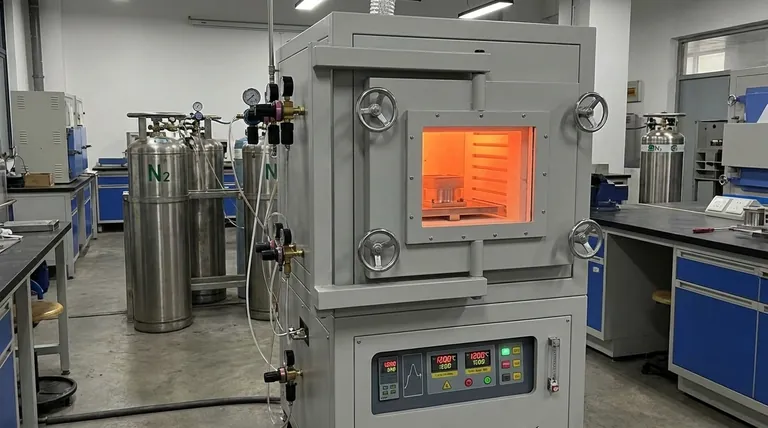
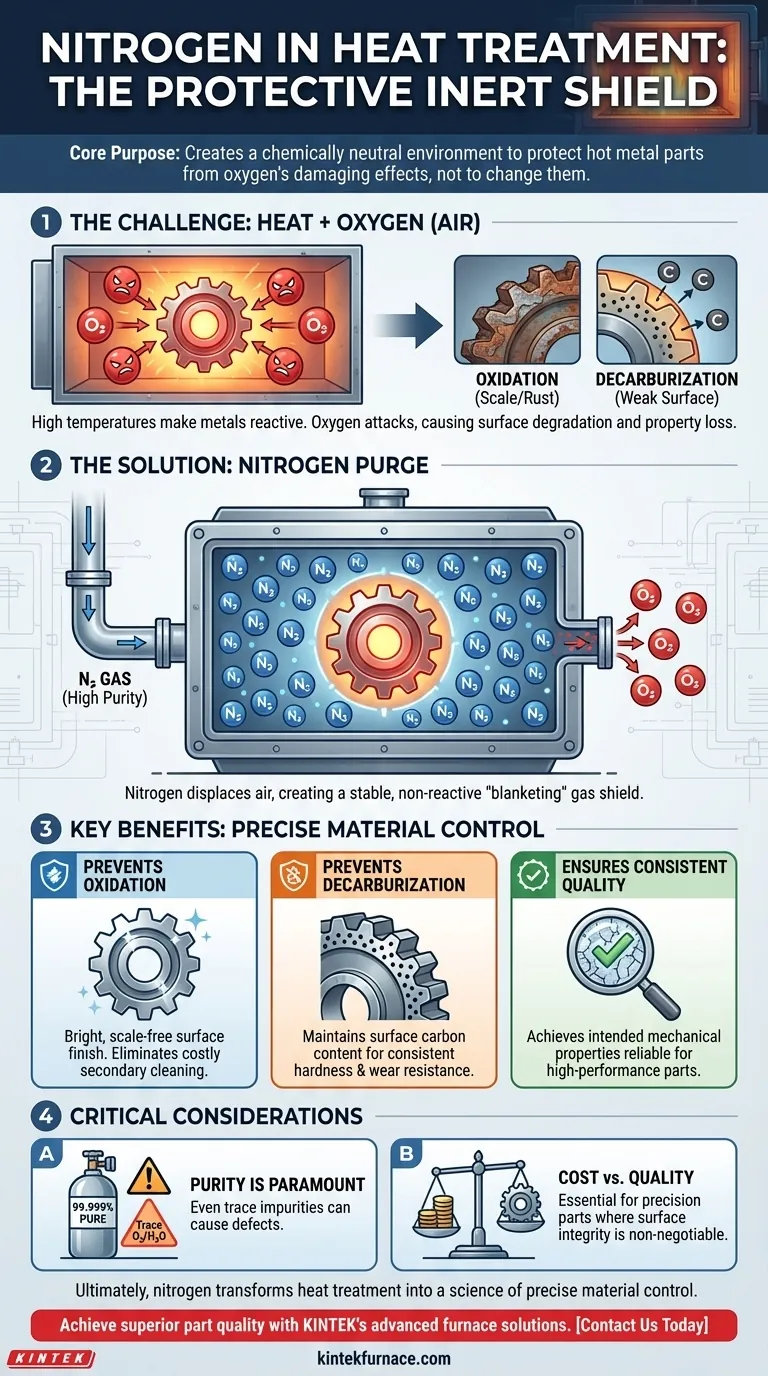
In the context of heat treatment, nitrogen serves as a protective, inert atmosphere inside the furnace. This controlled atmosphere is critical for shielding hot, reactive metal parts from the damaging effects of oxygen. By displacing the air, nitrogen prevents undesirable chemical reactions like oxidation (scaling) and decarburization, ensuring the final component maintains its intended surface quality and mechanical properties.
The core purpose of using nitrogen is not to change the metal, but to protect it. It creates a chemically neutral environment that prevents the high-temperature process from degrading the very properties it is meant to enhance.

The Fundamental Challenge: Heat and Air
Heat treatment is a foundational process in metallurgy, used to alter a material's physical and mechanical properties. However, the high temperatures required also create a significant chemical problem.
Why Heat Is Applied
Heat treatment modifies the microscopic crystal structure, or "microstructure," of a metal. This controlled heating and cooling cycle is what allows us to achieve specific outcomes like increased hardness, improved toughness, or reduced internal stresses.
The Problem with an Open Atmosphere
At elevated temperatures, metals become highly reactive. The oxygen present in ambient air (about 21%) will aggressively attack the hot metal surface.
This unwanted reaction leads to two primary forms of degradation: oxidation and decarburization.
How Nitrogen Provides the Solution
To counteract the destructive effects of oxygen, furnaces are purged with a high-purity gas that will not react with the metal. Nitrogen is the most common and cost-effective choice for this role.
Creating an Inert Shield
Before and during the heating cycle, nitrogen gas is pumped into the sealed furnace. This displaces the oxygen-rich air, surrounding the parts in a stable, non-reactive environment often called a "shielding" or "blanketing" gas.
Preventing Oxidation
Oxidation is the formation of a brittle, flaky layer of oxide—commonly known as scale or rust—on the metal's surface. This scale ruins the part's surface finish, alters its precise dimensions, and often requires costly secondary cleaning operations like sandblasting to remove.
A nitrogen atmosphere starves the reaction of its fuel: oxygen. This results in a bright, clean, scale-free surface straight out of the furnace.
Preventing Decarburization
For carbon-based steels, decarburization is a major concern. At high temperatures, the carbon atoms near the surface can react with oxygen, diffusing out of the steel as CO or CO2 gas.
This loss of carbon makes the surface layer softer and weaker than the core, compromising the part's wear resistance and fatigue life. The inert nitrogen shield prevents this reaction from ever occurring.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for quality, implementing a nitrogen atmosphere is not without its considerations. It represents a deliberate choice to prioritize control over simplicity.
Purity Is Paramount
The effectiveness of the shield depends entirely on the purity of the nitrogen. Even trace amounts of oxygen or moisture (H₂O) in the gas supply can be enough to cause surface discoloration or light oxidation on sensitive materials.
When Inert Is Not Enough
For some advanced processes like carburizing (adding carbon) or nitriding (adding nitrogen into the steel itself), the atmosphere must be "active." In these cases, nitrogen is still used as the primary carrier gas, but it is mixed with small, precisely controlled amounts of reactive gases (like methane or ammonia) to achieve a specific chemical change in the part's surface.
Cost vs. Quality
Using a controlled nitrogen atmosphere adds complexity and cost compared to treating parts in an open-air furnace. The decision hinges on the final requirements of the component. For a low-cost, non-critical part where surface scale is acceptable, open-air heating may suffice. For any precision or high-performance application, it is non-negotiable.
Applying This to Your Process
Choosing the right atmosphere is about matching the process to the desired outcome. The need for nitrogen is dictated by your quality and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is a clean, scale-free surface finish: A high-purity nitrogen atmosphere is the most reliable way to prevent oxidation.
- If your primary focus is maintaining precise mechanical properties: Preventing decarburization with a nitrogen shield is critical for ensuring consistent hardness and strength.
- If your primary focus is on non-critical, low-cost components: Treating in open air might be an acceptable trade-off if subsequent cleaning and minor property variations are tolerable.
Ultimately, nitrogen transforms heat treatment from an art of managing degradation into a science of precise material control.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Creates an Inert Shield | Displaces oxygen in the furnace | Prevents unwanted chemical reactions |
| Prevents Oxidation | Stops scale/rust formation | Maintains surface finish and dimensions |
| Prevents Decarburization | Protects carbon content in steel | Ensures consistent hardness and strength |
Achieve precise material control and superior part quality with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique heat treatment requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise and reliable nitrogen atmosphere systems can protect your critical components and enhance your process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality



















