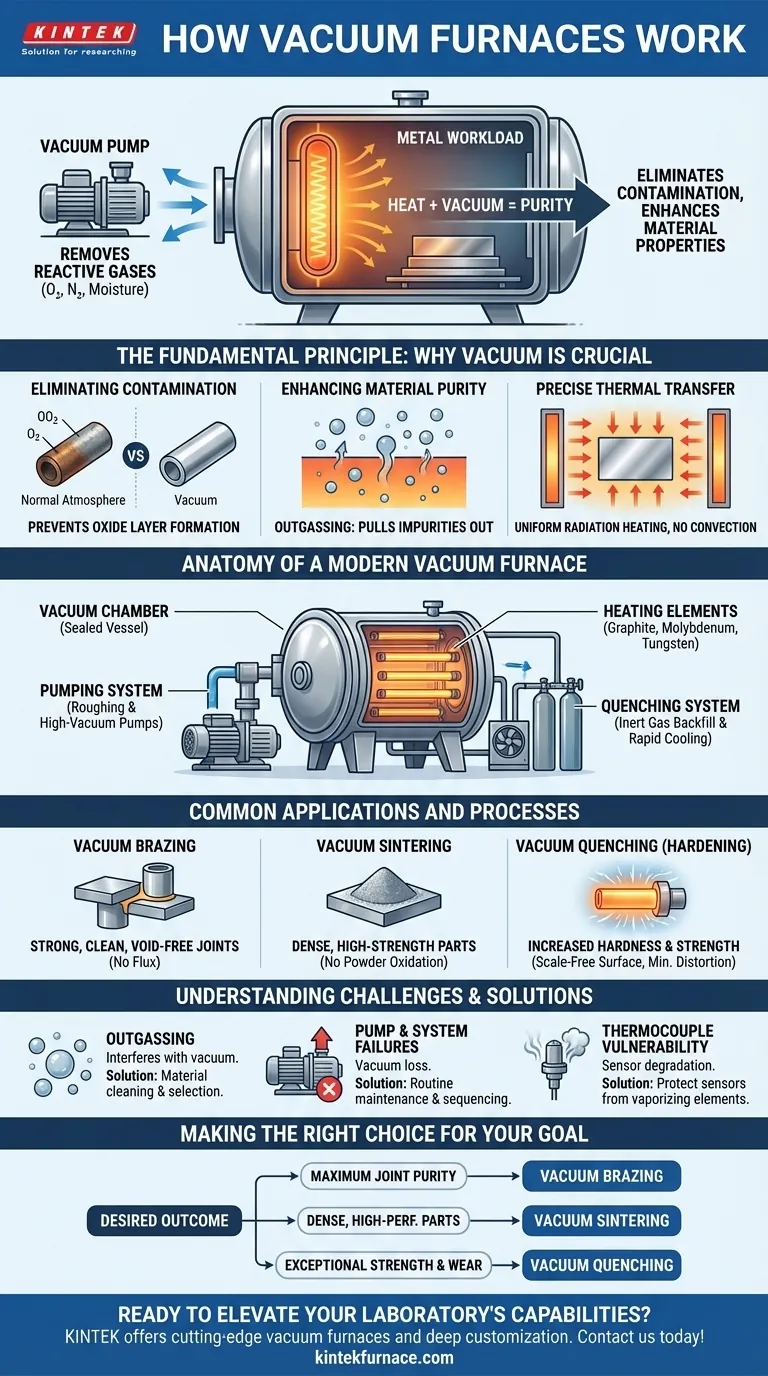
At its core, a vacuum furnace works by heating materials inside a sealed chamber after removing all the air. By creating a vacuum, the process eliminates reactive gases like oxygen and moisture that would otherwise contaminate or damage the material at high temperatures. This allows for exceptionally clean, bright, and high-purity results that are impossible to achieve in a conventional furnace.
The true purpose of a vacuum furnace is not just to generate heat, but to create a perfectly controlled, impurity-free environment. This control over the atmosphere unlocks advanced metallurgical processes, leading to superior material strength, purity, and overall performance.

The Fundamental Principle: Why Vacuum is Crucial
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the need to control a material's environment at a molecular level during heat treatment. Removing the atmosphere solves several critical problems.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
When metals are heated, they become highly reactive. In a normal atmosphere, oxygen will immediately bond with the hot surface, creating an oxide layer (scale).
A vacuum physically removes the oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor from the chamber, preventing these unwanted chemical reactions. This results in clean, bright parts with no surface discoloration or degradation.
Enhancing Material Purity
The vacuum environment doesn't just prevent contaminants from getting in; it also helps pull impurities out.
During heating, volatile elements trapped within the material can be drawn out by the low-pressure environment, a process known as outgassing. This purifies the base material, improving its structural and electrical properties.
Enabling Precise Thermal Transfer
In a normal furnace, heat is transferred through convection (air currents), conduction, and radiation. This can lead to uneven heating.
In a vacuum, convection is eliminated. Heat is transferred almost entirely by radiation from the heating elements to the workload. This allows for extremely uniform and predictable temperature control across the entire part, which is critical for consistent results.
Anatomy of a Modern Vacuum Furnace
A vacuum furnace is a system of integrated components working together to control both temperature and pressure with high precision.
The Vacuum Chamber and Pumping System
The process takes place inside a robust, sealed vessel. A multi-stage pumping system works to create the vacuum. Typically, a mechanical "roughing" pump removes the bulk of the air before a high-vacuum pump (like a diffusion or turbomolecular pump) takes over to achieve extremely low pressures.
The Heating Elements
Most vacuum furnaces use electric resistance heating elements. These are made from materials that can withstand extreme temperatures without degrading, such as graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten. They convert electrical energy into thermal energy, radiating heat throughout the chamber.
The Quenching System
After the heating cycle, many processes require rapid cooling (quenching) to lock in the desired material properties. This is often achieved by backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas like argon or nitrogen, which is then circulated by a high-power fan to cool the part quickly and evenly.
Common Applications and Processes
The unique capabilities of vacuum furnaces make them indispensable for a range of high-performance applications.
Vacuum Brazing
This process joins two or more materials using a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the base materials. Performing this in a vacuum prevents oxidation, resulting in an exceptionally strong, clean, and void-free joint without the need for flux.
Vacuum Sintering
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder by applying heat. In a vacuum, fine metal powders can be fused into dense, high-strength parts without the risk of the tiny particles oxidizing, which would severely compromise the final product's integrity.
Vacuum Quenching (Hardening)
This is a heat treatment process where a material is heated to a specific temperature and then rapidly cooled to increase its hardness and strength. Vacuum quenching produces a clean, scale-free surface and minimizes distortion compared to traditional oil or salt bath quenching methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, vacuum furnaces present unique operational complexities that require expert oversight.
The Issue of Outgassing
As mentioned, materials can release trapped gases and contaminants when heated in a vacuum. This outgassing can interfere with the process by preventing the system from reaching the target vacuum level. Careful material selection and cleaning are essential to manage this.
Pump and System Failures
The multi-stage pumping system is a common point of failure. Issues like vacuum level inconsistencies or pump failures can halt production. Proper sequencing and routine maintenance are critical to ensure reliability.
Thermocouple Vulnerability
The thermocouples that measure temperature can be degraded by certain elements that vaporize from the workload at high temperatures. This high vapor pressure can cause the sensors to fail, leading to inaccurate temperature control and ruined batches.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The process you choose is dictated entirely by your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is joining components with maximum joint purity: Vacuum brazing is the ideal process, as it prevents oxide formation at the interface for a superior bond.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, high-performance parts from metal powders: Vacuum sintering offers unparalleled control over part density and prevents the contamination of fine particles.
- If your primary focus is hardening components for exceptional strength and wear resistance: Vacuum quenching provides a clean, predictable method to achieve the desired material microstructure without surface scaling.
By mastering the principles of vacuum furnace operation, you gain the ability to create materials and components with properties that are otherwise unattainable.
Summary Table:
| Component/Process | Key Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber & Pumping System | Removes air and gases to create a vacuum | Prevents oxidation and contamination, enabling clean results |
| Heating Elements (e.g., graphite, molybdenum) | Radiate heat in the vacuum environment | Ensures uniform and precise temperature control |
| Quenching System | Rapidly cools materials using inert gases | Locks in material properties with minimal distortion |
| Vacuum Brazing | Joins materials without flux in a vacuum | Produces strong, void-free joints with high purity |
| Vacuum Sintering | Fuses metal powders in a vacuum | Creates dense, high-strength parts free from oxidation |
| Vacuum Quenching | Hardens materials in a controlled atmosphere | Enhances strength and wear resistance with scale-free surfaces |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with advanced high-temperature solutions?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide cutting-edge vacuum furnaces tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're focused on vacuum brazing, sintering, or quenching, we deliver precise, reliable equipment to enhance material purity and performance.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can transform your heat treatment processes and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing



















