In short, a vacuum furnace is used for a wide range of thermal processes where protecting the material from atmospheric contamination is critical. This includes treatments like hardening and quenching, annealing, tempering, brazing, sintering, and specialized surface modifications like carburizing and nitriding. The key advantage is the ability to achieve clean, bright parts with superior metallurgical properties.
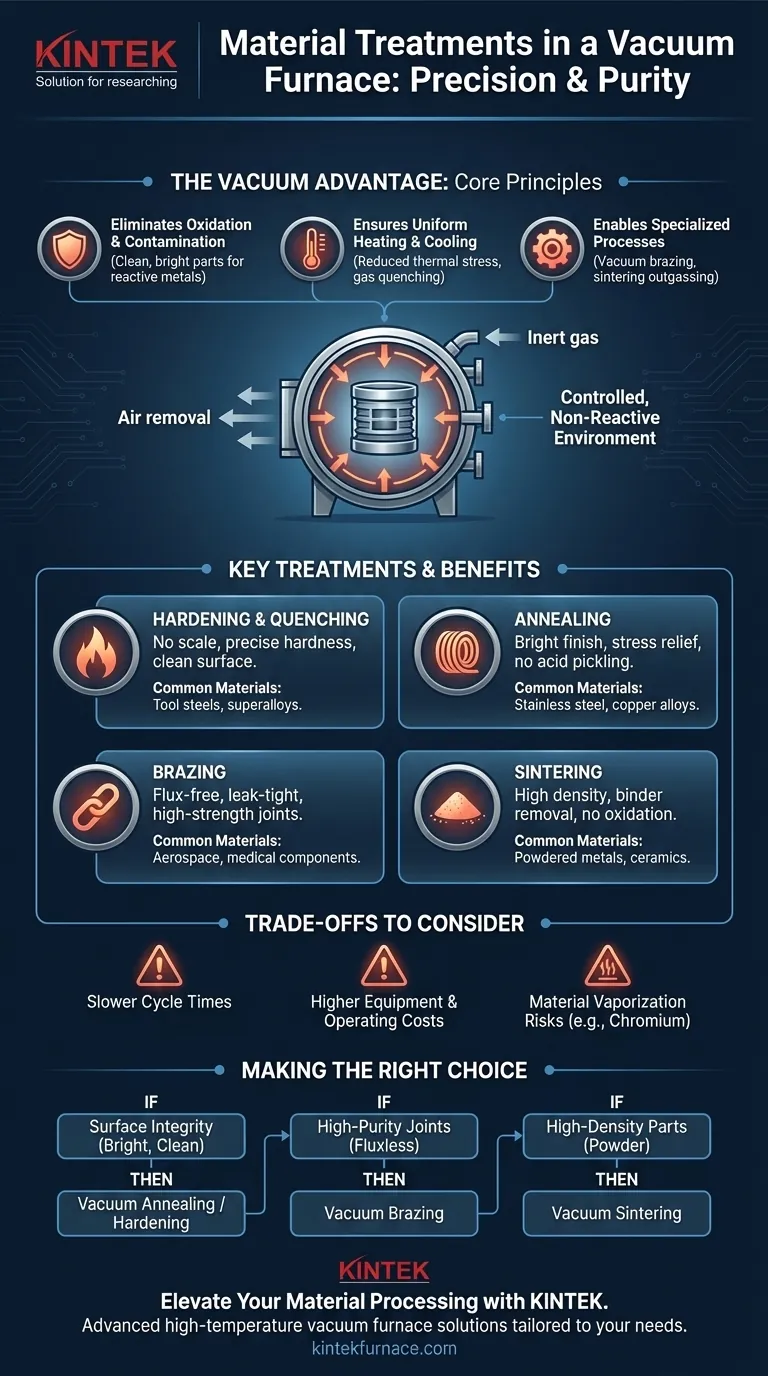
The fundamental purpose of using a vacuum furnace is not just to heat a material, but to create a highly controlled, non-reactive environment. By removing air, you eliminate the risk of oxidation and other surface reactions, enabling treatments that are impossible to achieve with the same quality in a conventional furnace.

The Core Principle: Why Use a Vacuum?
A vacuum furnace works by removing the atmosphere—primarily oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor—from a sealed chamber before and during the heating process. This seemingly simple step provides several profound advantages for material processing.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
The most immediate benefit of a vacuum is the prevention of oxidation. At high temperatures, most metals will readily react with oxygen to form a scale or oxide layer on their surface.
This is especially critical for reactive materials like titanium alloys, high-chromium stainless steels, and superalloys. A vacuum environment ensures these materials remain clean, bright, and free from surface contamination.
Ensuring Uniform Heating and Cooling
Without air to create convection currents, heat is transferred primarily through radiation. This results in extremely uniform heating across the entire workload, reducing the risk of thermal stress and distortion in complex parts.
During cooling, a process called gas quenching can be used, where a high-pressure, inert gas like argon or nitrogen is rapidly introduced. This allows for controlled, fast cooling without the surface reactions that would occur in open air.
Enabling Specialized Processes
Certain processes rely on the unique properties of a vacuum. For example, vacuum brazing uses the absence of pressure to help pull molten filler metal deep into a joint through capillary action, creating exceptionally strong and clean bonds without the need for corrosive flux.
Similarly, it allows for the removal of trapped gases and binders from powdered metal parts during sintering, a process known as outgassing.
Key Treatments and Their Vacuum Advantage
While many processes can be performed in both atmospheric and vacuum furnaces, the vacuum environment offers distinct benefits that improve the final outcome for each.
Hardening, Quenching, and Tempering
In a vacuum, parts can be heated to their austenitizing temperature without forming any surface scale. The subsequent high-pressure gas quench achieves predictable hardness and a clean surface finish, often eliminating the need for post-treatment cleaning or machining. Tempering follows to reduce brittleness and achieve the desired final toughness.
Annealing
Vacuum annealing is used to soften materials, relieve internal stresses, and refine their grain structure. For materials like stainless steel and copper alloys, it produces a bright, clean surface that is ready for the next manufacturing step without any need for acid pickling or blasting.
Brazing
Vacuum brazing is a premier process for joining components. The clean environment ensures the braze alloy wets and flows perfectly, creating strong, leak-tight joints that are free from flux residue. This is essential for applications in the aerospace, medical, and semiconductor industries.
Sintering
For parts made from powdered metal, vacuum sintering is used to bond the particles together into a solid, dense object. The vacuum is crucial for removing lubricants and binders used in the powder compaction stage and preventing oxidation, which would inhibit proper bonding and weaken the final component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not the universal solution for all heat treatment needs. It's important to recognize their limitations to make an informed decision.
Slower Cycle Times
Pulling a vacuum, stabilizing the environment, and performing controlled cooling cycles can take longer than comparable atmospheric processes. This makes vacuum furnaces less suitable for high-volume, low-margin parts where throughput is the primary concern.
Higher Equipment and Operating Costs
Vacuum furnaces are more complex and expensive to build, operate, and maintain than their atmospheric counterparts. They require robust vacuum pumps, precise controls, and more intensive maintenance schedules.
Material Vaporization Risks
Under a deep vacuum, some alloying elements—most notably chromium in steels—can vaporize from the material's surface at high temperatures. This can be managed by using a partial pressure of an inert gas, but it adds a layer of complexity to the process control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace should be driven by the required properties of the final product.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity and brightness: Vacuum annealing or hardening is the ideal choice for reactive materials like titanium, stainless steel, and tool steels.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity, strong joints: Vacuum brazing provides a fluxless solution that delivers superior joint quality for critical applications.
- If your primary focus is producing high-density powdered metal parts: Vacuum sintering is essential for removing contaminants and achieving the best possible mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is simple stress relief on non-reactive metals: A conventional atmospheric furnace may be a more cost-effective and faster solution.
Ultimately, leveraging a vacuum furnace is a strategic decision to achieve a level of material quality and cleanliness that is unattainable through other methods.
Summary Table:
| Treatment Type | Key Benefits in Vacuum | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening & Quenching | No oxidation, clean surfaces, precise hardness | Tool steels, superalloys |
| Annealing | Bright finish, stress relief, no acid cleaning | Stainless steel, copper alloys |
| Brazing | Flux-free joints, high strength, leak-tight | Aerospace, medical components |
| Sintering | High density, removal of binders, no contamination | Powdered metals, ceramics |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with reactive metals like titanium or need high-purity joints for critical applications, KINTEK delivers reliable, contamination-free results. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can optimize your lab's performance and achieve superior outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance



















