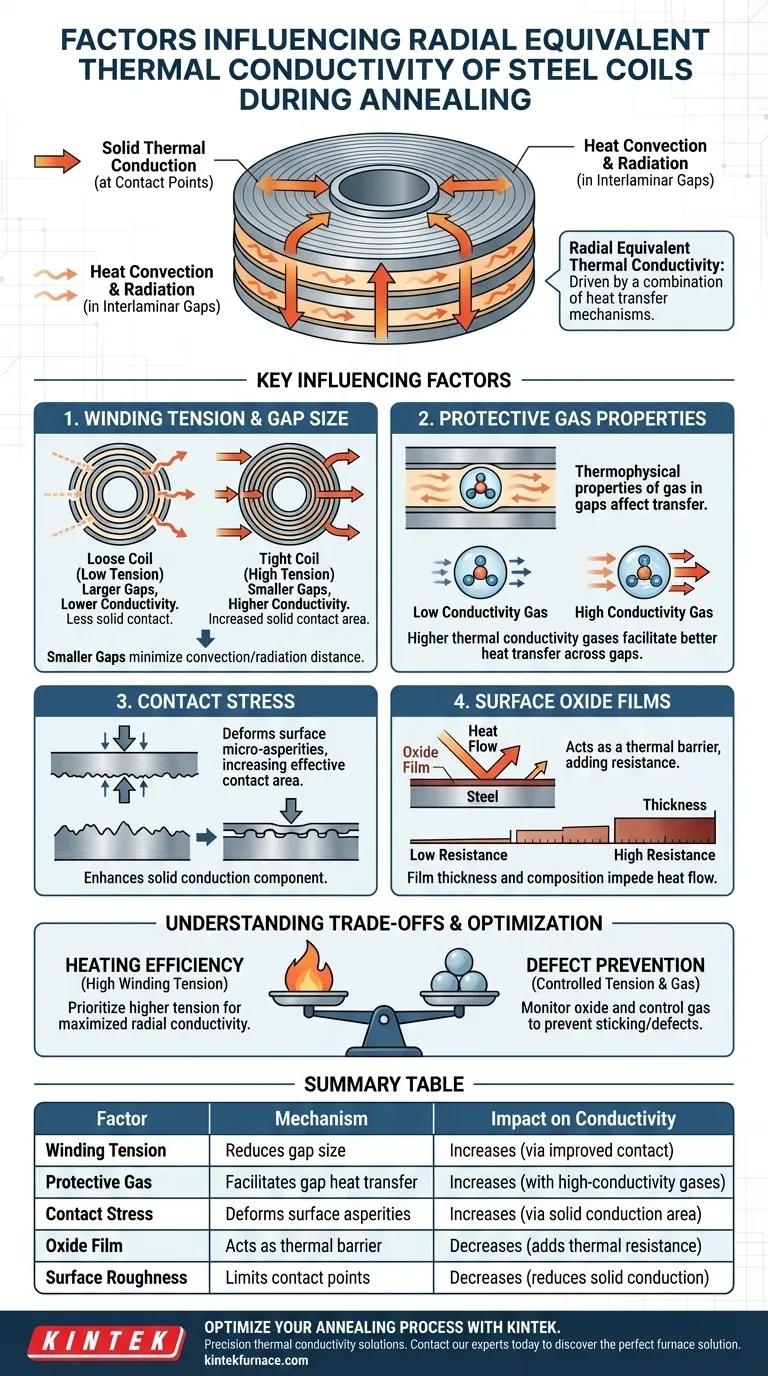
The radial equivalent thermal conductivity of steel coils during annealing is driven by a combination of heat convection, radiation within interlaminar gaps, and solid thermal conduction at contact points. The primary factors influencing this process include the size of interlaminar gaps (dictated by winding tension), the thermophysical properties of the protective gas, the contact stress between layers, and the thermal resistance of any oxide film present on the steel surface.
The efficiency of heat transfer toward the center of a steel coil is ultimately determined by a complex resistance network formed by the interaction between solid steel layers and the gas-filled gaps separating them.
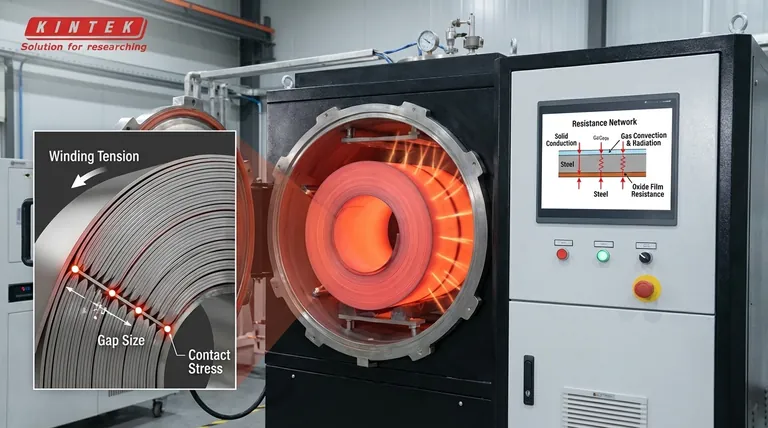
Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
The Role of Interlaminar Gaps
Heat transfer in a coiled structure does not behave like conduction through a solid block. The process is heavily influenced by the air or gas gaps that exist between the layers of steel.
Within these gaps, heat is transferred via convection and radiation. These mechanisms dominate where physical contact between layers is absent, acting as a bridge across the empty space.
Solid Thermal Conduction
Direct heat transfer occurs only at specific contact points where steel layers physically touch.
This solid thermal conduction provides the path of least resistance. However, it is limited by the surface roughness and flatness of the strip, which prevents perfect contact across the entire area.
Key Influencing Factors
Winding Tension and Gap Size
The winding tension applied during the coiling process is the most critical structural variable.
Higher tension compresses the coil, effectively reducing the size of the interlaminar gaps. Smaller gaps minimize the distance heat must travel via convection/radiation and increase the surface area available for solid conduction.
Protective Gas Properties
The environment inside the annealing furnace plays a significant role. The type and thermophysical properties of the protective gas occupying the interlaminar gaps directly affect conductivity.
Gases with higher thermal conductivity facilitate better heat transfer across the gaps where metal-to-metal contact is missing.
Surface Oxide Films
The surface condition of the steel strip introduces an additional layer of thermal resistance.
An oxide film on the steel surface acts as a thermal barrier. The thickness and composition of this film contribute to the overall resistance network, impeding the flow of heat from one layer to the next.
Contact Stress
Beyond the initial gap size, the actual contact stress between layers influences conductivity.
Higher contact stress deforms micro-asperities (surface roughness), increasing the effective contact area. This enhances the solid conduction component of the total thermal conductivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Tension Balance
While increasing winding tension improves radial thermal conductivity, it is not a cure-all solution.
Excessive tension can lead to mechanical issues, such as sticking (diffusion bonding) between layers or deformation of the coil geometry.
Limits of Gas Convection
Relying heavily on gas convection in loose coils can lead to uneven heating.
Large gaps may allow for better gas flow, but they disrupt the uniformity of the radial heat front, potentially causing thermal stresses within the coil structure.
Optimizing Process Parameters
To manage the annealing process effectively, you must balance mechanical constraints with thermal requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximizing heating efficiency: Prioritize higher winding tension to minimize gap size and maximize solid contact stress, thereby increasing radial conductivity.
- If your primary focus is preventing surface defects: Monitor the oxide film thickness and control the protective gas atmosphere to ensure consistent thermal properties without relying solely on mechanical compression.
Understanding the specific contribution of gap size and contact stress allows for precise control over the coil's thermal history.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Mechanism of Influence | Impact on Thermal Conductivity |
|---|---|---|
| Winding Tension | Reduces interlaminar gap size | Increases conductivity via improved contact |
| Protective Gas | Facilitates heat transfer in gaps | High-conductivity gases enhance radial heat flow |
| Contact Stress | Deforms surface micro-asperities | Increases solid conduction area between layers |
| Oxide Film | Acts as a thermal barrier | Decreases conductivity by adding thermal resistance |
| Surface Roughness | Limits physical contact points | Higher roughness typically reduces solid conduction |
Optimize Your Annealing Process with KINTEK
Precision thermal conductivity is the backbone of high-quality steel production. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique metallurgical needs.
Whether you are refining winding tension parameters or optimizing protective gas environments, our expert systems provide the uniform heating and precise control required to eliminate defects and maximize efficiency.
Ready to elevate your heat treatment results? Contact our experts today to discover the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory or production line!
Visual Guide
References
- Yang Xiao-jing, Yu-Ren Li. Study of heat transfer model and buried thermocouple test of bell-type annealing furnace based on thermal equilibrium. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-97422-4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the two main purposes of controlled atmosphere conditions in furnaces? Protect or Transform Materials for Peak Performance
- What is the function of low-oxygen controlled powder sintering in Cu-Fe-Zn alloys? Master Interstitial Strengthening
- How do high-temperature ovens and nitrogen purging systems facilitate the regeneration of activated carbon? Restore Performance
- What are the key benefits of using argon in furnaces? Ensure Maximum Purity and Performance
- Why must a high-purity argon protective atmosphere be maintained during mechanical alloying? Ensure Peak Material Purity
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- Why are inert ovens important in electronics manufacturing? Prevent Oxidation and Boost Component Reliability
- What is the use of nitrogen in heat treatment? Protect Your Metal Parts from Oxidation & Decarburization
















