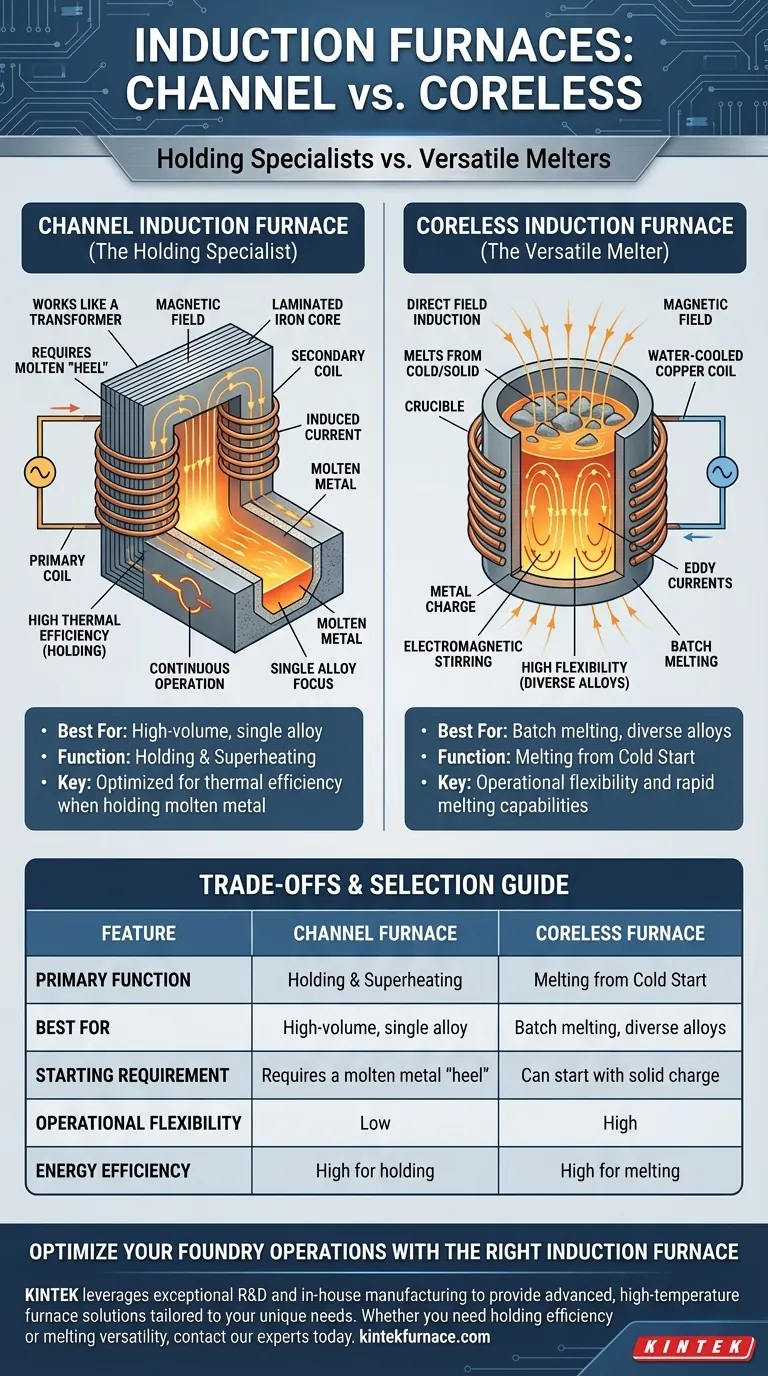
The two primary types of induction furnaces are the channel furnace (also known as a core-type furnace) and the coreless furnace. A channel furnace operates like a transformer, using an iron core to induce current into a loop of molten metal. In contrast, a coreless furnace induces current directly into the entire metal charge contained within a crucible, without the need for an iron core.
Your choice between a channel and a coreless furnace is not a matter of which is "better," but which is suited to your operational goal. Channel furnaces are masters of holding and maintaining large volumes of metal, while coreless furnaces provide the flexibility and speed needed for melting diverse materials from a cold start.

The Channel Induction Furnace: The Holding Specialist
A channel furnace is designed for high-volume, continuous operation with a single alloy. Its structure is optimized for thermal efficiency when holding metal that is already molten.
How It Works: The Transformer Principle
The channel furnace functions precisely like an electrical transformer. An alternating current flows through a primary coil wrapped around a laminated iron core.
A loop of molten metal, contained within a narrow "channel" in the refractory, passes through this same core. This molten loop acts as a single-turn secondary coil, and the current induced within it generates the heat.
Because of this design, a channel furnace cannot be started from cold, solid material. It requires a starting pool, or "heel," of molten metal to complete the secondary circuit.
Primary Applications
These furnaces excel at holding large quantities of molten metal at a specific temperature for extended periods. They are commonly used in large iron foundries and for duplexing—receiving molten metal from a primary melter and adjusting its temperature or chemistry before pouring.
The Coreless Induction Furnace: The Versatile Melter
The coreless furnace is the most common type of induction furnace, valued for its operational flexibility and rapid melting capabilities. It is essentially a refractory-lined crucible surrounded by a water-cooled copper coil.
How It Works: Direct Field Induction
When alternating current flows through the outer coil, it generates a powerful, reversing magnetic field. This field penetrates the metal charge placed inside the crucible.
The magnetic field directly induces strong eddy currents within the metal itself, causing it to heat rapidly and melt. This process also creates an inherent electromagnetic stirring action, which ensures the molten bath is homogenous in both temperature and chemical composition.
Primary Applications
Coreless furnaces are ideal for melting metal from a solid state, including scrap. Their ability to be completely emptied makes them perfect for foundries that need to produce castings from a wide variety of different alloys without cross-contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Channel vs. Coreless
The fundamental design difference between the two furnaces creates a clear set of operational trade-offs.
Flexibility and Startup
The coreless furnace is the clear winner in flexibility. It can be started with a cold, solid charge and can be used for nearly any alloy.
The channel furnace is rigid. It requires a continuous molten bath to operate and is best suited for a single, dedicated alloy to avoid the difficult process of changing the heel.
Energy Efficiency
For holding metal at temperature, the channel furnace is more energy-efficient due to its transformer-like design and lower heat loss.
For melting metal from solid, the coreless furnace's high power density and direct heating make it faster and more efficient for the melting phase itself.
Maintenance and Refractory Wear
In a channel furnace, the channel loop is subject to intense heat and metal flow, making it a critical wear point that can be complex to replace.
In a coreless furnace, the entire refractory lining is a consumable. While it requires regular replacement, the process is generally more straightforward than servicing a channel inductor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace technology is critical to operational efficiency and product quality. Your decision should be guided by your primary production goal.
- If your primary focus is holding and superheating large, continuous volumes of a single metal: The channel furnace is your most energy-efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is melting diverse alloys from a cold, solid state in batches: The coreless furnace offers unparalleled flexibility and melting speed.
- If your primary focus is achieving high metallurgical purity and alloy homogeneity: The inherent stirring action of the coreless furnace provides a distinct advantage.
Understanding this fundamental design difference empowers you to select the precise tool for your metallurgical objective.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Channel Furnace | Coreless Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Holding & Superheating | Melting from Cold Start |
| Best For | High-volume, single alloy | Batch melting, diverse alloys |
| Starting Requirement | Requires a molten metal "heel" | Can start with solid charge |
| Operational Flexibility | Low | High |
| Energy Efficiency | High for holding | High for melting |
Optimize Your Foundry Operations with the Right Induction Furnace
Choosing between a channel and coreless furnace is a critical decision that impacts your productivity, energy costs, and product quality. KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced, high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs.
Our expertise in induction heating technology, combined with deep customization capabilities, ensures you get a furnace that precisely matches your operational goals—whether you need the holding efficiency of a channel furnace or the melting versatility of a coreless furnace.
Ready to enhance your melting and holding processes? Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover the ideal KINTEK solution for your laboratory or foundry.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















