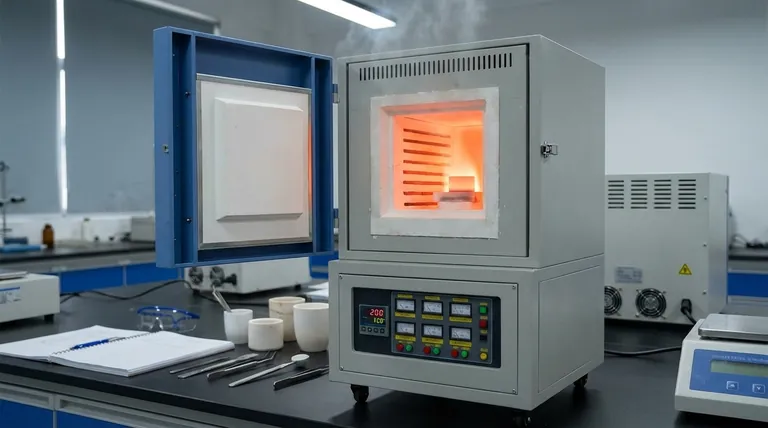
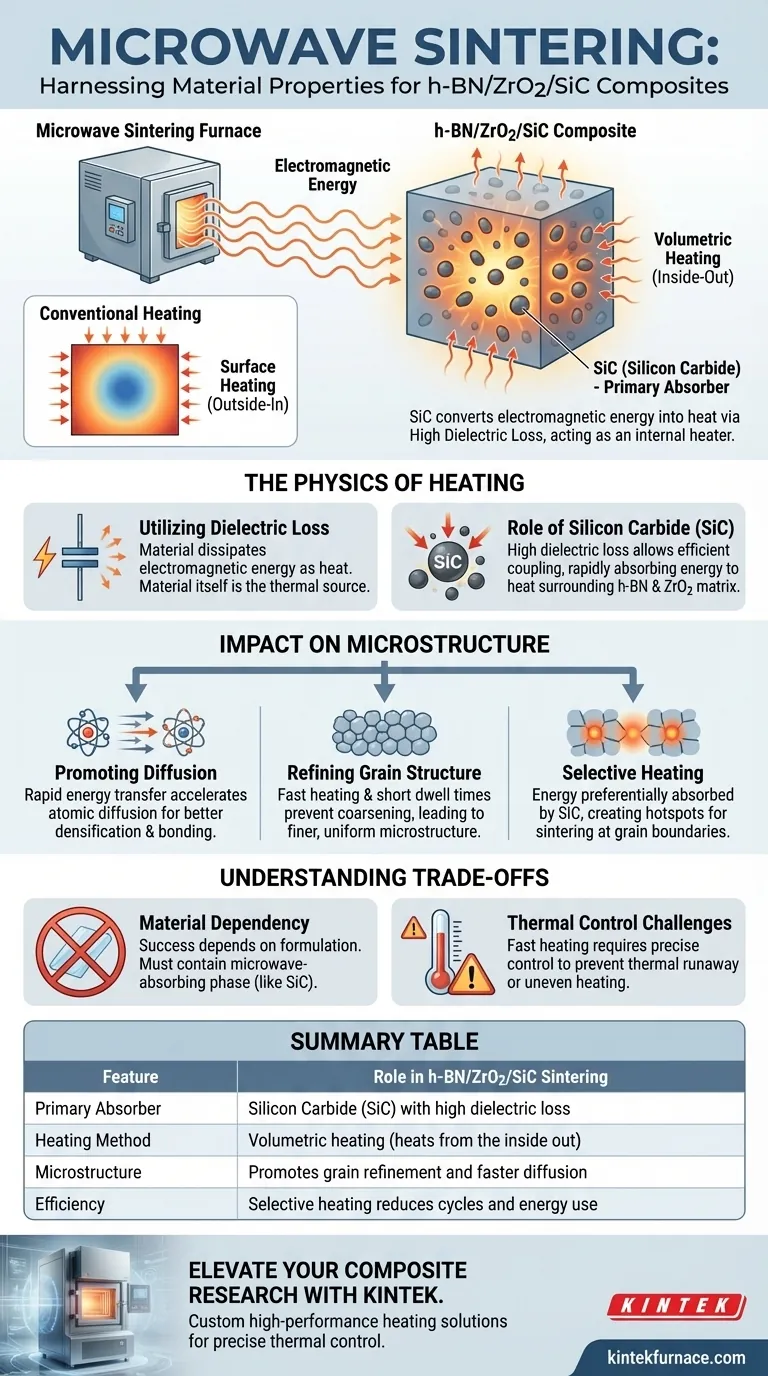
Microwave sintering furnaces leverage the specific dielectric properties of ceramic components to generate heat directly within the material itself. In the context of h-BN/ZrO2/SiC composites, the furnace relies heavily on the microwave-absorbing capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) to act as a primary heat source. The SiC absorbs electromagnetic energy and converts it into heat through dielectric loss, initiating a "volumetric" heating process that warms the composite from the inside out.
The core advantage of this technique lies in utilizing the high dielectric loss of SiC to drive rapid, volumetric heating. This internal energy generation promotes faster diffusion and finer grain structures, leading to a superior microstructure compared to conventional external heating methods.

The Physics of Microwave Heating
Utilizing Dielectric Loss
Microwave sintering does not rely on external heating elements to transfer heat via conduction or convection. Instead, it exploits the dielectric loss characteristics of the composite materials.
This property determines a material's ability to dissipate electromagnetic energy as heat. The furnace generates a microwave field, and the material itself becomes the source of thermal energy.
The Role of Silicon Carbide (SiC)
In an h-BN/ZrO2/SiC composite, the materials do not absorb energy equally. Silicon Carbide (SiC) serves as the critical microwave-absorbing component.
Because SiC has high dielectric loss, it efficiently couples with the microwave field. It absorbs the energy rapidly, effectively acting as an internal heater for the surrounding h-BN (Hexagonal Boron Nitride) and ZrO2 (Zirconium Dioxide) matrix.
Volumetric Heating
Traditional sintering heats a material from the surface inward, which can create thermal gradients. Microwave sintering achieves volumetric heating, meaning heat is generated throughout the entire volume of the part simultaneously.
This process often results in the core being slightly hotter than the surface, driving heat from the inside outward. This inversion of the thermal profile helps eliminate the "cold center" issues often found in conventional processing.
Impact on Composite Microstructure
Promoting Diffusion
The direct coupling of microwave energy with the material leads to fast heating rates and high thermal efficiency.
This rapid energy transfer accelerates atomic diffusion mechanisms. Enhanced diffusion is essential for proper densification and bonding between the h-BN, ZrO2, and SiC phases.
Refining Grain Structure
One of the distinct advantages of this method is the ability to control grain growth.
Because the heating rates are fast and the dwell times are typically shorter, there is less time for grains to coarsen. This leads to grain refinement, creating a finer, more uniform microstructure which generally correlates with improved mechanical properties.
Selective Heating
The furnace utilizes selective heating, meaning the energy is preferentially absorbed by the phases with the highest dielectric loss (SiC).
This localized heating can create microscopic hotspots that facilitate sintering at the grain boundaries without subjecting the entire bulk material to excessive thermal loads unnecessarily.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Material Dependency
The success of this process is entirely dependent on the material formulation.
If the composite lacks a sufficient microwave-absorbing phase like SiC, the furnace cannot generate heat efficiently. The process requires a precise balance of dielectric properties to function; materials transparent to microwaves will simply not heat up.
Thermal Control Challenges
While fast heating rates are beneficial for efficiency, they require precise control.
The rapid internal generation of heat can sometimes lead to thermal runaway or uneven heating if the SiC is not dispersed specifically and uniformly. The "inside-out" heating profile must be carefully managed to prevent thermal stress within the composite part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When deciding whether to utilize microwave sintering for your ceramic composites, consider your specific performance targets.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Integrity: This method is ideal for achieving fine grain sizes and preventing the coarsening often seen in long conventional sintering cycles.
- If your primary focus is Process Efficiency: This technique offers significantly faster heating rates and higher thermal efficiency, reducing overall processing time.
Microwave sintering transforms the material formulation itself into the heating element, offering a pathway to superior composite properties through rapid, volumetric energy transfer.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in h-BN/ZrO2/SiC Sintering |
|---|---|
| Primary Absorber | Silicon Carbide (SiC) with high dielectric loss |
| Heating Method | Volumetric heating (heats from the inside out) |
| Microstructure | Promotes grain refinement and faster diffusion |
| Efficiency | Selective heating reduces cycles and energy use |
Elevate Your Composite Research with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect microstructure in h-BN/ZrO2/SiC composites requires precise thermal control and expert equipment. Backed by industry-leading R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance heating solutions tailored to your laboratory's unique needs.
Our extensive range of customizable lab high-temp furnaces includes:
- Muffle & Tube Furnaces for standard heat treatments.
- Rotary & Vacuum Systems for specialized material processing.
- CVD Systems for advanced chemical vapor deposition.
Ready to enhance your sintering efficiency and material integrity? Contact KINTEK today to find your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does uniform heating and cooling benefit materials in vacuum furnaces? Prevent Stress and Boost Performance
- Why is a vacuum oven necessary for drying ZnO-Co3O4 electrode slurries? Preserve Material Integrity at 60°C
- Why is a vacuum oven required for the 120 °C treatment of electrodes? Ensuring Battery Purity and Performance
- What function does a high vacuum sintering furnace serve in Ti6Al4V densification? Achieve Superior Material Purity
- How does a vacuum impregnation device facilitate PCMs into biomimetic composites? Boost Filling Rates to 96%
- What material treatments can be performed in a vacuum furnace? Achieve Clean, High-Quality Results
- How does vacuum level affect the annealing process? Optimize Material Purity and Performance
- Why are high-temperature quenching furnaces required for tungsten alloys? Unlock Workability and Stress Relief



















