In electronics manufacturing, an inert oven is critical because it allows sensitive components to be heated without being damaged by the surrounding air. Normal air contains oxygen, which causes materials to oxidize and degrade at high temperatures. An inert oven replaces the reactive air with a non-reactive (inert) gas, ensuring the integrity and performance of the final product.
The core problem is not heat itself, but the chemical reactions that heat accelerates in the presence of oxygen. An inert oven protects components by creating a sterile, non-reactive atmosphere, typically using nitrogen, to prevent these destructive reactions from ever occurring.

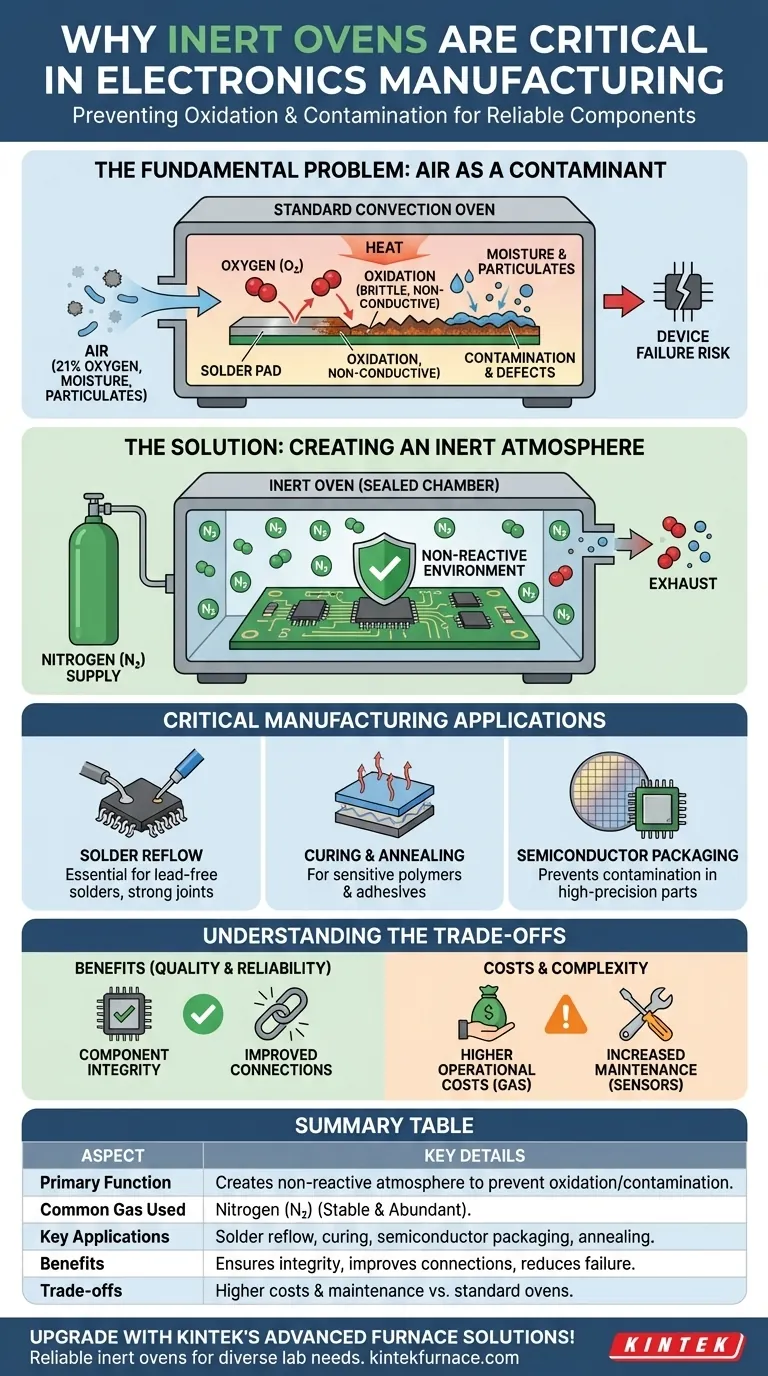
The Fundamental Problem: Air as a Contaminant
At the microscopic level of modern electronics, the normal air we breathe becomes a significant source of contamination during heating processes.
Why a Standard Oven Fails
A standard "convection" oven simply circulates hot air. While this is effective for heating, it constantly exposes the product to roughly 21% oxygen and variable amounts of moisture.
At the high temperatures required for processes like soldering or curing, this oxygen becomes highly reactive.
The Threat of Oxidation
Oxidation is the primary chemical reaction that inert ovens are designed to prevent. Think of it as a rapid, microscopic form of rusting.
When metal surfaces like solder pads or component leads are heated in the presence of oxygen, a thin layer of metal oxide forms. This oxide layer is non-conductive and brittle, leading to poor solder joints, weak electrical connections, and ultimately, device failure.
Beyond Oxygen: Moisture and Particulates
The ambient air that is pulled into a standard oven also contains moisture and microscopic dust particles.
During heating, this moisture can cause its own set of problems, and particulates can settle on sensitive surfaces, creating defects that compromise the function of semiconductors and other high-precision components.
How an Inert Oven Solves the Problem
An inert oven is a precisely controlled system that directly counteracts the threats of oxidation and contamination.
Creating an Inert Atmosphere
The principle is simple: replace the reactive air with something that is non-reactive (inert). The oven chamber is sealed and purged with a high-purity inert gas.
This process displaces the oxygen, moisture, and particulates, creating an ideal environment for heating sensitive materials.
The Role of Nitrogen (N2)
The most commonly used inert gas in electronics manufacturing is nitrogen (N2). Nitrogen is ideal because it is abundant (making up ~78% of Earth's atmosphere), relatively inexpensive to isolate, and extremely stable.
The strong triple bond holding the two nitrogen atoms together makes the N2 molecule very non-reactive, so it will not interfere with the chemical or metallurgical processes happening inside the oven.
Critical Manufacturing Applications
Inert atmospheres are not a luxury; they are a requirement for many modern processes. They are essential for solder reflow, especially with lead-free solders which require higher temperatures.
They are also used for curing specific polymers and adhesives and for semiconductor packaging and annealing, where even the slightest contamination can destroy the component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for quality, implementing an inert atmosphere introduces costs and complexity that are important to acknowledge.
Higher Operational Costs
Operating an inert oven requires a constant supply of high-purity nitrogen gas, which represents a significant and ongoing consumable cost compared to using a standard oven that just uses ambient air.
Increased Complexity and Maintenance
These ovens require gas delivery systems, flow regulators, and oxygen sensors to constantly monitor the atmosphere inside the chamber (often measured in parts-per-million, or PPM). This adds layers of process control, calibration, and maintenance.
When It's Not Necessary
It's crucial to recognize that not every heating process requires an inert atmosphere. For baking out moisture from bare circuit boards or curing robust, non-sensitive coatings, a standard oven is often perfectly adequate and far more cost-effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating process depends entirely on the sensitivity of your materials and your final quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability and performance: Use an inert oven for solder reflow to create strong, clean, and reliable solder joints, especially with fine-pitch components.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials: An inert atmosphere is non-negotiable for semiconductor packaging, annealing, or curing materials that degrade in the presence of oxygen.
- If your primary focus is cost control for non-critical assemblies: A standard convection oven is often sufficient for basic drying or curing processes where slight surface oxidation is acceptable.
Ultimately, understanding the role of the atmosphere is just as critical as controlling the temperature to achieve high-quality, reliable electronics.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates a non-reactive atmosphere to prevent oxidation and contamination during heating. |
| Common Gas Used | Nitrogen (N2) due to its stability and abundance. |
| Key Applications | Solder reflow, curing polymers, semiconductor packaging, and annealing. |
| Benefits | Ensures component integrity, improves electrical connections, and reduces device failure. |
| Trade-offs | Higher operational costs and increased maintenance compared to standard ovens. |
Upgrade your electronics manufacturing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable inert ovens, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing product quality and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity



















