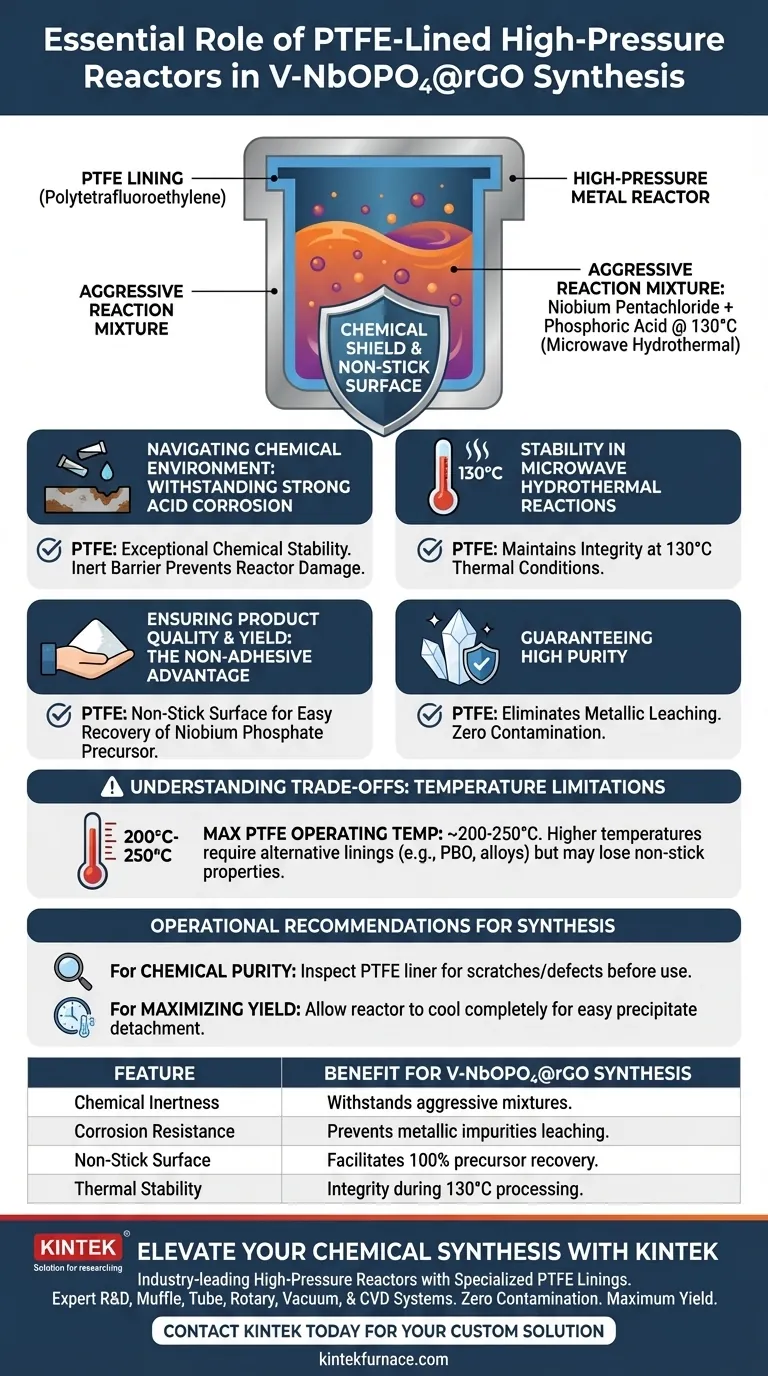
The use of a high-pressure reactor with a PTFE lining is non-negotiable for this synthesis due to the extreme chemical hostility of the reaction environment. This lining is specifically required to withstand the strongly acidic mixture generated by niobium pentachloride and phosphoric acid, preventing reactor corrosion and ensuring the final material is not contaminated by the vessel itself.
The PTFE lining acts as both a chemical shield against strong acids and a non-stick surface that facilitates the recovery of high-purity precipitates in the 130°C microwave hydrothermal environment.

Navigating the Chemical Environment
Withstanding Strong Acid Corrosion
The synthesis of V-NbOPO4@rGO involves a highly aggressive chemical mixture. The combination of niobium pentachloride and phosphoric acid creates a strongly acidic environment that would rapidly corrode standard metallic reactor walls.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers exceptional chemical stability. It serves as an inert barrier, ensuring the reactor structure remains intact despite the corrosive nature of the precursors.
Stability in Microwave Hydrothermal Reactions
This synthesis utilizes a microwave hydrothermal reaction carried out at 130°C.
While this temperature is moderate for some materials, the combination of heat and acidity increases the corrosive potential of the fluid. The PTFE lining maintains its structural integrity and protective qualities effectively under these specific thermal conditions.
Ensuring Product Quality and Yield
The Non-Adhesive Advantage
Beyond chemical resistance, physical recovery of the material is a critical challenge.
The precipitate formed—the niobium phosphate precursor—must be collected efficiently. The non-adhesive surface of the PTFE lining prevents the product from sticking to the reactor walls, significantly facilitating the collection process.
Guaranteeing High Purity
The ultimate goal of using a specialized liner is to protect the integrity of the V-NbOPO4@rGO.
By preventing the reaction mixture from interacting with the metal shell of the reactor, the PTFE lining eliminates the risk of metallic impurities leaching into the product. This ensures the high purity of the synthesized precursor.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Limitations
While PTFE is excellent for this specific reaction at 130°C, it is not a universal solution for all hydrothermal syntheses.
PTFE typically has a maximum operating temperature of around 200°C to 250°C before it softens or degrades. For reactions requiring significantly higher temperatures, alternative linings like PBO (Zylon) or specialized alloys would be required, though they may lack the same non-stick properties.
Operational Recommendations for Synthesis
To maximize the success of your V-NbOPO4@rGO synthesis, align your equipment choice with your specific outcome requirements.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Ensure the PTFE liner is inspected for scratches or defects before use, as any breach could allow acid to contact the metal vessel and introduce impurities.
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Yield: Utilize the non-stick properties of PTFE by allowing the reactor to cool completely before collection, which helps the precipitate detach easily from the smooth walls.
The correct reactor lining is not just a safety measure; it is a fundamental control variable for chemical purity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for V-NbOPO4@rGO Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Withstands aggressive niobium pentachloride and phosphoric acid mixtures. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Prevents metallic reactor walls from leaching impurities into the product. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Facilitates 100% recovery of the niobium phosphate precursor precipitates. |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains integrity during 130°C microwave hydrothermal processing. |
Elevate Your Chemical Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in material science starts with the right environment. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-pressure reactors and specialized laboratory equipment designed to withstand the most aggressive chemical reactions.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable hydrothermal reactors featuring high-purity PTFE linings. Whether you are synthesizing advanced V-NbOPO4@rGO composites or developing next-gen energy materials, our equipment ensures zero contamination and maximum yield.
Ready to optimize your lab’s high-temperature and high-pressure workflows?
Contact KINTEK Today to Discuss Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Zhongteng Chen, Zhipeng Sun. Tuning the Electronic Structure of Niobium Oxyphosphate/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites by Vanadium‐Doping for High‐Performance Na<sup>+</sup> Storage Application. DOI: 10.1002/cnl2.70010
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What role does a vertical air-circulating oven play in the drying stage of Cu2Co1-xNaxSnS4 thin films?
- What is the graphite furnace technique? A Guide to Ultra-Trace Metal Analysis
- Why is a standard constant temperature and humidity curing box used for magnesium slag mortar? Key Pre-treatment Facts
- Why is dual heat treatment required for SnO2 nanoparticles? Optimize Oxidation for Superior Performance
- What is the purpose of using an industrial oven for low-temperature drying? Expert Glass Processing Guide
- What is the function of planetary ball mills or industrial mixing granulators prior to RHF? Optimize FMDS Reactivity
- What are the specific functions of a flowing 5% H2/Ar gas mixture? Master Thermal Reduction of Nanoparticles
- What is the purpose of using a furnace at 500 °C for catalyst support pretreatment? Optimize Purity and Performance



















