination |
| Microwave Compatibility | Transparent; allows direct heating | Opaque; shields/blocks energy |
| Observational Capability | Transparent; supports high-speed filming | Opaque; no internal visibility |
| High-Temp Stability | Excellent (stable > 700°C) | Risk of volatile impurity release |
| Primary Application | Electronic-grade material research | General-purpose low-purity industrial use |
Elevate Your Material Purity with KINTEK Precision
Don't let reactor contamination compromise your research results. At KINTEK, we understand that achieving 4.5N electronic-grade purity requires the perfect balance of chemical inertness and thermal stability.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized high-purity quartz solutions. Our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring absolute chemical isolation and precise microwave transparency.
Ready to optimize your reduction experiments?
Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution
Visual Guide
References
- Alexander Logunov, Sergey S. Suvorov. Plasma–Chemical Low-Temperature Reduction of Aluminum with Methane Activated in Microwave Plasma Discharge. DOI: 10.3390/met15050514
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What manufacturing processes rely on laboratory furnaces? Precision Heat Treatment for Advanced Materials
- How does the choice of high-purity ceramic crucibles impact glass phantoms? Unlock Optical Precision in Sintering
- What is the role of a vacuum pass-box and a high-capacity vacuum pump? Ensuring Safety in Battery Recycling
- Why is rhenium selected as a material for sample capsules? Key Benefits for High-Temperature Experimental Success
- Why are alumina crucibles and mother-powder necessary for LLZO sintering? Ensure High Ionic Conductivity
- What are the primary functions of high-purity graphite crucibles? Optimize Mg-Zn-xSr Alloy Purity and Efficiency
- What are the common uses for Alumina ceramic tubes? Ideal for High-Temp, Insulation, and Corrosion Resistance
- What is the primary function of a vacuum-sealed quartz tube in MnBi2Te4 growth? Ensure High-Purity Crystal Synthesis



















