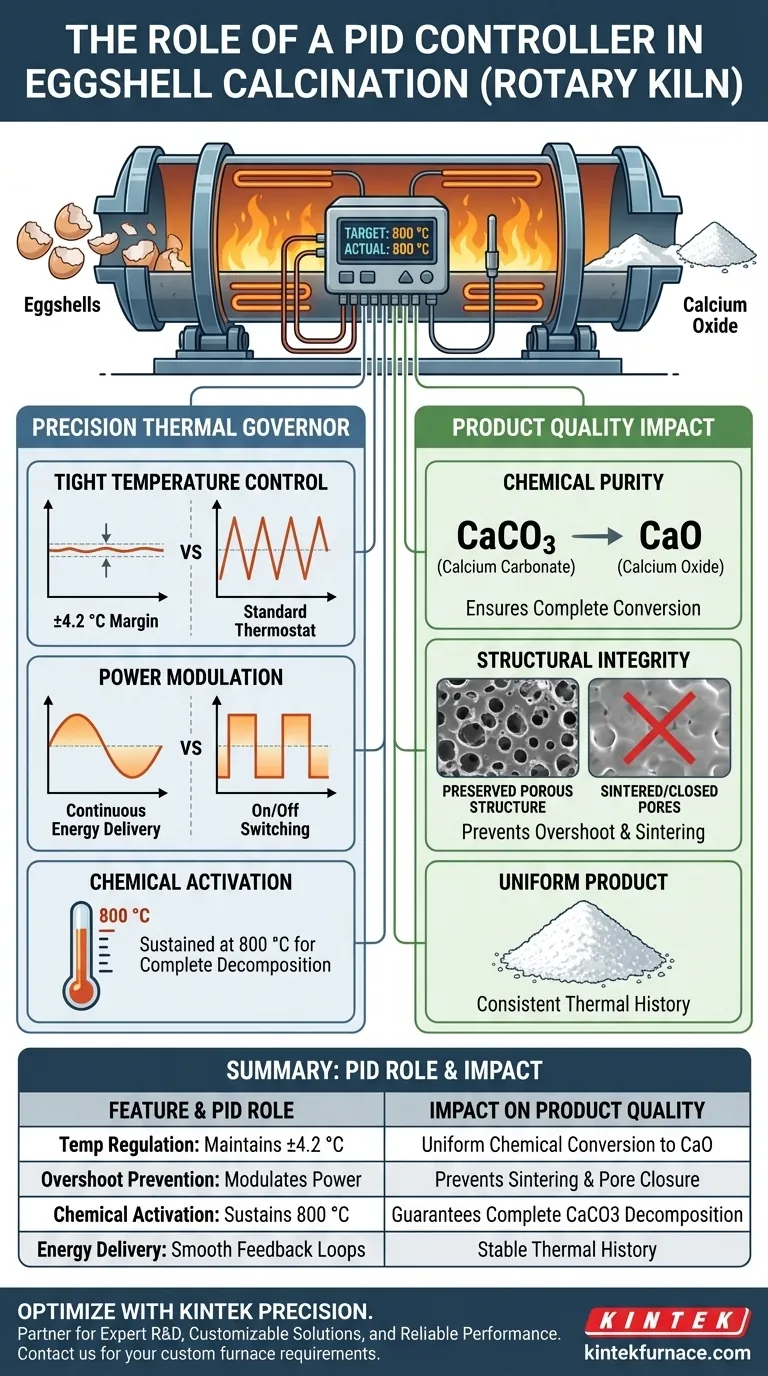
The primary role of a PID controller in a rotary kiln is to act as a precise thermal governor, regulating the power supplied to heating elements through continuous feedback loops. By constantly measuring the discrepancy between the actual temperature and the target setpoint, it maintains temperature fluctuations within an extremely narrow margin, specifically around ±4.2 °C. This tight control is the mechanical foundation required to process temperature-sensitive biomass like eggshells without destroying them.
While the PID controller manages the mechanics of heating, its true value lies in ensuring chemical purity and structural integrity. It guarantees the complete decomposition of Calcium Carbonate ($\text{CaCO}_3$) into Calcium Oxide ($\text{CaO}$) while preventing the heat damage that destroys the material's useful pore structure.

The Criticality of Thermal Precision
In the context of calcining eggshells, the PID controller is not simply keeping the kiln "hot." It is navigating a specific chemical window.
Driving Chemical Decomposition
The target reaction is the conversion of Calcium Carbonate ($\text{CaCO}_3$) into Calcium Oxide ($\text{CaO}$).
This transformation requires a sustained temperature of approximately 800 °C.
The PID controller ensures the kiln reaches this activation energy threshold efficiently and holds it there long enough for the reaction to complete throughout the entire batch.
Preserving Microstructure
The most significant risk in this process is sintering.
If temperatures rise even slightly too high due to poor control, the material begins to fuse.
This results in the closure of pore structures, rendering the final Calcium Oxide product less reactive and less valuable. The PID controller's ability to prevent overshoot is what preserves this delicate porous architecture.
How the Control Loop Works
To achieve the necessary precision, the PID controller operates differently than a standard thermostat.
Regulating Power, Not Just Switching
A standard thermostat turns heat fully "on" or "off," leading to jagged temperature swings.
A PID controller modulates the magnitude of power delivered to the heating elements.
This creates a smooth, continuous delivery of energy that matches the heat loss of the kiln, rather than reacting clumsily after a drop occurs.
Minimizing Variance
Rotary kilns are dynamic environments where loads shift and thermal dynamics change.
The PID logic calculates the error between the desired and actual temperature to minimize variance.
By keeping fluctuations to ±4.2 °C, the controller ensures that every fragment of eggshell experiences the same thermal history, resulting in a uniform product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PID control is superior for this application, it introduces specific challenges that must be managed to ensure success.
Complexity of Calibration
A PID controller is only as good as its tuning parameters (Proportional, Integral, and Derivative).
If these parameters are not perfectly calibrated to the thermal mass of the eggshells, the system can become unstable.
Incorrect tuning can lead to oscillation, where the temperature swings wildly above and below the setpoint, potentially causing the exact sintering damage you are trying to avoid.
The Limits of Cooling
The PID controller regulates heating power, but it generally has less direct control over cooling in a standard electric rotary kiln.
If the system overshoots significantly, the controller can cut power to zero, but it cannot force the temperature down instantly.
This "thermal inertia" means that the prevention of overshoot via the PID algorithm is far more critical than the system's ability to recover from it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your calcined eggshells, you must align your control strategy with your specific chemical objectives.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Ensure your setpoint is locked firmly at 800 °C to guarantee the full conversion of $\text{CaCO}_3$ to $\text{CaO}$.
- If your primary focus is Surface Area (Porosity): Prioritize a tuning strategy that minimizes overshoot, as even brief spikes above the target range can trigger pore closure and sintering.
By mastering the PID control loop, you transform a crude heating process into a precise tool for chemical synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PID Controller Role in Eggshell Calcination | Impact on Product Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Temp Regulation | Maintains tight control within ±4.2 °C | Ensures uniform chemical conversion to CaO |
| Overshoot Prevention | Modulates power magnitude rather than simple on/off | Prevents sintering and closure of pore structures |
| Chemical Activation | Sustains constant 800 °C threshold | Guarantees complete CaCO3 decomposition |
| Energy Delivery | Smooth, continuous feedback loops | Matches heat loss for stable thermal history |
Optimize Your Thermal Processing with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect balance between chemical purity and structural integrity requires more than just heat—it requires precise control. KINTEK provides industry-leading Rotary, Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum systems designed to meet the most rigorous lab and industrial standards.
Why partner with KINTEK?
- Expert R&D: Our high-temp furnaces are backed by specialized research and development.
- Customizable Solutions: Tailor our systems to your unique biomass calcination or material synthesis needs.
- Reliable Performance: Achieve the thermal precision necessary to prevent sintering and preserve microstructures.
Ready to elevate your material science outcomes? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace requirements.
Visual Guide
References
- Suwanan Chuakham, Apipong Putkham. Scalable production of bio-calcium oxide via thermal decomposition of solid - hatchery waste in a laboratory-scale rotary kiln. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-84889-w
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do segmented heating and cooling cycles affect the microwave-assisted synthesis of 2D iron oxide (Fe2O3)?
- What role does a high-temperature furnace play in the chemical activation of carbon materials? Master KOH Activation
- What role do high-precision laboratory ovens play in assessing the energy potential of MSW? Enhancing Biomass Accuracy
- What is the function of a Laboratory Forced Air Drying Oven in fruit waste pretreatment? Ensure Superior Carbon Yields
- How does CFD simulation software optimize fuel combustion? Transform Furnace Efficiency with Digital Twins
- What role does high-temperature calcination play in the purification of volcanic ash? Achieve Ultra-Pure Silica Results
- What role does high-flow nitrogen play in ITO thin film annealing? Protect Conductivity & Surface Purity
- Why is Magnesium Hydride (MgH2) preferred for SiOx pre-magnesiation? Optimize Thermal Control and Battery Stability

















