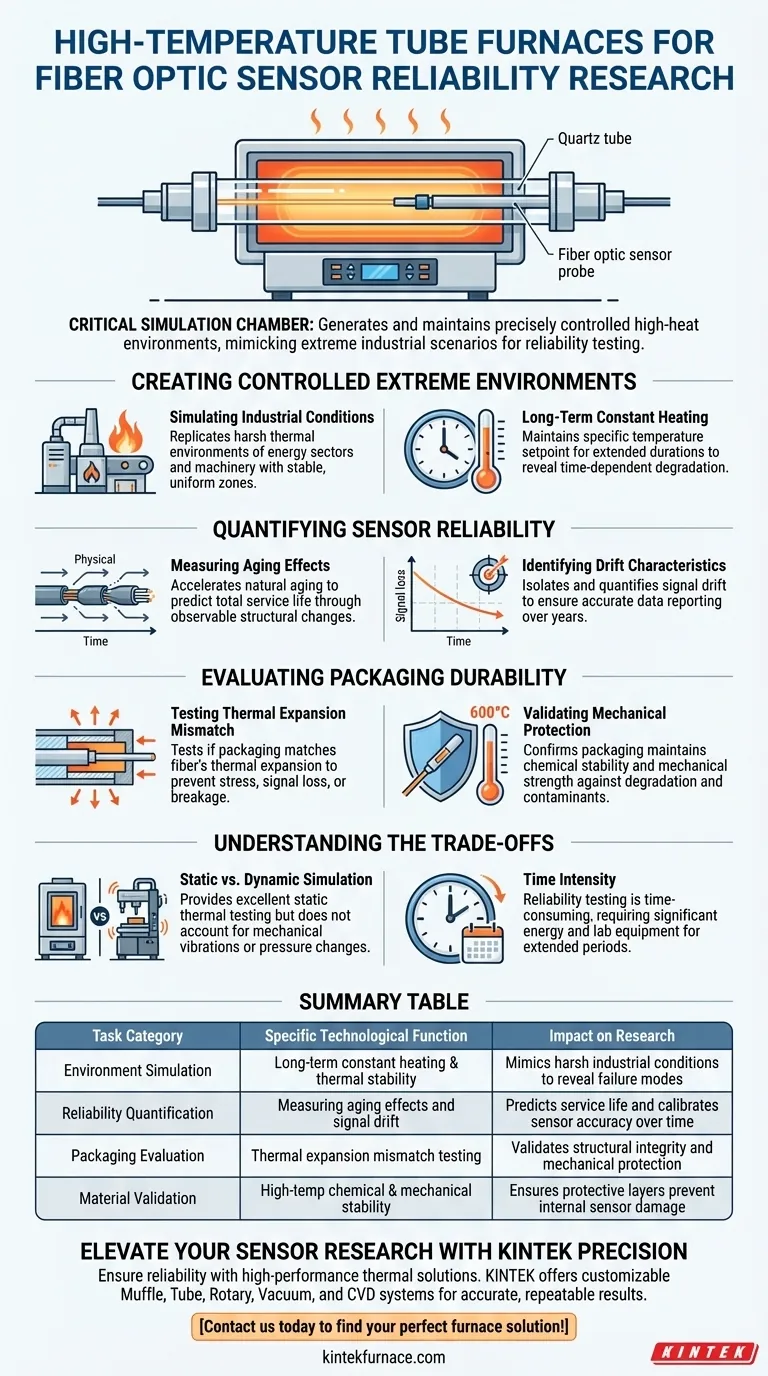
A high-temperature tube furnace functions as a critical simulation chamber for fiber optic reliability testing. Its primary technological task is to generate and maintain a precisely controlled high-heat environment that mimics extreme industrial scenarios. This allows researchers to subject sensors to long-term constant temperature heating, exposing potential failure mechanisms before the sensors are deployed in critical energy sectors.
By maintaining rigorous thermal consistency, these furnaces allow researchers to quantify signal drift and aging mechanics that only appear over extended periods. This process is indispensable for validating the long-term structural integrity of sensor packaging against thermal stress.
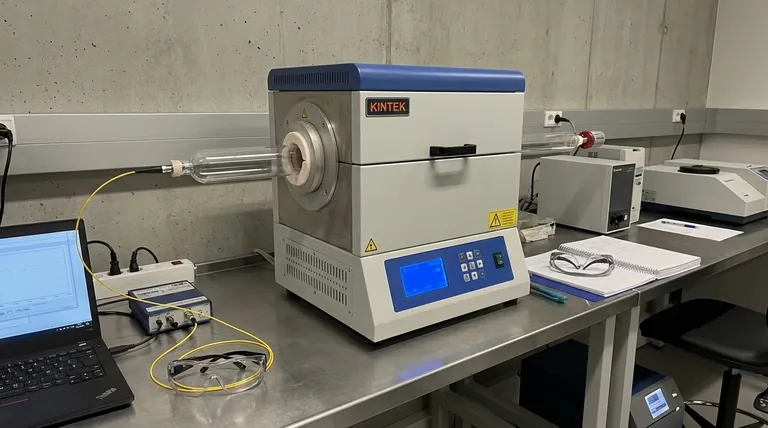

Creating Controlled Extreme Environments
Simulating Industrial Conditions
The core function of the furnace is to replicate the harsh thermal environments found in the energy sector.
Rather than simple heating, the furnace provides a stable, uniform zone that mimics the specific operating temperatures of industrial machinery or power generation systems.
Long-Term Constant Heating
Reliability testing requires more than a momentary spike in temperature; it demands endurance.
The tube furnace performs the task of maintaining a specific temperature setpoint for extended durations. This sustained exposure is the only way to reveal time-dependent degradation in the fiber optics.
Quantifying Sensor Reliability
Measuring Aging Effects
High temperatures accelerate the natural aging process of optical fibers.
By using the furnace to fast-track this timeline, researchers can observe physical changes in the fiber structure. This data is used to predict the total service life of the sensor under normal operating conditions.
Identifying Drift Characteristics
Sensors often lose accuracy when exposed to heat for long periods, a phenomenon known as "drift."
The furnace creates a baseline environment where this drift can be isolated and quantified. Understanding these characteristics is essential for calibrating sensors to ensure the data they report remains accurate over years of use.
Evaluating Packaging Durability
Testing Thermal Expansion Mismatch
The "packaging" (such as quartz tubes) protects the delicate fiber, but different materials expand at different rates when heated.
The furnace tests whether the packaging material matches the thermal expansion of the fiber itself. If the furnace reveals a mismatch, the resulting stress could cause signal loss or physical breakage.
Validating Mechanical Protection
The furnace ensures that the packaging maintains its chemical stability and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures (often up to 600°C).
This task confirms that the protective layer will not degrade or allow external contaminants to damage the internal microstructures of the sensor probe.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Static vs. Dynamic Simulation
While a tube furnace is excellent for thermal testing, it generally provides a static environment.
It simulates heat perfectly but does not account for mechanical vibrations or pressure changes often found in real-world industrial machinery. It isolates the thermal variable, but it is not a comprehensive field test.
Time Intensity
Reliability testing is inherently time-consuming.
Because the technological task involves "long-term" heating, obtaining actionable data can take days or weeks. This requires significant energy consumption and occupies lab equipment for extended periods for a single dataset.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To get the most value from your testing process, align your furnace usage with your specific research objective:
- If your primary focus is Life-Cycle Prediction: Prioritize long-term constant heating cycles to accurately model aging curves and predict failure points.
- If your primary focus is Material Selection: Focus on high-temperature stability tests to ensure your packaging materials (like quartz) do not induce stress on the fiber through thermal mismatch.
Reliability is not just about surviving heat; it is about maintaining precision while doing so.
Summary Table:
| Task Category | Specific Technological Function | Impact on Research |
|---|---|---|
| Environment Simulation | Long-term constant heating & thermal stability | Mimics harsh industrial conditions to reveal failure modes |
| Reliability Quantification | Measuring aging effects and signal drift | Predicts service life and calibrates sensor accuracy over time |
| Packaging Evaluation | Thermal expansion mismatch testing | Validates structural integrity and mechanical protection |
| Material Validation | High-temp chemical & mechanical stability | Ensures protective layers prevent internal sensor damage |
Elevate Your Sensor Research with KINTEK Precision
Ensure the reliability of your fiber optic technology with high-performance thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a wide range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory requirements. Whether you are conducting long-term aging studies or testing material expansion, our high-temp furnaces provide the uniform heat control you need to achieve accurate, repeatable results.
Ready to optimize your testing process? Contact us today to find your perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Stephan Krenek, K. Anhalt. Fibre-optic thermometry to support the clean energy transition. DOI: 10.1515/teme-2025-0044
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the technical necessity of using a tube furnace in the synthesis of CoFe@HNCS? Master Co-Shell Nanostructures
- What materials can be melted in horizontal tube furnaces? Unlock precise high-temperature melting for metals, ceramics, and more
- Why is environment control in a tube furnace critical for NASICON? Optimize Ionic Conductivity and Density
- Why is a horizontal tube furnace used for CVD in catalyst synthesis? Achieve Precise Nano-Material Growth
- Why is the chemical composition of the alloy used in tube reactors critical? Insights into Ethane Cracking Results
- Why use a tube furnace instead of a muffle furnace for annealing? Achieve Superior Process Control
- What does the horizontal orientation refer to in tube furnaces? Discover Its Benefits and Applications
- How does a high-temperature quartz tube reactor facilitate the synthesis of PC-CNT microspheres? Expert Insights



















