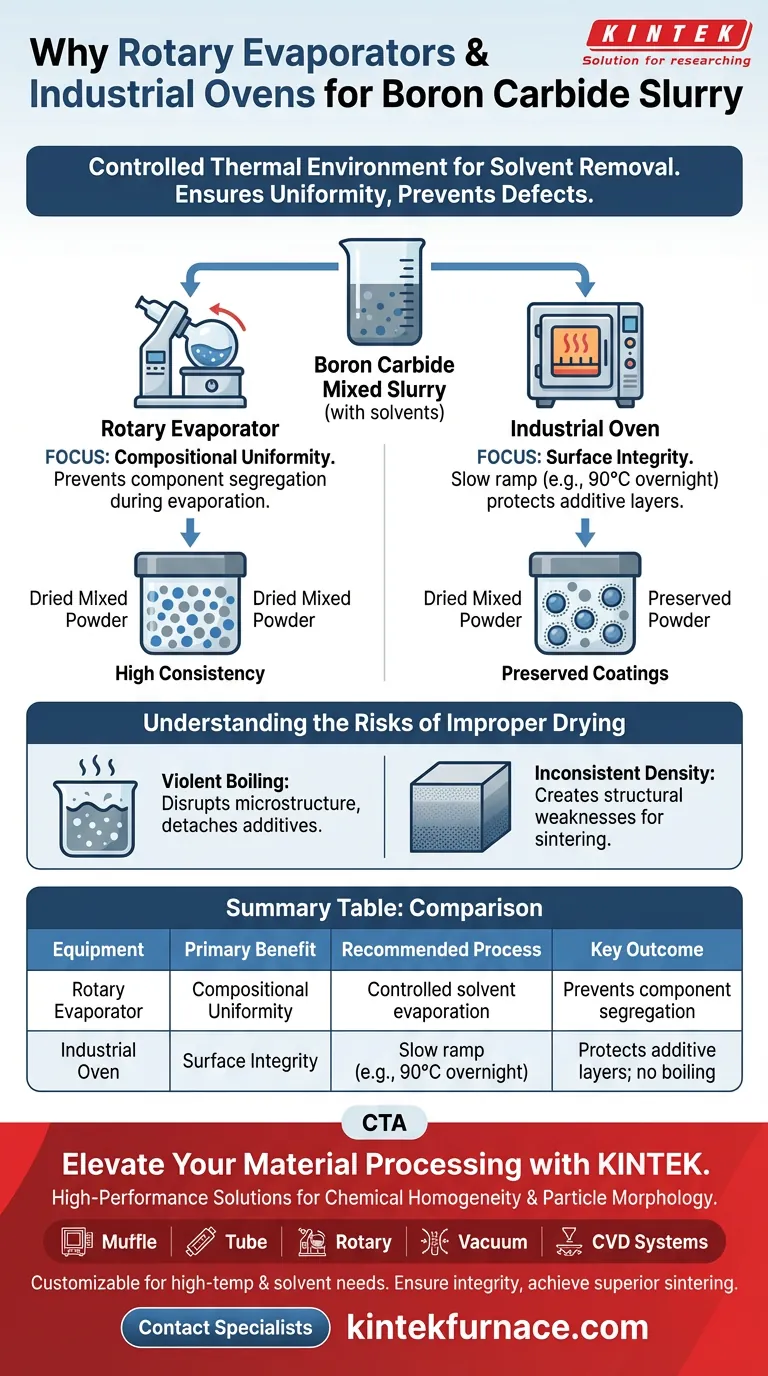
Rotary evaporators and industrial ovens are essential for processing Boron Carbide slurries because they provide a precise, controlled thermal environment for solvent removal. These devices ensure that as organic solvents like ethanol evaporate, the critical mixture of ingredients remains uniform, preventing defects in the final ceramic product.
The core value of this equipment lies in regulating drying speed to prevent component segregation. By avoiding uncontrolled evaporation, you preserve the chemical homogeneity and physical structure of the powder, which is a prerequisite for successful molding and sintering.

The Science of Controlled Drying
Preventing Component Segregation
When a Boron Carbide slurry is dried, the solvents (often ethanol) evaporate, leaving the solids behind.
Without controlled drying, heavier and lighter particles within the slurry tend to separate.
Rotary evaporators and industrial ovens manage the evaporation rate to ensure that the "dried mixed powder maintains high compositional consistency."
Preserving Particle Morphology
Boron Carbide particles are often coated with additive layers during the mixing process.
If the drying environment allows for violent boiling or rapid phase changes, these delicate additive layers can peel off or redistribute unevenly.
Industrial ovens utilize specific protocols, such as heating at 90°C overnight, to remove moisture slowly and keep these precursor coatings intact.
Ensuring Sintering Success
The quality of the drying phase directly dictates the quality of the final product.
If the powder components segregate or coatings are damaged during drying, the material will behave unpredictably during the subsequent molding and sintering stages.
Using specialized equipment ensures the powder retains the necessary physical properties for high-temperature calcination.
Understanding the Risks of Improper Drying
The Danger of Violent Boiling
The most significant risk in drying slurries is uncontrolled heating, which leads to "violent boiling."
This physical agitation disrupts the microstructure of the slurry, detaching critical additives from the Boron Carbide surface.
Inconsistent Density
When solvents are removed unevenly, it creates density gradients in the final dried powder.
These inconsistencies lead to structural weaknesses and failures when the powder is eventually pressed and sintered into a solid part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your Boron Carbide components, align your drying strategy with your specific processing needs.
- If your primary focus is compositional uniformity: Use rotary evaporators to ensure solvents are removed without causing the segregation of mixed powder components.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity: Use an industrial oven with a slow ramp (e.g., 90°C overnight) to prevent violent boiling and protect additive layers.
Control the drying variable now to guarantee material performance later.
Summary Table:
| Equipment Type | Primary Benefit | Recommended Process | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Evaporator | Compositional Uniformity | Controlled solvent evaporation | Prevents component segregation |
| Industrial Oven | Surface Integrity | Slow ramp (e.g., 90°C overnight) | Protects additive layers; no boiling |
Elevate Your Material Processing with KINTEK
Don't let improper drying compromise your Boron Carbide performance. KINTEK provides high-performance laboratory and industrial solutions designed to preserve chemical homogeneity and particle morphology.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique lab high-temp and solvent-handling needs. Ensure the integrity of your precursors and achieve superior sintering results today.
Ready to optimize your drying process? Contact us today to consult with our technical specialists.
Visual Guide
References
- Hala Mohamed, Rehab Mahmoud. Waste Biomass Utilization for the Production of Adsorbent and Value-Added Products for Investigation of the Resultant Adsorption and Methanol Electro-Oxidation. DOI: 10.3390/catal14090574
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an aluminum foil mask regulate temperature in the Floating-Zone process? Optimize Crystal Growth Precision
- What are the advantages of mastering the sintering step? Achieve Cost Savings and Complex Designs
- What is the role of a rapid thermal processing furnace in CdO/CdS/ZnO fabrication? Achieve High-Quality Heterojunctions
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum drying oven for BiVO4/COF composite photoanodes? Preserve Material Integrity
- Why is a high vacuum necessary for solar absorbers? Ensure Precise Optical Properties in Thin Film Coating
- How does the orientation of glass within a tempering furnace affect quality? Optimize Optical and Physical Properties
- Why is a constant temperature drying oven used for activated carbon? Ensure Pore Integrity and Adsorption Efficiency
- How do precision temperature-controlled ovens function for SiC-Ti3SiC2 preform curing? Expert Thermal Control Guide



















