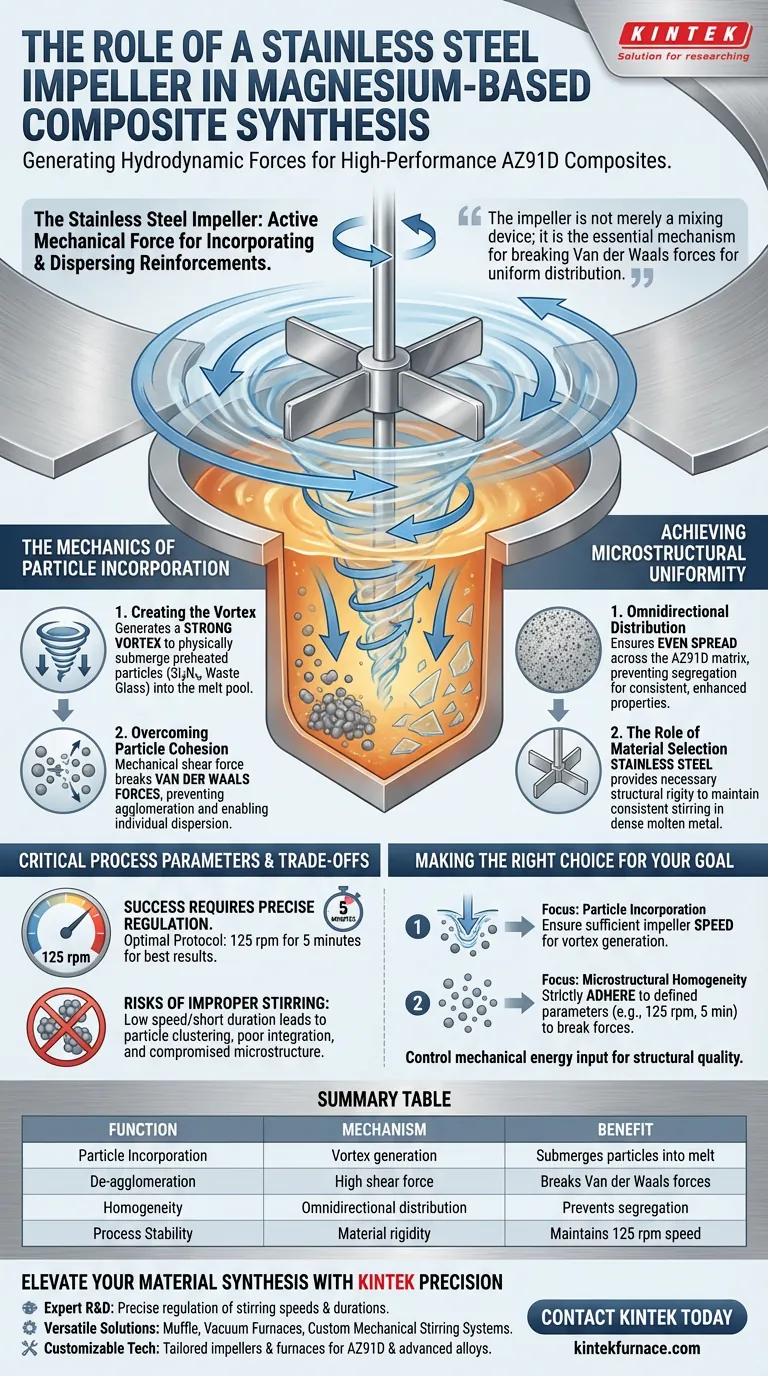
The stainless steel impeller serves as the active mechanical force required to successfully incorporate and disperse solid reinforcements into a liquid magnesium matrix. By generating a hydrodynamic vortex, the impeller physically submerges preheated particles—specifically silicon nitride and waste glass—into the melt pool while actively shearing apart particle clusters.
The impeller is not merely a mixing device; it is the essential mechanism for breaking Van der Waals forces between particles to ensure the uniform, omnidirectional distribution required for high-performance AZ91D composites.
The Mechanics of Particle Incorporation
Creating the Vortex
The primary function of the impeller is to generate a strong vortex within the molten magnesium.
Without this vortex, lightweight reinforcement particles would likely float on the surface rather than mixing with the alloy.
The mechanical action forces preheated silicon nitride and waste glass particles directly into the melt pool, initiating the composite synthesis.
Overcoming Particle Cohesion
At the microscopic level, particles naturally attract one another due to Van der Waals forces.
If left unchecked, these forces cause particles to agglomerate, leading to weak spots in the final material.
The mechanical stirring action provides the shear force necessary to break these bonds, separating the particles for individual dispersion.
Achieving Microstructural Uniformity
Omnidirectional Distribution
For a magnesium-based composite to perform well, the reinforcement phases must be spread evenly throughout the material.
The impeller ensures an omnidirectional distribution of particles within the AZ91D matrix.
This uniformity prevents segregation, ensuring that the enhanced properties of the composite are consistent in all directions.
The Role of Material Selection
The use of a stainless steel impeller is specific to this environment.
It provides the necessary structural rigidity to maintain consistent stirring speeds within the dense, molten metal environment.
This durability is essential for sustaining the mechanical action throughout the duration of the synthesis.
Critical Process Parameters and Trade-offs
The Necessity of Precise Regulation
Success in this process is not guaranteed simply by turning on the mixer; it requires precise regulation of stirring parameters.
The mechanical action is highly sensitive to variables such as stirring speed and duration.
Optimal results, as indicated by specific synthesis protocols, often require a speed of 125 rpm maintained for a duration of 5 minutes.
Risks of Improper Stirring
If the stirring speed is too low or the duration too short, the Van der Waals forces may not be fully overcome.
This results in particle clustering and poor integration with the matrix.
Conversely, while not explicitly detailed in the source, deviating significantly from established parameters like the 125 rpm benchmark risks compromising the high-performance microstructure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the successful synthesis of magnesium-based composites, you must treat the stirring process as a precise science rather than a general mixing step.
- If your primary focus is Particle Incorporation: Ensure the impeller speed is sufficient to create a vortex that physically pulls preheated silicon nitride and waste glass particles below the surface of the melt.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Homogeneity: Strictly adhere to defined parameters, such as 125 rpm for 5 minutes, to effectively break Van der Waals forces and achieve uniform distribution in the AZ91D matrix.
Control the mechanical energy input with precision to dictate the structural quality of your final composite.
Summary Table:
| Function | Mechanism | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Incorporation | Vortex generation | Submerges particles (Si3N4, waste glass) into melt |
| De-agglomeration | High shear force | Breaks Van der Waals forces between particles |
| Homogeneity | Omnidirectional distribution | Prevents segregation in the AZ91D matrix |
| Process Stability | Material rigidity | Maintains 125 rpm speed in dense molten metal |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect microstructural uniformity in magnesium-based composites requires more than just mixing—it requires engineering excellence. KINTEK provides high-performance stirring systems designed to withstand the rigors of molten metal synthesis.
Why partner with KINTEK?
- Expert R&D: Our systems are engineered for precise regulation of stirring speeds and durations.
- Versatile Solutions: From Muffle and Vacuum furnaces to custom Mechanical Stirring Systems, we support your entire high-temp workflow.
- Customizable Tech: Tailor your impeller and furnace specs to meet the unique demands of AZ91D and other advanced alloys.
Contact KINTEK today to discover how our advanced lab furnaces and stirring solutions can enhance your composite research and production!
Visual Guide
References
- Shubham Sharma, Emad A. A. Ismail. Enhancing tribo-mechanical, microstructural morphology, and corrosion performance of AZ91D-magnesium composites through the synergistic reinforcements of silicon nitride and waste glass powder. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-52804-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 304 316 Stainless Steel High Vacuum Ball Stop Valve for Vacuum Systems
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three Section Clamp
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What makes induction furnaces suitable for precious metals processing? Unlock Purity and Efficiency in Metal Melting
- What solutions are implemented for vacuum induction melting (VIM)? Achieve Superior Alloy Purity and Performance
- What is the role of a vacuum arc furnace in the synthesis of AlCrFeNi HEAs? Achieve High-Purity Material Homogeneity
- What are the two types of induction furnaces? Channel vs. Coreless Furnace Explained
- What factors should be considered when selecting an induction melting furnace for a business? Maximize Efficiency and ROI
- Why is repeated flipping and remelting necessary when producing Sm-Co-Fe alloy ingots in an arc furnace? Key Insights
- How does induction heating work in a vacuum environment? Achieve High-Purity, Contamination-Free Heat Treatment
- What experimental environment does a vacuum induction furnace provide for HRB400? Ensure Ultra-Purity Steel Research



















