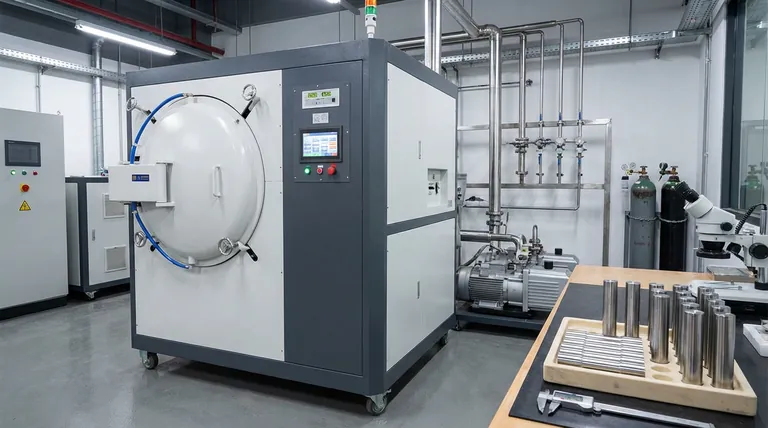
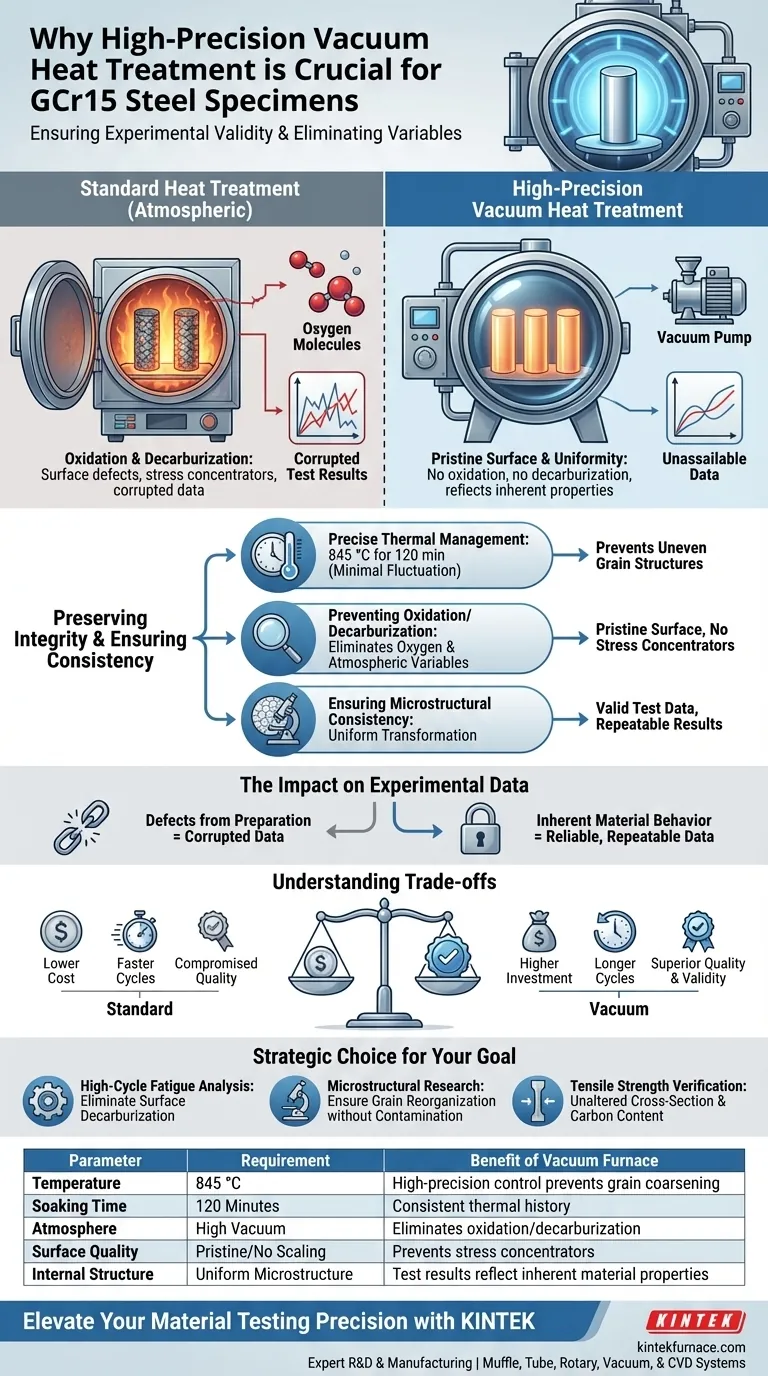
A high-precision vacuum heat treatment furnace is essential for GCr15 steel specimens to ensure the accuracy of fatigue and tensile test data. By maintaining a strict temperature profile—specifically heating at 845 °C for 120 minutes—within a vacuum environment, the process completely eliminates the risk of oxidation and decarburization. This safeguards the specimen's surface and internal structure, ensuring that test results reflect the steel's true properties rather than defects introduced during preparation.
The Core Value Experimental validity in fatigue testing relies on isolating the material's inherent behavior from processing artifacts. A vacuum furnace guarantees this by providing a contaminant-free environment and precise thermal control, ensuring that failure during testing is caused by the material's limits, not by heat treatment defects.

Preserving Surface and Structural Integrity
Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
Standard heat treatment environments expose steel to oxygen, leading to surface scaling (oxidation) and the loss of carbon (decarburization). For GCr15 steel, these surface defects can act as stress concentrators.
A vacuum furnace removes these atmospheric variables entirely. By eliminating oxygen, the furnace ensures the surface remains pristine during the critical heating phases.
Ensuring Microstructural Consistency
GCr15 steel requires specific mechanical strength and microstructural uniformity to yield valid test data. The furnace facilitates precise vacuum quenching and tempering protocols.
This controlled environment ensures that the transformation of the steel's microstructure is uniform throughout the cylindrical specimen.
Precise Thermal Management
The preparation of GCr15 specifically calls for maintaining a temperature of 845 °C for 120 minutes. High-precision furnaces are designed to hold these specific parameters with minimal fluctuation.
This strict adherence to thermal parameters prevents the formation of uneven grain structures that could skew tensile strength readings.
The Impact on Experimental Data
Isolating Inherent Characteristics
The primary goal of preparing these specimens is to study the material's fatigue resistance. If the heat treatment introduces defects, the resulting data is corrupted.
Using a high-precision vacuum furnace ensures that the observed fatigue behaviors are a result of the material's inherent structural characteristics. It removes the ambiguity of wondering if a failure was caused by the steel or a poor heat treatment process.
Repeatability and Reliability
Scientific testing demands repeatability. Industrial vacuum furnaces deliver consistent results by automating the environment and cooling rates.
This ensures that every specimen in a batch—and across multiple batches—possesses identical thermal history and physical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Operational Complexity and Cost
While vacuum furnaces offer superior quality, they represent a significant investment compared to standard atmospheric furnaces. The equipment is complex, requiring maintenance of vacuum seals and pumps to ensure the "ultra-clean" environment is not compromised.
Cycle Time Considerations
The process of pumping down to a high vacuum adds time to the overall heat treatment cycle. Unlike continuous atmospheric furnaces, vacuum processing is typically a batch operation, which may reduce throughput speed in favor of precision.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your GCr15 specimens yield valid scientific data, align your equipment choice with your specific testing requirements:
- If your primary focus is High-Cycle Fatigue Analysis: Use a high-precision vacuum furnace to eliminate surface decarburization, as surface defects significantly accelerate fatigue failure.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Research: Prioritize the vacuum environment to ensure grain reorganization and precipitation strengthening occur without oxide contamination.
- If your primary focus is Tensile Strength Verification: Rely on the vacuum furnace to ensure the cross-sectional area and carbon content remain unaltered by environmental factors.
Ultimately, the use of a vacuum furnace is not just about heating steel; it is about eliminating variables to ensure your data is unassailable.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Requirement | Benefit of Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 845 °C | High-precision control prevents grain coarsening |
| Soaking Time | 120 Minutes | Consistent thermal history throughout the batch |
| Atmosphere | High Vacuum | Eliminates oxidation and surface decarburization |
| Surface Quality | Pristine / No Scaling | Prevents stress concentrators in fatigue testing |
| Internal Structure | Uniform Microstructure | Ensures test results reflect inherent material properties |
Elevate Your Material Testing Precision with KINTEK
Don’t let preparation defects compromise your research integrity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous demands of metallurgical analysis. Our customizable high-temperature lab furnaces provide the precise thermal control and ultra-clean environments necessary to eliminate variables in GCr15 steel testing.
Ready to achieve unassailable data? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your unique laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Yingxin Zhao, Aiguo Zhao. Influence of Non-Metallic Inclusions on Very High-Cycle Fatigue Performance of High-Strength Steels and Interpretation via Crystal Plasticity Finite Element Method. DOI: 10.3390/met14080948
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do the cooling properties of argon and nitrogen differ in vacuum furnaces? Compare Speed, Safety, and Material Suitability
- Why is a vacuum system with argon protection required for melting zirconium alloys? Ensure Pure Hydrogen Storage.
- How does a microwave sintering furnace utilize material properties for heating h-BN/ZrO2/SiC? Optimize Results
- What are modified atmosphere furnaces and how do they differ from vacuum furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Process
- Why are laboratory vacuum furnaces vital for scientific research? Unlock Purity and Precision in Experiments
- How do vacuum furnaces work? Unlock Clean, High-Purity Heat Treatment
- What role does a laboratory vacuum drying oven play in the treatment of filtered Y2O3-MgO precursors? Expert Insights
- What is the function of the crucible in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Purity and Performance in High-Temp Processes



















