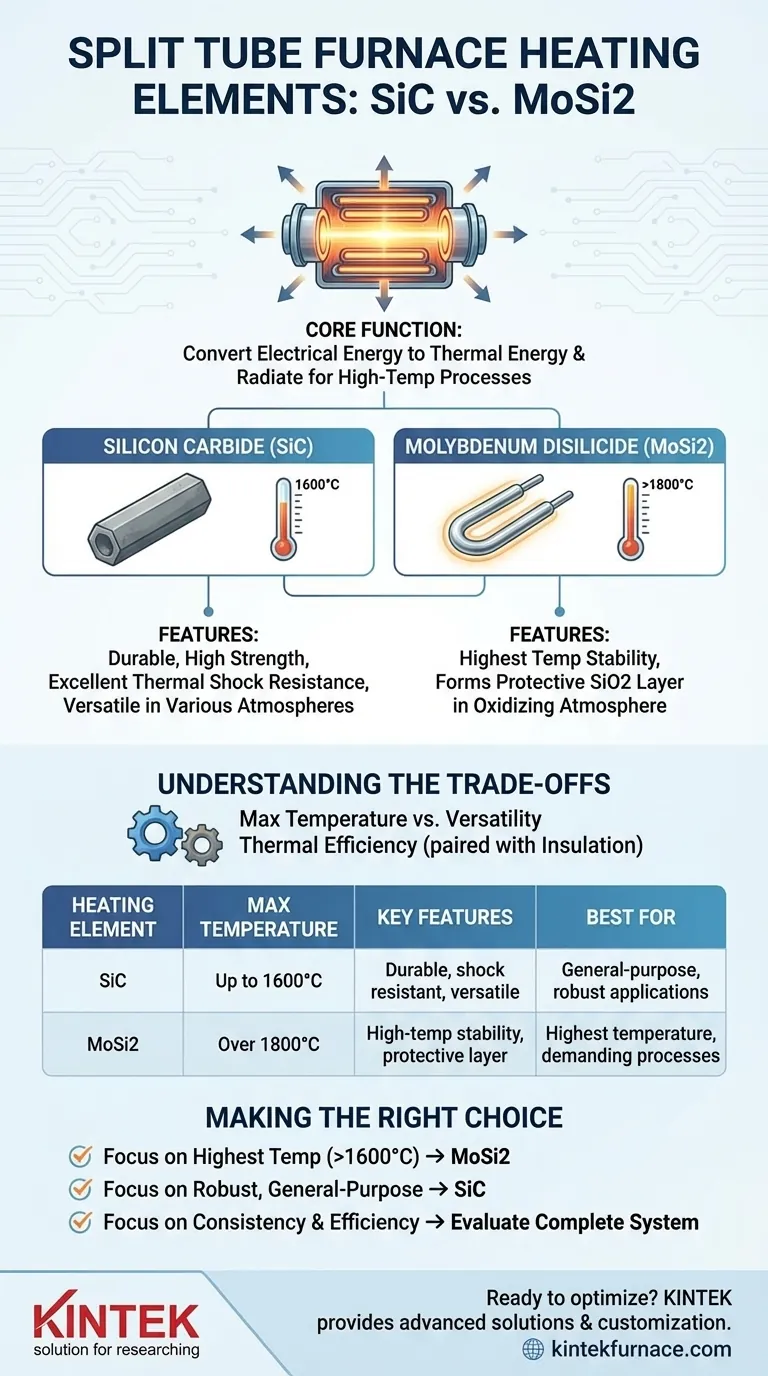
The primary heating elements used in modern split tube furnaces are overwhelmingly one of two materials: silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2). The choice between them is not arbitrary; it is dictated by the specific temperature requirements and atmospheric conditions of the intended application. These advanced ceramic materials are chosen for their ability to withstand extreme heat and efficiently transfer thermal energy.
The decision between heating elements is a critical engineering choice. While both SiC and MoSi2 are used for high-temperature work, MoSi2 is selected for the highest operational temperatures, whereas SiC offers robust performance across a slightly lower, yet still extensive, temperature range.
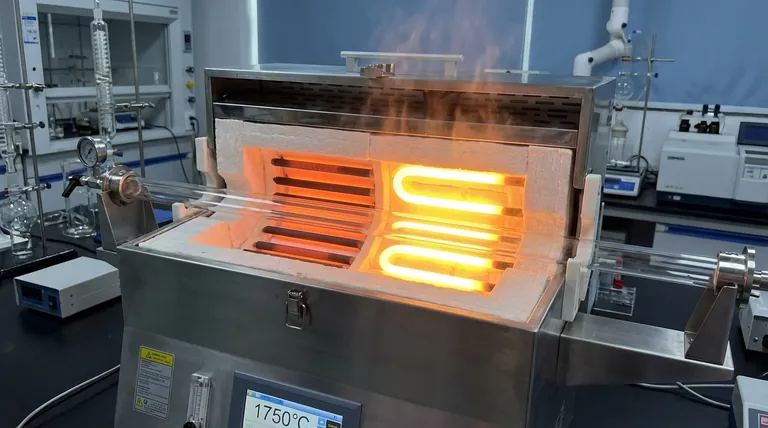

The Core Function of a Heating Element
A heating element is the heart of the furnace. Its sole purpose is to convert electrical energy into thermal energy and radiate that heat into the furnace chamber, enabling sophisticated material processing.
Transferring Thermal Energy
The element's material and design are optimized to generate and sustain high temperatures uniformly within the furnace's process tube. This ensures consistent results for sensitive applications like alloy treatment or crystal growth.
Enabling High-Temperature Processes
Researchers and engineers rely on these furnaces for processes that require precise thermal control. This includes metal and alloy heat treatment, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), sintering, and annealing, all of which are governed by the performance of the heating element.
A Closer Look at the Key Materials
The selection of a heating element material is a direct function of the process requirements. Both MoSi2 and SiC are standards in the industry, but they serve different operational envelopes.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
Molybdenum disilicide is the material of choice for the most demanding, highest-temperature applications, often capable of reaching over 1800°C.
It operates by forming a protective quartz-silica (SiO2) layer on its surface during heating in an oxidizing atmosphere. This layer prevents further oxidation of the underlying material, allowing it to function at extreme temperatures.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon carbide is an extremely durable and reliable heating element used for a vast range of high-temperature processes, typically up to 1600°C.
SiC elements are known for their high strength and excellent thermal shock resistance. They are versatile and can be used in a variety of atmospheres, making them a common workhorse in many research and industrial labs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace involves more than just looking at the maximum temperature. The heating element's properties create a series of trade-offs that impact performance, longevity, and cost.
Maximum Temperature vs. Versatility
While MoSi2 elements provide the highest temperature ceiling, they are most stable in an oxidizing atmosphere where their protective layer can form. Using them in other atmospheres can limit their lifespan or maximum temperature.
SiC elements, while having a lower maximum temperature, are often more forgiving and can operate effectively in a wider range of oxidizing, inert, or reducing atmospheres, offering greater process flexibility.
Thermal Efficiency and Furnace Design
The heating element does not work in isolation. For maximum efficiency, split tube furnaces incorporate graded layers of high-quality insulation and insulated vestibules at the ends of the chamber.
This complete thermal system is designed to minimize heat loss and ensure temperature uniformity. A high-performance element is only as effective as the insulation package that contains its energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection should be guided by a clear understanding of your primary experimental or production goal.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures (above 1600°C): A furnace equipped with molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements is the necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is robust, general-purpose heat treatment up to 1600°C: A silicon carbide (SiC) element provides an excellent balance of performance, durability, and operational flexibility.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and efficiency: Evaluate the heating element in the context of the furnace’s complete insulation system and temperature controls.
Understanding these core material properties empowers you to select a furnace configured precisely for your research or production goals.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element | Max Temperature | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C | Durable, thermal shock resistant, versatile in atmospheres | General-purpose heat treatment, robust applications |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Over 1800°C | High-temperature stability, protective SiO2 layer in oxidizing atmospheres | Highest temperature processes, demanding applications |
Ready to optimize your lab's high-temperature processes? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced split tube furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our heating elements can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















