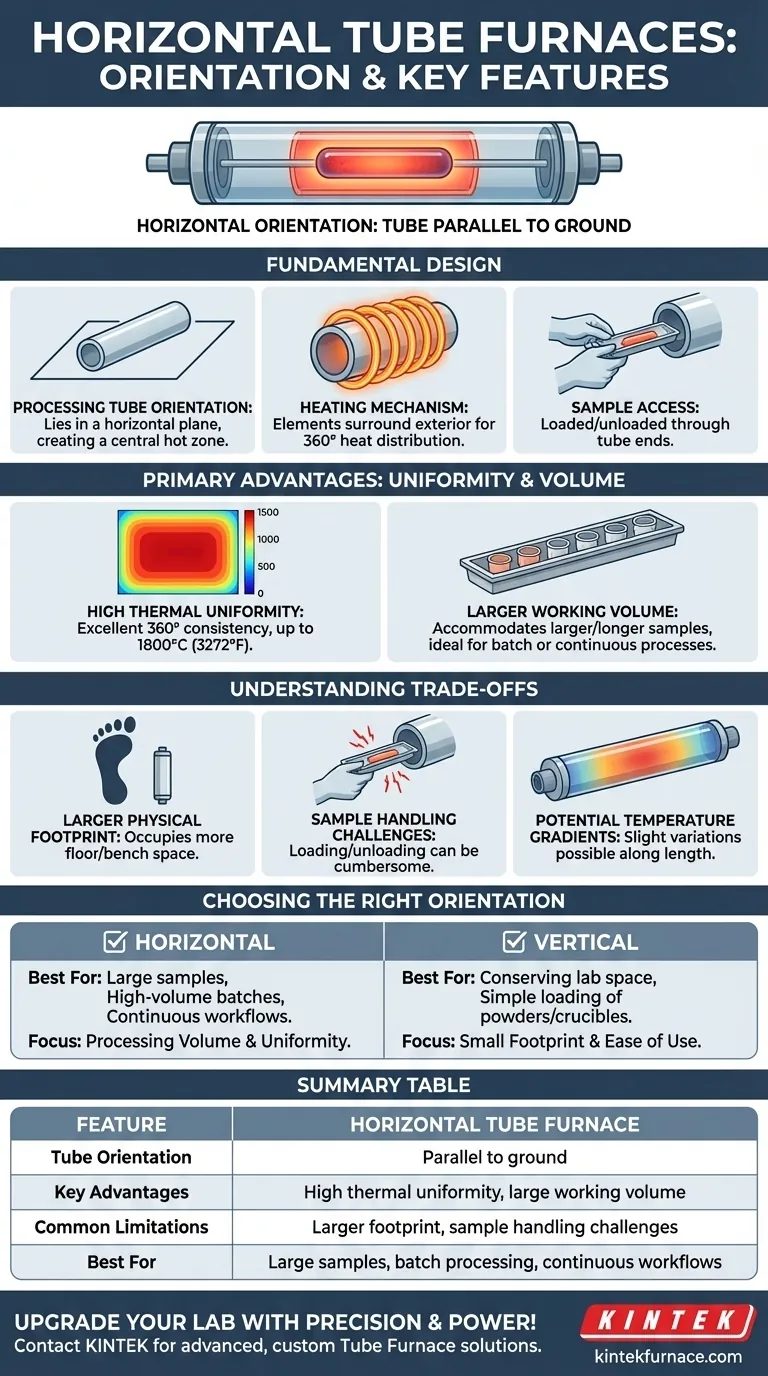
In the context of tube furnaces, horizontal orientation refers to the design where the cylindrical processing tube is positioned parallel to the ground. This configuration means the sample is loaded into a chamber that lies flat, passing through a central heated zone, much like a log resting on the floor.
A horizontal tube furnace prioritizes a large processing volume and excellent thermal uniformity around the sample's circumference. However, this design comes at the cost of a larger physical footprint and can introduce specific challenges in sample handling compared to a vertical orientation.

The Fundamental Design of a Horizontal Tube Furnace
A horizontal tube furnace is defined by its core structural layout, which directly influences its operation and best-fit applications.
The Processing Tube Orientation
The defining feature is that the tube, which contains the sample, lies in a horizontal plane. The furnace body is built around this tube, creating a central "hot zone" where the highest and most uniform temperatures are achieved.
Heating Mechanism
Heating elements, such as wire or silicon carbide rods, typically surround the exterior of the processing tube. This ensures heat is applied to the sample from its full 360° axis, which is crucial for consistent heat distribution around its circumference.
Sample Access
Samples are loaded and unloaded through the ends of the tube. These access points often feature end plugs or caps that may protrude from the furnace body, allowing for easier handling and the creation of controlled atmospheres within the tube.
Primary Advantages: Uniformity and Volume
The horizontal design offers two significant advantages that make it the preferred choice for certain industrial and laboratory processes.
High Potential for Thermal Uniformity
The 360-degree heating inherent in a tube furnace design provides excellent temperature consistency around the sample. Horizontal furnaces are engineered to extend this uniformity along the length of the sample, capable of sustaining temperatures up to 1800°C (3272°F).
Larger Working Volume
By design, horizontal furnaces can accommodate larger and longer samples compared to their vertical counterparts. This makes them highly suitable for processing multiple samples simultaneously in batches or for handling continuous production workflows where material is fed through the tube.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the horizontal orientation is not without its practical limitations. Acknowledging these trade-offs is critical for making an informed decision.
Larger Physical Footprint
Horizontal furnaces inherently occupy more floor or bench space. Their length requires a dedicated area, which can be a significant constraint in laboratories where space is at a premium.
Challenges in Sample Handling
Loading and unloading samples can be more cumbersome in a horizontal tube. Unlike a vertical furnace where gravity can assist in positioning samples, materials must be carefully pushed into and pulled from the horizontal chamber, which can be difficult.
Potential for Temperature Gradients
While uniformity is a key goal, the horizontal orientation can sometimes introduce slight temperature variations along the length of the tube. Achieving a perfectly flat temperature profile often requires careful furnace design and process optimization.
Choosing the Right Orientation for Your Application
Your choice between a horizontal or vertical furnace should be driven by your specific goals and physical constraints.
- If your primary focus is processing large samples or high-volume batches: A horizontal furnace is the superior choice due to its larger working volume and suitability for continuous workflows.
- If your primary focus is conserving lab space: A vertical furnace is generally more suitable due to its smaller, benchtop-friendly footprint.
- If your primary focus is simple loading of powders or crucibles: A vertical furnace may be more convenient, as it allows samples to be easily lowered or dropped into the hot zone.
Ultimately, understanding these core design trade-offs empowers you to select the furnace that directly aligns with your processing requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Horizontal Tube Furnace |
|---|---|
| Tube Orientation | Parallel to ground |
| Key Advantages | High thermal uniformity, large working volume |
| Common Limitations | Larger footprint, sample handling challenges |
| Best For | Large samples, batch processing, continuous workflows |
Upgrade your lab with precision and power! KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces, designed to meet your unique needs. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization for optimal performance in thermal uniformity and large-volume processing. Whether you're handling industrial batches or complex experiments, our expertise ensures reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What advantages do multi zone tube furnaces offer for chemical reaction studies? Achieve Precise Thermal Control
- What preparations are needed before starting a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safety and Accuracy in Your Lab
- How do multi zone tube furnaces improve laboratory efficiency? Boost Throughput with Parallel Processing
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- What safety precautions should be followed when operating a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Lab Operations



















