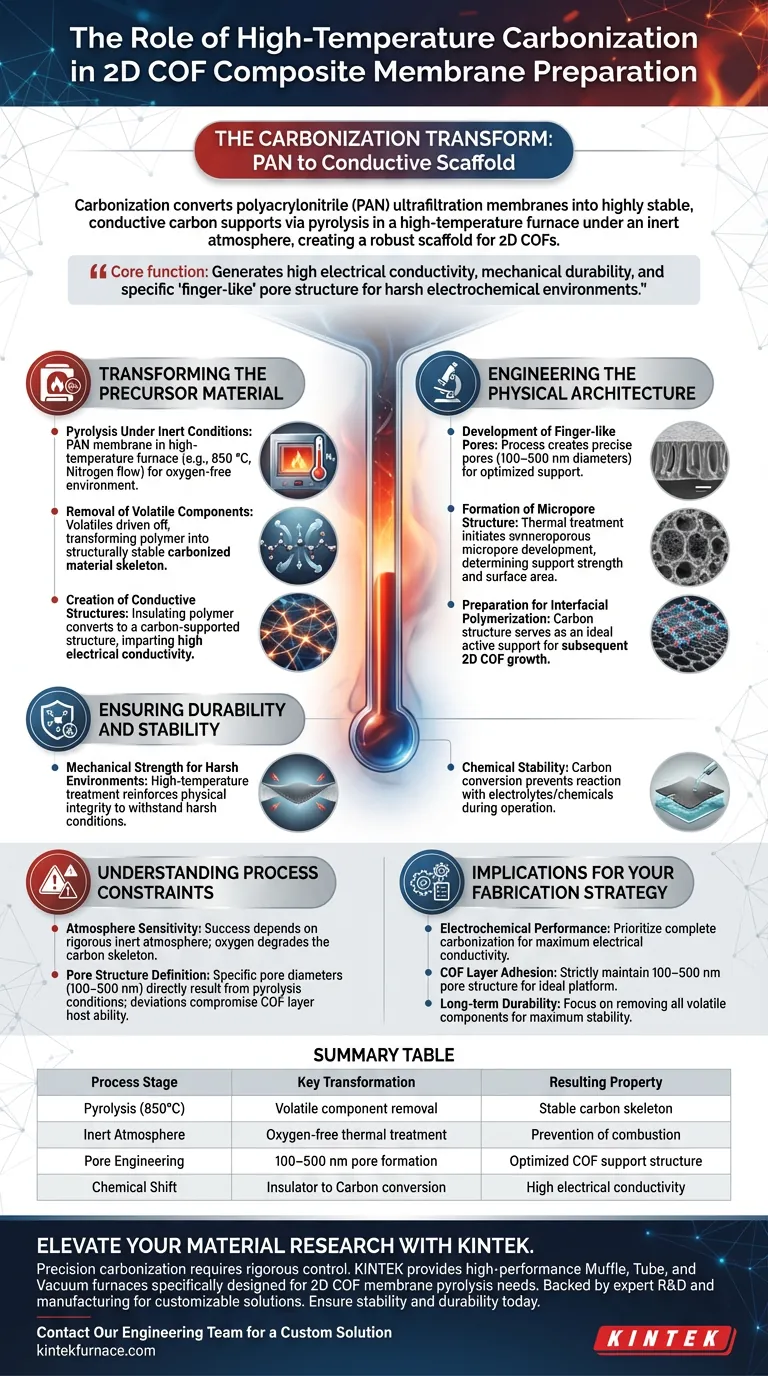
The carbonization process acts as a transformative step that converts polyacrylonitrile (PAN) ultrafiltration membranes into highly stable, conductive carbon supports. By subjecting the polymer to pyrolysis in a high-temperature furnace under an inert atmosphere, the process creates a robust scaffold optimized for the subsequent growth of 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs).
The core function of this thermal treatment is to fundamentally alter the material's chemistry, generating the high electrical conductivity, mechanical durability, and specific "finger-like" pore structure required to support the active COF layer in harsh electrochemical environments.

Transforming the Precursor Material
Pyrolysis Under Inert Conditions
The process utilizes a high-temperature furnace to subject the PAN membrane to pyrolysis. This must occur in a strictly oxygen-free environment (such as a nitrogen flow at 850 °C) to prevent combustion.
Removal of Volatile Components
As the temperature rises, volatile components within the organic precursors are driven off. This removal transforms the original polymer into a structurally stable carbonized material skeleton.
Creation of Conductive Structures
The most critical chemical change is the conversion of the insulating polymer into a carbon-supported structure. This imparts high electrical conductivity to the membrane, a property essential for its function in electrochemical applications.
Engineering the Physical Architecture
Development of Finger-like Pores
Carbonization does not just harden the material; it engineers its porosity. The process creates finger-like pore structures with precise diameters ranging from 100 to 500 nanometers.
Formation of the Micropore Structure
Beyond the larger finger-like pores, the thermal treatment initiates the development of a micropore structure. This internal architecture determines the support strength and provides the necessary surface area for subsequent steps.
Preparation for Interfacial Polymerization
The resulting carbon structure serves as an ideal active support platform. It provides the physical foundation necessary for the subsequent interfacial polymerization growth of the 2D COFs.
Ensuring Durability and Stability
Mechanical Strength for Harsh Environments
The high-temperature treatment reinforces the physical integrity of the membrane. This ensures the material possesses the mechanical strength required to withstand harsh operating conditions without degrading.
Chemical Stability
By converting the organic polymer into carbon, the membrane achieves superior chemical stability. This prevents the support layer from reacting strictly with the electrolytes or other chemicals it may encounter during operation.
Understanding the Process Constraints
Atmosphere Sensitivity
The success of this process is entirely dependent on maintaining a rigorous inert atmosphere. Any introduction of oxygen during the high-temperature phase will degrade the carbon skeleton rather than strengthen it.
Pore Structure Definition
The specific pore diameters (100–500 nm) are a direct result of the pyrolysis conditions. Deviations in temperature or ramp rates could alter this pore size, potentially compromising the ability of the support to host the 2D COF layer effectively.
Implications for Your Fabrication Strategy
To apply these principles effectively to your membrane fabrication, consider your specific performance targets:
- If your primary focus is Electrochemical Performance: Prioritize the completeness of the carbonization to maximize electrical conductivity within the support scaffold.
- If your primary focus is COF Layer Adhesion: Ensure the pyrolysis conditions strictly maintain the 100–500 nm pore structure to provide the ideal physical platform for interfacial polymerization.
- If your primary focus is Long-term Durability: Focus on the removal of all volatile components to ensure the carbon skeleton achieves maximum chemical and mechanical stability.
The carbonization process is the bridge between a raw polymer precursor and a functional, conductive platform capable of hosting advanced 2D materials.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Transformation | Resulting Property |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis (850°C) | Volatile component removal | Stable carbon skeleton |
| Inert Atmosphere | Oxygen-free thermal treatment | Prevention of combustion |
| Pore Engineering | 100–500 nm pore formation | Optimized COF support structure |
| Chemical Shift | Insulator to Carbon conversion | High electrical conductivity |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision carbonization requires rigorous control over temperature and atmosphere. KINTEK provides high-performance Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum furnaces specifically designed to handle the complex pyrolysis needs of 2D Covalent Organic Framework (COF) membranes.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to help you achieve the precise pore structures and conductivity your electrochemical applications demand. Ensure the stability and durability of your composite membranes today.
Contact Our Engineering Team for a Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Jin Hyuk Cho, Soo Young Kim. Advancements in two-dimensional covalent organic framework nanosheets for electrocatalytic energy conversion: current and future prospects. DOI: 10.20517/energymater.2023.72
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does a bidirectional alternating cyclic gas quenching system improve results? Eliminate the Shadow Effect
- How does a high-temp vacuum sintering furnace facilitate RS-SiC sintering? Achieve Peak Density & Purity
- Why are modern vacuum furnaces designed with gas injection systems up to 20 bar? Unlock Rapid Quenching Versatility
- How does a vacuum furnace improve smelting quality? Achieve Purer, Stronger Metals for Your Applications
- Why is precise cooling control essential in sintering stainless steel MIM parts? Unlock Peak Material Integrity
- How does a vacuum furnace work? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What factors should be considered when choosing a vacuum furnace model? Key Insights for Optimal Performance
- What is a vacuum furnace and what are its main advantages? Discover Superior Material Processing



















