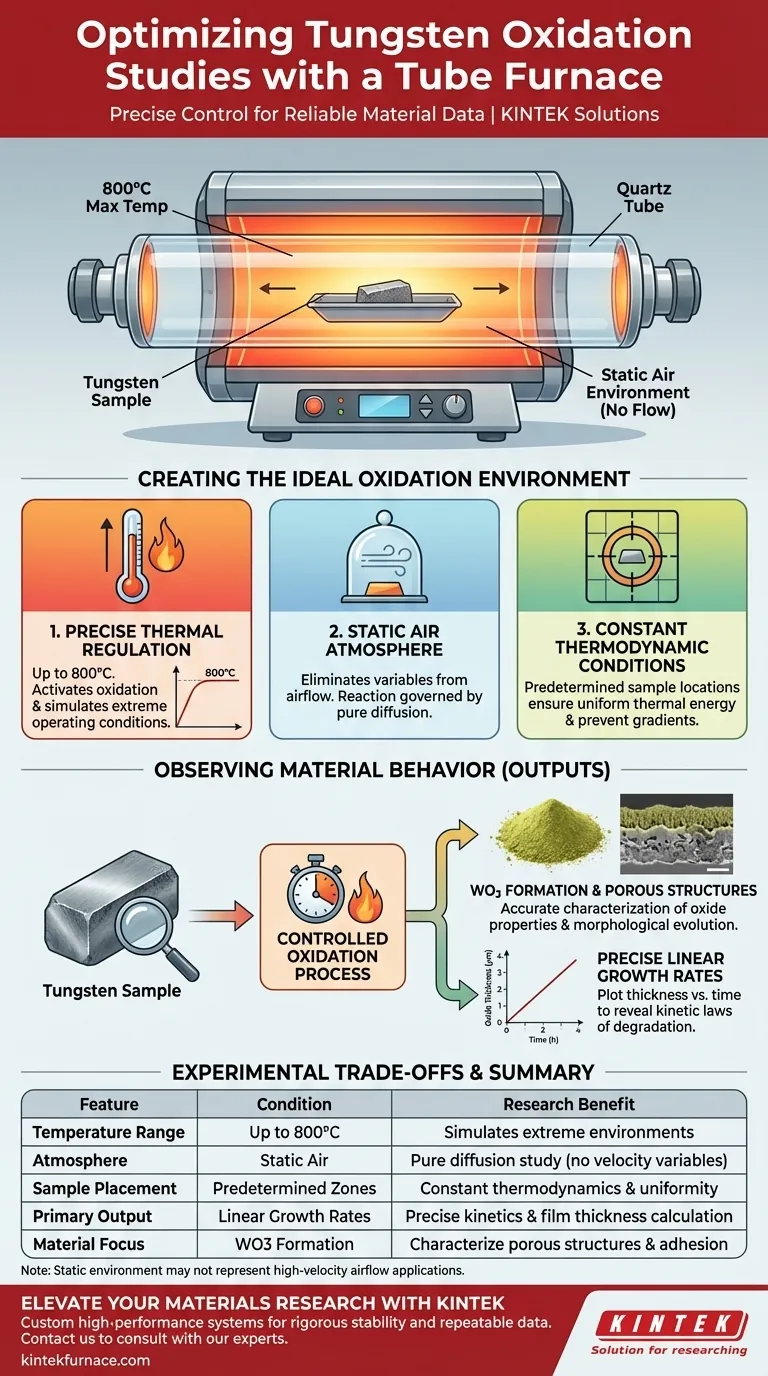
To study the oxidation characteristics of tungsten, a Tube Furnace provides a precisely controlled, high-temperature static air environment. Specifically, it allows for heat treatment up to 800°C, creating a stable thermal zone where samples are placed at predetermined locations. This setup ensures constant thermodynamic conditions, which are critical for isolating the variables necessary to accurately measure oxidation kinetics.
The primary value of the Tube Furnace in this context is stability. By eliminating environmental fluctuations, it allows researchers to accurately correlate temperature and time with the linear growth rate of tungsten trioxide films and the formation of porous structures.
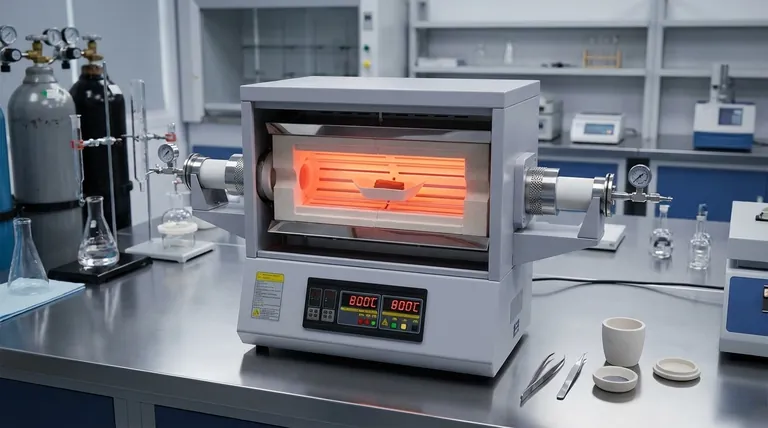

Creating the Ideal Oxidation Environment
To generate reliable data on material degradation and oxide formation, the experimental environment must be rigorously controlled. The Tube Furnace achieves this through three specific mechanisms.
Precise Thermal Regulation
The furnace is capable of reaching and maintaining temperatures up to 800°C.
This high-temperature capability is essential for activating the oxidation process in tungsten. It allows researchers to simulate extreme operating environments or accelerate aging processes to study material lifecycles.
Static Air Atmosphere
The equipment provides a static air environment rather than a dynamic flow.
This eliminates variables introduced by air velocity or fluctuating gas concentrations. In a static environment, the interaction between the tungsten surface and oxygen is governed purely by diffusion and chemical reaction rates, simplifying the analysis of kinetic data.
Constant Thermodynamic Conditions
By positioning samples at predetermined locations within the heating zone, the furnace maintains constant thermodynamic conditions.
This spatial precision ensures that the thermal energy applied to the sample remains uniform throughout the experiment. It prevents thermal gradients that could skew data regarding reaction rates or structural changes.
Observing Material Behavior
The conditions provided by the Tube Furnace are specifically tuned to observe how tungsten transforms chemically and physically over time.
Measuring Linear Growth Rates
The stable environment allows for the precise measurement of the linear growth rate of oxidation films.
Because the temperature and atmosphere are held constant, researchers can plot the thickness of the oxide layer against time. This reveals the specific kinetic laws governing the degradation of the material.
Formation of Tungsten Trioxide
The furnace facilitates the specific chemical reaction required to form tungsten trioxide (WO3).
By controlling the heat input, researchers can drive the oxidation reaction to this specific state. This allows for detailed characterization of the oxide's properties and its adhesion to the base metal.
Developing Porous Structures
The setup is instrumental in studying the formation process of porous structures within the oxide layer.
Understanding how and why these pores form is vital for predicting material failure. The controlled heat treatment reveals the morphological evolution of the surface, providing insights into the material's long-term durability.
Understanding Experimental Trade-offs
While the Tube Furnace is essential for these experiments, it is important to recognize the inherent limitations of the setup described to ensure your data is interpreted correctly.
Static vs. Dynamic Limitations
The system utilizes a static air environment, which is excellent for studying fundamental kinetics but may not represent real-world applications where airflow is present.
If your ultimate application involves high-velocity gas flows (such as in aerospace turbines), data derived from a static environment may need to be adjusted. The static nature focuses on intrinsic material properties rather than aerodynamic interactions.
Temperature Ceilings
The specific configuration described operates up to 800°C.
While sufficient for studying tungsten trioxide formation, this may not capture behaviors that occur at ultra-high refractory temperatures. Researchers must ensure that 800°C covers the full phase transformation range relevant to their specific study.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
When utilizing a Tube Furnace for tungsten oxidation, align your experimental design with the specific capabilities of the equipment.
- If your primary focus is Kinetics: Utilize the constant thermodynamic conditions to derive precise linear growth rates of the oxide film without environmental noise.
- If your primary focus is Morphology: Use the predetermined sample positioning to ensure uniform heat distribution, allowing for the consistent formation and analysis of porous surface structures.
By leveraging the stability of the Tube Furnace, you transform variable heat treatment into quantifiable scientific data.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Experimental Condition | Research Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Up to 800°C | Simulates extreme environments & activates oxidation |
| Atmosphere | Static Air | Eliminates air velocity variables for pure diffusion study |
| Sample Placement | Predetermined Zones | Ensures constant thermodynamic conditions & uniformity |
| Primary Output | Linear Growth Rates | Precise calculation of oxidation kinetics & film thickness |
| Material Focus | WO3 Formation | Accurate characterization of porous structures & adhesion |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precision is the backbone of scientific discovery. KINTEK provides high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to deliver the rigorous stability required for advanced oxidation studies and material characterization.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique temperature and atmospheric needs—ensuring your data remains accurate and repeatable.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact KINTEK Today to Consult with Our Experts
Visual Guide
References
- James R. Miller, T.W. Clyne. Profilometry‐Based Indentation Plastometry Testing of Tungsten at High Temperature. DOI: 10.1002/adem.202500292
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of quartz tube furnaces? Limitations in Durability and Temperature
- In which fields are fluidized bed vertical tube furnaces commonly applied? Explore Key Uses in Materials Science and Energy
- Why are vacuum sealing and quartz tubes needed for FeSiBPCCuNb heat treatment? Achieve Pure Magnetic Properties
- What are the main components of a 70mm tube furnace? Uncover Key Parts for Precise Thermal Processing
- What are the primary applications of high temperature tube furnaces? Unlock Precise Heat Control for Materials Science
- What is the material of the anode in a vacuum tube? Choosing the Right Metal for Power & Performance
- What is an atmosphere tube furnace? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What physical conditions does a high-temperature tube furnace provide? Optimize Lignin Carbonization Success



















