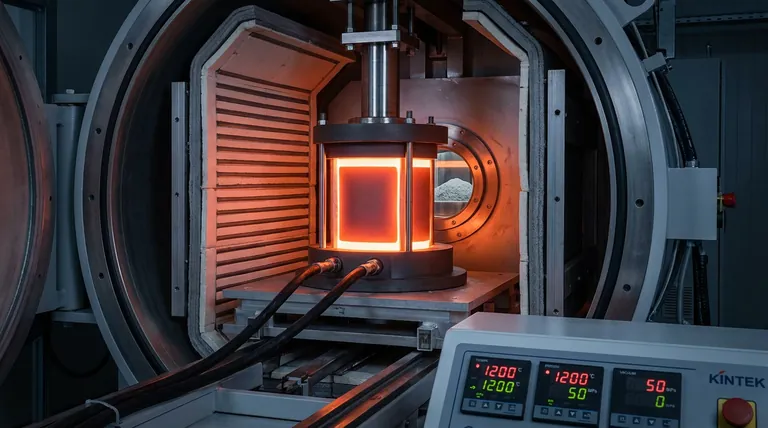
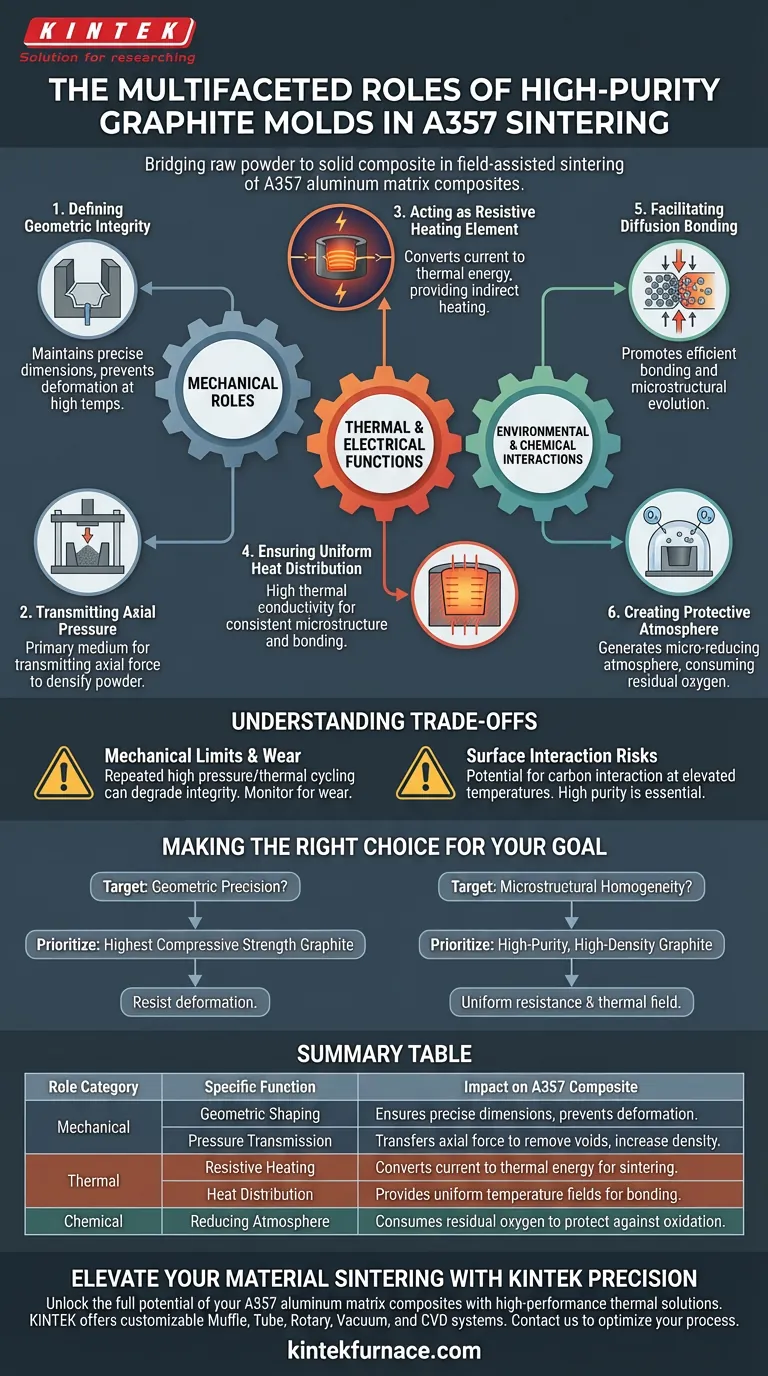
High-purity graphite molds act as the functional heart of the sintering process, bridging the gap between raw powder and a solid composite. In field-assisted sintering of A357 aluminum matrix composites, these molds serve a trifecta of roles: they act as a precise forming container, a mechanical medium for transmitting high axial pressure, and an active heating element that converts electrical current into thermal energy.
Core Takeaway Graphite molds are not merely passive containers; they are active thermal and mechanical components that drive the densification process. By enabling simultaneous heating and pressure application in a vacuum, they facilitate the diffusion bonding and microstructural evolution required for high-performance composites.
Mechanical Roles in Densification
Defining Geometric Integrity
The most immediate role of the high-purity graphite mold is acting as a shaping container.
It defines the final geometry of the A357 aluminum matrix composite sample.
Because graphite maintains excellent mechanical strength at high temperatures, it ensures the sample retains its specific dimensions (such as a precise diameter) without deformation.
Transmitting Axial Pressure
Sintering often requires significant force to densify the powder into a bulk solid.
The graphite mold functions as the primary mechanical medium to transmit this force.
It transfers externally applied axial pressure (often hydraulic) directly to the powder, facilitating the compaction necessary to remove voids and increase density.
Thermal and Electrical Functions
Acting as a Resistive Heating Element
In field-assisted sintering processes, the mold takes on an active electrical role.
Due to its excellent electrical conductivity, the graphite generates heat when current passes through it.
This provides "indirect heating" to the composite sample, converting electrical energy into the thermal energy required for sintering.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Distribution
Achieving a consistent microstructure requires an even temperature field.
Graphite’s high thermal conductivity ensures that the heat generated is distributed uniformly across the composite powder.
This uniformity is critical for forming stable interfacial bonding layers and preventing localized defects within the aluminum matrix.
Environmental and Chemical Interactions
Facilitating Diffusion Bonding
The combination of pressure and heat provided by the mold creates a synergistic effect.
This environment promotes efficient diffusion bonding between the matrix and reinforcements.
It drives the evolution of the microstructure, ensuring that the final material achieves the desired mechanical properties.
Creating a Protective Atmosphere
Operating within a vacuum environment, the graphite mold helps manage the chemical stability of the process.
At high temperatures, graphite can generate a micro-reducing atmosphere.
This helps consume residual oxygen, offering a layer of protection against excessive oxidation of the aluminum or reinforcement interfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Mechanical Limits and Wear
While graphite is strong, it is not indestructible.
Repeated exposure to high pressures (e.g., 35–70 MPa) and thermal cycling can eventually degrade the mold's structural integrity.
Users must monitor molds for wear to prevent geometric inaccuracies in the final sintered part.
Surface Interaction Risks
Graphite is chemically active at elevated temperatures.
While the "self-lubricating" property of graphite generally assists in demolding, there is a potential for carbon to interact with the metal matrix if conditions are not precisely controlled.
High-purity graphite is essential to minimize contamination and ensure the surface quality of the composite is not compromised.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the sintering of A357 aluminum matrix composites, select your graphite specifications based on your specific processing targets:
- If your primary focus is Geometric Precision: Prioritize graphite grades with the highest available compressive strength to resist deformation under high axial loads.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Homogeneity: Ensure the use of high-purity, high-density graphite to guarantee uniform electrical resistance and consistent thermal field distribution.
Success in sintering lies in viewing the mold not as a consumable, but as a critical process parameter that dictates the final quality of your material.
Summary Table:
| Role Category | Specific Function | Impact on A357 Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Geometric Shaping | Ensures precise dimensions and prevents sample deformation. |
| Mechanical | Pressure Transmission | Transfers axial force to remove voids and increase material density. |
| Thermal | Resistive Heating | Converts electrical current into thermal energy for efficient sintering. |
| Thermal | Heat Distribution | Provides uniform temperature fields for stable interfacial bonding. |
| Chemical | Reducing Atmosphere | Consumes residual oxygen to protect against aluminum oxidation. |
Elevate Your Material Sintering with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your A357 aluminum matrix composites with high-performance thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory and production requirements.
Whether you need superior thermal uniformity or high-pressure capabilities, our expert team is ready to help you optimize your process. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our lab high-temperature furnaces can drive your next material breakthrough!
Visual Guide
References
- Sarah Johanna Hirsch, Thomas Lampke. Combined Effect of Particle Reinforcement and T6 Heat Treatment on the Compressive Deformation Behavior of an A357 Aluminum Alloy at Room Temperature and at 350 °C. DOI: 10.3390/cryst14040317
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of the laboratory furnace? Master Material Transformation with Precision Heating
- What are the technical considerations for selecting a graphite crucible? Expert Insights for Molten Salt Electrolysis
- How does a high-precision heating stage contribute to the drying and crystallization of FAPbBr3 nanosheets?
- What is the role of a Teflon-lined autoclave in CQD synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Carbonization for Precision Carbon Dots
- What is the primary function of an alumina crucible in CsV3Sb5 growth? Ensure High Purity and Thermal Stability
- How is a dual-color infrared thermometer used to evaluate (Hf─Zr─Ti)C ceramic coatings? Precision Thermal Monitoring
- What characteristics are required for reaction vessels in PI-COFs synthesis? Ensure High-Pressure Safety and Purity
- What is the technical purpose of double-sealing raw materials in vacuum quartz tubes? Expert Synthesis Guide















