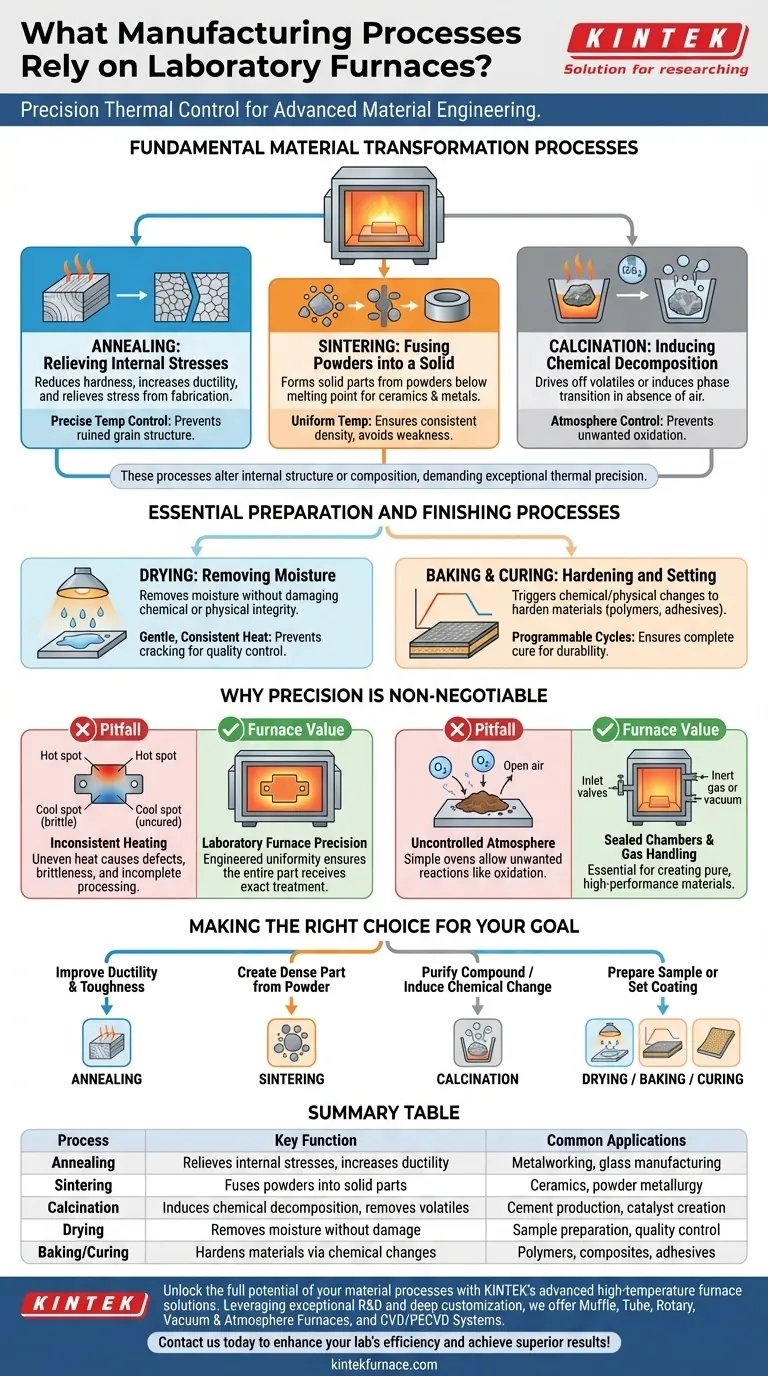
At their core, laboratory furnaces are indispensable for manufacturing processes that fundamentally alter a material's internal structure or composition. Key processes include annealing, sintering, calcination, and sample preparation steps like drying, baking, and curing, all of which demand exceptionally precise thermal control to achieve desired outcomes.
The critical function of a laboratory furnace is not simply heating, but creating a perfectly uniform and stable thermal environment. This precision is what allows manufacturers and researchers to reliably engineer materials with specific properties like enhanced strength, purity, or conductivity.
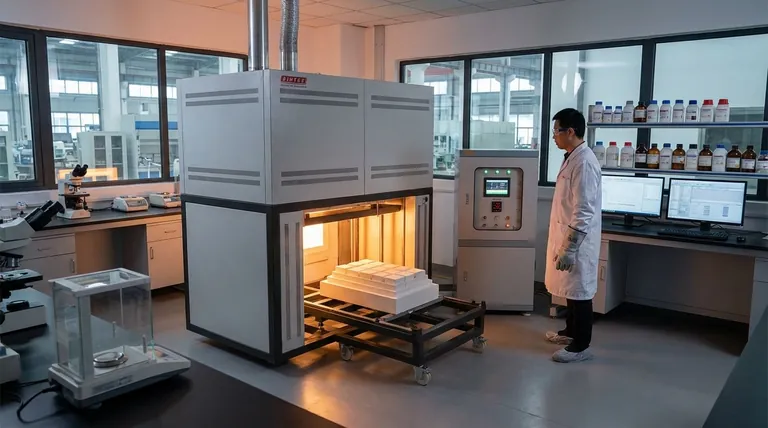

Fundamental Material Transformation Processes
Many advanced manufacturing techniques rely on furnaces to induce specific physical and chemical changes in materials. These processes are foundational in fields ranging from aerospace to electronics.
Annealing: Relieving Internal Stresses
Annealing involves heating a material to a specific temperature and then cooling it slowly. This process is used to reduce hardness, increase ductility, and relieve internal stresses that may have built up during fabrication.
The precise temperature control of a laboratory furnace is crucial. Too little heat will not relieve the stress, while too much can ruin the material's grain structure, making it weak.
Sintering: Fusing Powders into a Solid
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder by applying heat below its melting point. This is how many ceramic and metallic components are made.
Success in sintering depends on maintaining a uniform temperature throughout the material. Uneven heating leads to a component with inconsistent density and structural weaknesses, which a high-quality furnace prevents.
Calcination: Inducing Chemical Decomposition
Calcination involves heating a solid material to high temperatures in the absence of air to drive off volatile substances or induce a phase transition. It is essential for producing cement, removing water from hydrated minerals, and creating certain catalysts.
The furnace's ability to control both temperature and atmosphere is vital. This ensures the intended chemical reaction occurs without introducing unwanted oxidation or other side reactions.
Essential Preparation and Finishing Processes
Beyond core transformations, furnaces are critical for preparing samples for analysis or finishing components to meet final specifications.
Drying: Removing Moisture
Drying is the process of removing moisture from a sample using heat. In a laboratory or manufacturing setting, this must be done without damaging the sample's chemical or physical integrity.
A laboratory furnace provides gentle, consistent heat to ensure moisture is removed evenly, preventing the sample from cracking or degrading, which is critical for quality control and research.
Baking and Curing: Hardening and Setting
Baking and curing are processes that use heat to trigger a chemical or physical change, such as hardening a polymer, setting an adhesive, or strengthening a composite material.
These processes require a precise temperature-over-time profile. A programmable laboratory furnace can execute these complex heating cycles flawlessly, ensuring the material cures completely and develops its intended properties, like durability and chemical resistance.
Why Precision is Non-Negotiable
Using a simple oven or a less-controlled heat source is the most common pitfall in material processing. The value of a laboratory furnace is rooted in its ability to eliminate variables that lead to product failure.
The Impact of Temperature Uniformity
Inconsistent heating across a component is a primary cause of defects. A spot that is too hot can become brittle, while a spot that is too cool may not be fully cured or sintered. Laboratory furnaces are engineered for exceptional temperature uniformity, ensuring the entire part receives the exact same thermal treatment.
The Role of Atmospheric Control
Many advanced material processes, like calcination, require a specific atmosphere (e.g., inert gas or vacuum) to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation. Laboratory furnaces provide sealed chambers and gas-handling capabilities that are impossible to achieve with simpler heating equipment. This control is fundamental to creating pure, high-performance materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific process you need depends entirely on your end objective.
- If your primary focus is improving a metal's ductility and toughness: You need annealing to relieve internal stresses and refine the grain structure.
- If your primary focus is creating a dense, solid part from a powder: You require sintering to fuse the particles together under precise thermal control.
- If your primary focus is purifying a compound or inducing a chemical change: You will use calcination to burn off impurities or trigger decomposition in a controlled atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is preparing a sample for analysis or setting a coating: You will rely on drying, baking, or curing to remove moisture or initiate a chemical hardening process.
Ultimately, these processes rely on laboratory furnaces because creating advanced materials is a science of control, not just heat.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Relieves internal stresses, increases ductility | Metalworking, glass manufacturing |
| Sintering | Fuses powders into solid parts | Ceramics, powder metallurgy |
| Calcination | Induces chemical decomposition, removes volatiles | Cement production, catalyst creation |
| Drying | Removes moisture without damage | Sample preparation, quality control |
| Baking/Curing | Hardens materials via chemical changes | Polymers, composites, adhesives |
Unlock the full potential of your material processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















